Antioxidants protect the body by neutralizing harmful free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage. Phytonutrients encompass a broader range of plant compounds, including antioxidants, that contribute to overall health by supporting immune function and reducing inflammation. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables ensures a rich intake of both antioxidants and phytonutrients for optimal well-being.
Table of Comparison
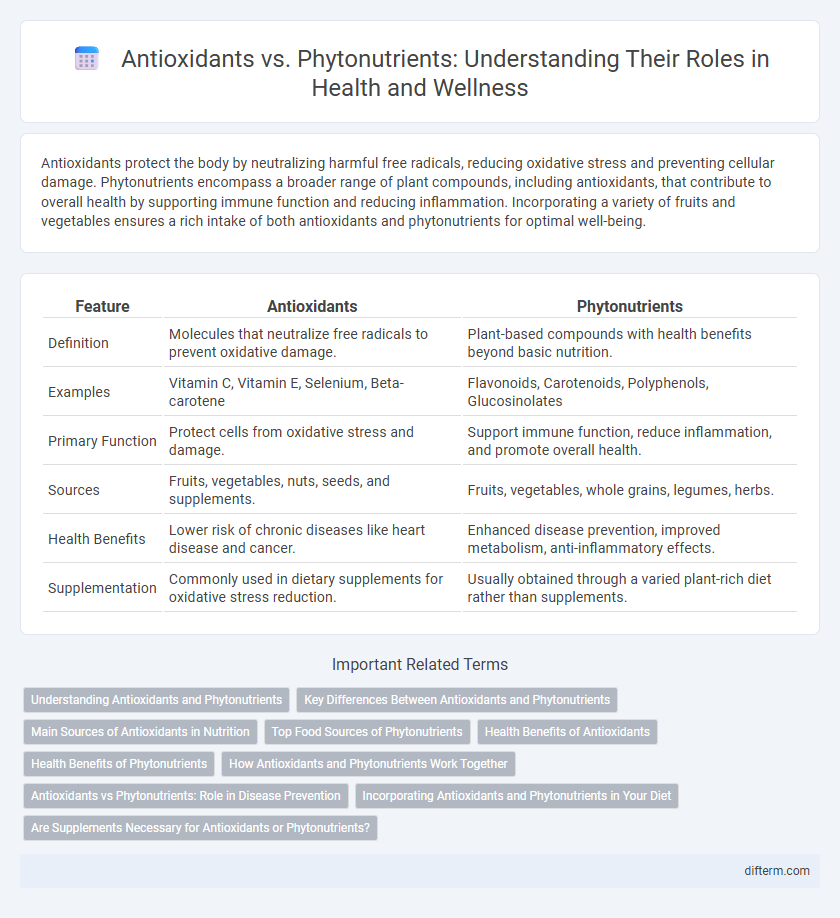
| Feature | Antioxidants | Phytonutrients |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Molecules that neutralize free radicals to prevent oxidative damage. | Plant-based compounds with health benefits beyond basic nutrition. |
| Examples | Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, Beta-carotene | Flavonoids, Carotenoids, Polyphenols, Glucosinolates |
| Primary Function | Protect cells from oxidative stress and damage. | Support immune function, reduce inflammation, and promote overall health. |
| Sources | Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and supplements. | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, herbs. |
| Health Benefits | Lower risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. | Enhanced disease prevention, improved metabolism, anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Supplementation | Commonly used in dietary supplements for oxidative stress reduction. | Usually obtained through a varied plant-rich diet rather than supplements. |
Understanding Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Antioxidants are compounds that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and lowering the risk of chronic diseases. Phytonutrients, also known as phytochemicals, include a broader group of plant-derived compounds such as flavonoids and carotenoids that offer additional health benefits beyond antioxidant activity, including anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting effects. Understanding the distinct roles of antioxidants and phytonutrients helps optimize dietary choices for enhanced cellular protection and overall wellness.
Key Differences Between Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Antioxidants are molecules that neutralize free radicals to prevent cellular damage, while phytonutrients are bioactive compounds in plants that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Antioxidants include specific substances such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, whereas phytonutrients encompass a broader range of compounds like flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols. The primary difference lies in antioxidants' direct role in reducing oxidative stress, compared to phytonutrients' diverse functions including anti-inflammatory effects and immune support.
Main Sources of Antioxidants in Nutrition
Main sources of antioxidants in nutrition include fruits such as berries, oranges, and grapes, as well as vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli. Nuts, seeds, dark chocolate, and green tea also provide significant antioxidant compounds such as vitamin C, vitamin E, flavonoids, and polyphenols. These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and supporting overall cellular health.
Top Food Sources of Phytonutrients
Top food sources of phytonutrients include colorful fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, kale, tomatoes, and carrots, which contain high levels of flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols. These compounds contribute to antioxidant activity, support immune function, and reduce inflammation, distinguishing phytonutrients from standard antioxidants. Incorporating a variety of plant-based foods ensures a rich intake of diverse phytonutrients essential for optimal health.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. These compounds, found in foods like berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, support immune function and slow the aging process by protecting cellular integrity. Unlike some phytonutrients, antioxidants have a direct impact on preventing cellular damage through their ability to donate electrons and stabilize harmful molecules.
Health Benefits of Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients, natural compounds found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, offer extensive health benefits by supporting immune function and reducing inflammation. Unlike antioxidants, which primarily neutralize free radicals, phytonutrients also enhance cellular communication and promote detoxification processes. Consuming a diverse range of phytonutrient-rich foods is linked to lower risks of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
How Antioxidants and Phytonutrients Work Together
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating electrons, preventing cellular damage and oxidative stress that contribute to chronic diseases. Phytonutrients, found in plants, enhance the body's defense by boosting antioxidant activity and supporting detoxification processes. Together, these compounds synergistically improve immune function and reduce inflammation for optimal health benefits.
Antioxidants vs Phytonutrients: Role in Disease Prevention
Antioxidants are molecules that neutralize free radicals, preventing cellular damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. Phytonutrients, including flavonoids and carotenoids found in fruits and vegetables, not only exhibit antioxidant properties but also modulate inflammation and enhance immune function. Together, antioxidants and phytonutrients contribute to disease prevention by protecting cells from oxidative stress and supporting overall health.
Incorporating Antioxidants and Phytonutrients in Your Diet
Incorporating antioxidants and phytonutrients into your diet enhances cellular health and reduces oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals. Consuming a diverse range of colorful fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains ensures an ample intake of flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols, key compounds known for their anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. Prioritizing foods rich in vitamins C, E, and selenium alongside plant-based bioactive compounds supports optimal metabolic function and long-term disease prevention.
Are Supplements Necessary for Antioxidants or Phytonutrients?
Antioxidants and phytonutrients both play crucial roles in neutralizing free radicals and supporting overall health, commonly obtained through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains. While supplements can provide concentrated doses of antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, the absorption and efficacy often improve when these compounds are consumed in whole foods alongside complementary nutrients. Research indicates that obtaining antioxidants and phytonutrients from dietary sources is generally more beneficial, and supplements are not necessary unless specific deficiencies or medical conditions warrant their use.
Antioxidants vs phytonutrients Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com