Judicial activism empowers courts to interpret the Constitution dynamically, often leading to progressive policy changes, while judicial restraint emphasizes adherence to legislative intent and precedent, limiting judicial interference in policymaking. The debate centers on balancing judicial authority with democratic principles, ensuring courts neither overreach nor abdicate their role in protecting rights. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for evaluating judicial decisions within government branches.
Table of Comparison
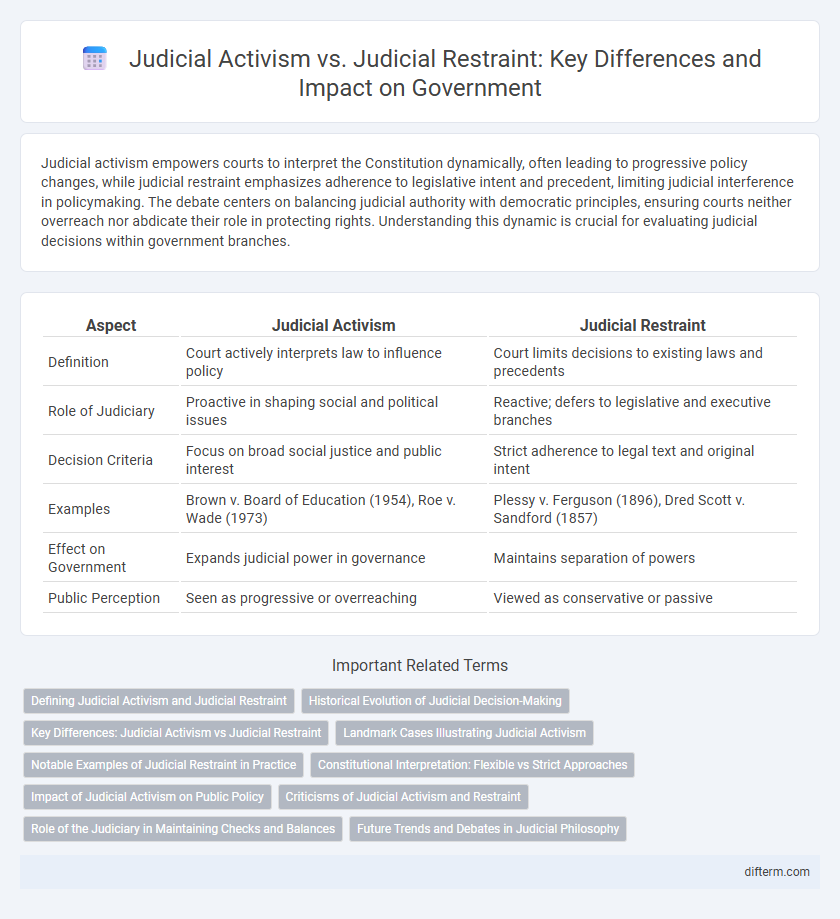
| Aspect | Judicial Activism | Judicial Restraint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Court actively interprets law to influence policy | Court limits decisions to existing laws and precedents |
| Role of Judiciary | Proactive in shaping social and political issues | Reactive; defers to legislative and executive branches |
| Decision Criteria | Focus on broad social justice and public interest | Strict adherence to legal text and original intent |
| Examples | Brown v. Board of Education (1954), Roe v. Wade (1973) | Plessy v. Ferguson (1896), Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857) |
| Effect on Government | Expands judicial power in governance | Maintains separation of powers |
| Public Perception | Seen as progressive or overreaching | Viewed as conservative or passive |
Defining Judicial Activism and Judicial Restraint
Judicial activism refers to the proactive role of courts in interpreting the Constitution and laws to address social injustices or correct legislative and executive actions when they are deemed unconstitutional. Judicial restraint emphasizes the limited role of judges, advocating for deference to the decisions of elected branches and strict adherence to statutory and constitutional text. The debate centers on balancing the judiciary's responsibility to uphold constitutional rights with respecting the separation of powers in government.
Historical Evolution of Judicial Decision-Making
Judicial activism emerged prominently during the early 20th century as courts increasingly interpreted laws to address social issues and expand civil rights beyond legislative intent. In contrast, judicial restraint, rooted in 19th-century principles, emphasizes deference to legislative bodies and limits judicial intervention to strict constitutional interpretation. Landmark cases such as Marbury v. Madison established judicial review, setting the foundation for ongoing debates between judicial activism and restraint in shaping government policy.
Key Differences: Judicial Activism vs Judicial Restraint
Judicial activism involves judges interpreting the Constitution broadly to address societal issues and promote social change, often resulting in policy-making from the bench. Judicial restraint emphasizes adherence to precedent and deference to legislative intent, limiting judicial interference in policymaking and preserving the balance of powers. Key differences hinge on the scope of judicial power, with activism favoring proactive rulings and restraint advocating judicial minimalism.
Landmark Cases Illustrating Judicial Activism
Landmark cases such as Brown v. Board of Education and Roe v. Wade exemplify judicial activism by showcasing the Supreme Court's role in shaping social policy through constitutional interpretation. In Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Court actively overturned segregation, emphasizing equality under the Fourteenth Amendment. Roe v. Wade (1973) further demonstrated judicial activism by establishing a woman's right to privacy and abortion access, significantly influencing public policy.
Notable Examples of Judicial Restraint in Practice
Judicial restraint is exemplified by the U.S. Supreme Court's decision in *Plessy v. Ferguson* (1896), where the Court deferred to legislative judgment on racial segregation laws, reflecting caution in overturning statutes. Another notable instance is the Court's stance in *Korematsu v. United States* (1944), where it upheld the government's wartime internment policy, demonstrating deference to executive authority during national emergencies. These cases underscore judicial restraint by emphasizing limited judicial interference in policy-making and respect for precedent.
Constitutional Interpretation: Flexible vs Strict Approaches
Judicial activism embraces a flexible approach to constitutional interpretation, allowing judges to adapt the Constitution's meaning to contemporary societal values and evolving norms. In contrast, judicial restraint advocates for strict constructionism, emphasizing adherence to the Constitution's original text and framers' intent, limiting judicial interference in legislative affairs. This dynamic shapes pivotal Supreme Court decisions, influencing the balance of power among government branches and the protection of individual rights.
Impact of Judicial Activism on Public Policy
Judicial activism significantly shapes public policy by allowing courts to interpret laws expansively, often addressing social issues unmet by legislative bodies. This approach enables the judiciary to promote civil rights, environmental protections, and social justice reforms, influencing policy direction beyond statutory constraints. However, it also raises concerns about undermining democratic processes and the separation of powers by shifting policymaking from elected representatives to judges.
Criticisms of Judicial Activism and Restraint
Critics of judicial activism argue that it undermines democratic principles by allowing judges to create law rather than interpret it, leading to judicial overreach and unpredictability in legal decisions. Opponents of judicial restraint contend that excessive deference to legislative and executive branches can perpetuate injustices and hinder the protection of constitutional rights. The debate centers on balancing judicial independence with accountability to maintain the rule of law and protect against governmental abuses.
Role of the Judiciary in Maintaining Checks and Balances
The judiciary plays a pivotal role in maintaining checks and balances by interpreting laws and ensuring executive and legislative actions comply with the Constitution. Judicial activism empowers courts to overturn laws or policies that infringe on fundamental rights, reinforcing accountability and protecting democratic principles. Conversely, judicial restraint emphasizes deference to elected branches, limiting judicial interference to preserve the separation of powers and respect legislative intent.
Future Trends and Debates in Judicial Philosophy
Future trends in judicial philosophy indicate a continued debate between judicial activism, advocating for courts to adapt legal principles to contemporary societal needs, and judicial restraint, emphasizing adherence to original texts and legislative intent. Emerging discussions focus on the impact of technological advancements and social change on constitutional interpretation, highlighting tensions between evolving norms and institutional limits. Scholars and policymakers examine how these contrasting approaches will shape the judiciary's role in balancing democratic governance and protecting individual rights.
judicial activism vs judicial restraint Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com