Interval training boosts cardiovascular fitness and burns more calories in less time by alternating intense bursts of effort with recovery periods. Steady-state cardio maintains a consistent pace, promoting endurance and fat oxidation for prolonged periods. Choosing between them depends on personal goals like weight loss, endurance, or improving overall cardiovascular health.
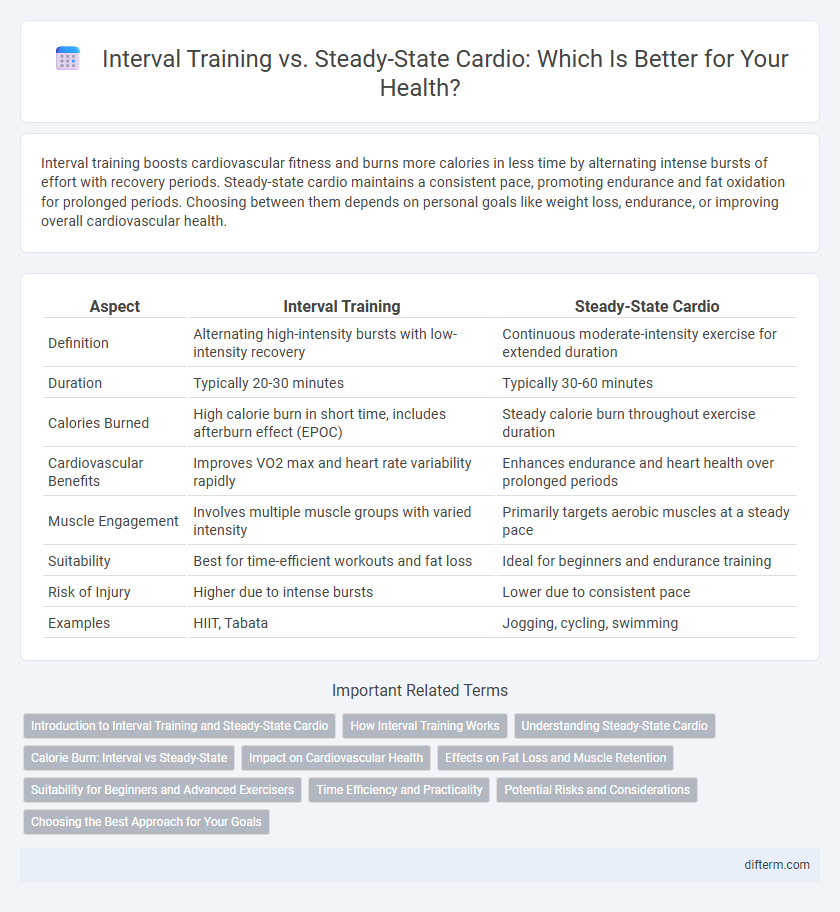
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Interval Training | Steady-State Cardio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alternating high-intensity bursts with low-intensity recovery | Continuous moderate-intensity exercise for extended duration |
| Duration | Typically 20-30 minutes | Typically 30-60 minutes |
| Calories Burned | High calorie burn in short time, includes afterburn effect (EPOC) | Steady calorie burn throughout exercise duration |
| Cardiovascular Benefits | Improves VO2 max and heart rate variability rapidly | Enhances endurance and heart health over prolonged periods |
| Muscle Engagement | Involves multiple muscle groups with varied intensity | Primarily targets aerobic muscles at a steady pace |
| Suitability | Best for time-efficient workouts and fat loss | Ideal for beginners and endurance training |
| Risk of Injury | Higher due to intense bursts | Lower due to consistent pace |
| Examples | HIIT, Tabata | Jogging, cycling, swimming |
Introduction to Interval Training and Steady-State Cardio
Interval training alternates short bursts of intense exercise with periods of lower intensity or rest, boosting cardiovascular fitness and calorie burn in less time. Steady-state cardio maintains a consistent, moderate intensity throughout the workout, promoting endurance and fat metabolism. Both methods enhance heart health but cater to different fitness goals and preferences.
How Interval Training Works
Interval training enhances cardiovascular fitness by alternating between high-intensity bursts and recovery periods, boosting the heart's efficiency and oxygen uptake. This method stimulates greater calorie burn and metabolic rate compared to steady-state cardio by engaging both aerobic and anaerobic energy systems. The varying intensity promotes improved endurance, muscle strength, and faster fat loss through elevated post-exercise oxygen consumption.
Understanding Steady-State Cardio
Steady-state cardio involves maintaining a consistent, moderate intensity level throughout the entire workout, typically ranging from 30 to 60 minutes. This form of exercise primarily utilizes aerobic metabolism, improving cardiovascular endurance and promoting fat oxidation. Common examples include jogging, cycling, and swimming performed at a steady pace without fluctuating intensity.
Calorie Burn: Interval vs Steady-State
Interval training burns significantly more calories in a shorter time than steady-state cardio due to high-intensity bursts elevating metabolism and promoting afterburn effects. Steady-state cardio maintains a consistent, moderate pace, leading to a steady calorie consumption but less impact on post-exercise oxygen consumption. For maximum calorie burn and fat loss, interval training offers superior benefits compared to traditional steady-state cardio workouts.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Interval training significantly improves cardiovascular health by increasing VO2 max and enhancing endothelial function, resulting in better heart efficiency and greater fat oxidation. Steady-state cardio promotes cardiovascular endurance by maintaining a consistent heart rate, which strengthens the heart muscle and improves circulation over time. Both methods reduce risks of heart disease, but interval training often yields faster improvements in heart rate variability and blood pressure regulation.
Effects on Fat Loss and Muscle Retention
Interval training significantly enhances fat loss by boosting metabolism and increasing post-exercise oxygen consumption, which accelerates calorie burn. Steady-state cardio primarily aids fat loss through prolonged calorie expenditure but may lead to muscle catabolism if overdone. Combining interval training with resistance exercises promotes muscle retention while optimizing fat reduction, offering a balanced approach for body composition improvement.
Suitability for Beginners and Advanced Exercisers
Interval training offers a high-intensity workout with alternating bursts of effort and recovery, making it ideal for advanced exercisers seeking to improve cardiovascular fitness and burn calories efficiently. Steady-state cardio, characterized by consistent, moderate-intensity exercise, is more suitable for beginners due to its lower impact and easier acclimation to endurance activities. Both methods can complement each other, but individual fitness levels and goals should guide the choice between interval training and steady-state cardio.
Time Efficiency and Practicality
Interval training burns more calories in less time by alternating high-intensity bursts with recovery, making it ideal for those with limited workout durations. Steady-state cardio, involving consistent moderate effort, is easier to maintain for longer sessions and beneficial for endurance building. Choosing between the two depends on personal goals, schedule constraints, and fitness levels, with interval training offering superior time efficiency and steady-state providing practical endurance benefits.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Interval training may pose a higher risk of injury due to its intense bursts of activity, especially for beginners or individuals with preexisting conditions like hypertension or joint problems. Steady-state cardio generally offers a lower risk profile by maintaining a consistent pace, but overuse can lead to repetitive strain injuries if proper rest and variation are neglected. Both exercise modalities require careful attention to individual fitness levels, proper warm-up routines, and gradual progression to minimize cardiovascular strain and musculoskeletal damage.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Goals
Interval training boosts cardiovascular fitness and burns more calories in less time by alternating high-intensity bursts with recovery periods. Steady-state cardio improves endurance and supports fat loss through consistent, moderate-intensity exercise over longer durations. Selecting the best approach depends on individual goals, fitness level, and time availability, with interval training ideal for fat burning and performance, while steady-state benefits sustained stamina and recovery.
Interval Training vs Steady-State Cardio Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com