The shadow cabinet serves as the opposition's team of spokespersons, mirroring the official cabinet's roles to scrutinize government policies and propose alternatives. Unlike the official cabinet, which holds executive power and implements legislation, the shadow cabinet operates without direct authority but plays a crucial role in holding the government accountable. This parallel structure enhances democratic debate and ensures continuous oversight within the parliamentary system.
Table of Comparison
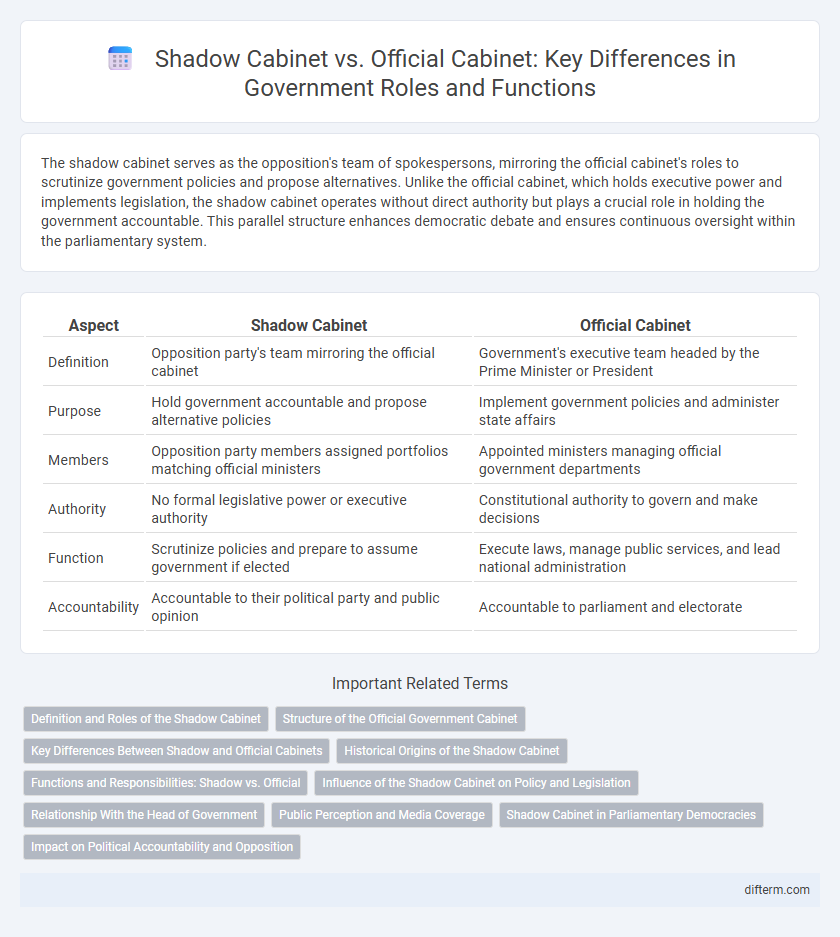
| Aspect | Shadow Cabinet | Official Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opposition party's team mirroring the official cabinet | Government's executive team headed by the Prime Minister or President |
| Purpose | Hold government accountable and propose alternative policies | Implement government policies and administer state affairs |
| Members | Opposition party members assigned portfolios matching official ministers | Appointed ministers managing official government departments |
| Authority | No formal legislative power or executive authority | Constitutional authority to govern and make decisions |
| Function | Scrutinize policies and prepare to assume government if elected | Execute laws, manage public services, and lead national administration |
| Accountability | Accountable to their political party and public opinion | Accountable to parliament and electorate |
Definition and Roles of the Shadow Cabinet
The shadow cabinet is a group of senior opposition party members tasked with scrutinizing and challenging the policies and actions of the official cabinet, which comprises government ministers responsible for executive decision-making. Each shadow cabinet member corresponds to an official cabinet minister, focusing on specific portfolios to provide alternative policies and hold the government accountable. This parallel structure enhances parliamentary democracy by promoting transparency, policy debate, and readiness to assume office.
Structure of the Official Government Cabinet
The structure of the official government cabinet consists of appointed ministers who head government departments and execute public policy under the leadership of the prime minister or president. Each cabinet member holds a specific portfolio such as finance, defense, or health, ensuring specialized governance and administrative oversight. This hierarchical organization facilitates coordinated decision-making and implementation of government agendas within constitutional frameworks.
Key Differences Between Shadow and Official Cabinets
The shadow cabinet consists of opposition party members who scrutinize government policies and propose alternatives, while the official cabinet is composed of appointed ministers responsible for implementing government policies and decisions. Shadow cabinets mirror the official cabinet's structure but lack executive power, serving primarily as a political watchdog. The official cabinet holds legislative authority and directs national administration, making it central to policy development and governance.
Historical Origins of the Shadow Cabinet
The shadow cabinet originated in the United Kingdom during the 19th century as an informal group of opposition party members shadowing each official cabinet minister. This concept allowed the opposition to present alternative policies and maintain readiness to govern, enhancing parliamentary democracy. Over time, the shadow cabinet formalized, influencing democratic systems worldwide by providing structured political accountability and policy debate.
Functions and Responsibilities: Shadow vs. Official
The official cabinet formulates and implements government policies, oversees public administration, and manages national affairs through ministerial departments. The shadow cabinet, composed of opposition members, scrutinizes government decisions, proposes alternative policies, and holds the official cabinet accountable. While the official cabinet executes governance, the shadow cabinet ensures democratic transparency and readiness to assume power.
Influence of the Shadow Cabinet on Policy and Legislation
The Shadow Cabinet plays a crucial role in shaping policy and legislation by scrutinizing and challenging the decisions of the Official Cabinet, thereby promoting transparency and accountability in government. Members of the Shadow Cabinet develop alternative policies and present these as viable options to the public and Parliament, influencing legislative debates and public opinion. Their oversight ensures that government actions are rigorously examined, often prompting modifications to official policies and contributing to more balanced governance.
Relationship With the Head of Government
The official cabinet, composed of ministers appointed by the head of government, holds executive authority and directly implements policies, maintaining a formal and authoritative relationship with the prime minister or president. In contrast, the shadow cabinet consists of opposition members who scrutinize and challenge the official cabinet's decisions, fostering a critical yet non-executive role that influences the head of government through parliamentary debate and public discourse. This dynamic creates a structured interplay where the shadow cabinet acts as a government-in-waiting, promoting accountability and preparedness for potential governance transitions.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
The shadow cabinet often receives media coverage as a critical voice challenging the official cabinet, shaping public perception through alternative policy proposals and critiques. Public perception tends to view the official cabinet as the authoritative decision-maker, while the shadow cabinet is seen as a government-in-waiting, holding the ruling party accountable. Media outlets frequently highlight the contrasts between the two, influencing how voters assess leadership effectiveness and political credibility.
Shadow Cabinet in Parliamentary Democracies
The Shadow Cabinet in parliamentary democracies serves as the opposition's counterpart to the official cabinet, closely scrutinizing government policies and offering alternative solutions. Composed of senior members from the main opposition party, each Shadow Minister is responsible for a specific government department, ensuring effective oversight and accountability. This system enhances democratic transparency by preparing the opposition to assume official roles and maintaining continuous policy debate.
Impact on Political Accountability and Opposition
The shadow cabinet plays a critical role in enhancing political accountability by systematically scrutinizing policies and decisions made by the official cabinet, providing structured opposition and alternative proposals. This parallel structure ensures government transparency and responsiveness, encouraging robust debate within parliamentary systems. The effectiveness of the shadow cabinet directly influences public trust and the democratic process by holding the official cabinet accountable and preparing the opposition for potential governance.
shadow cabinet vs official cabinet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com