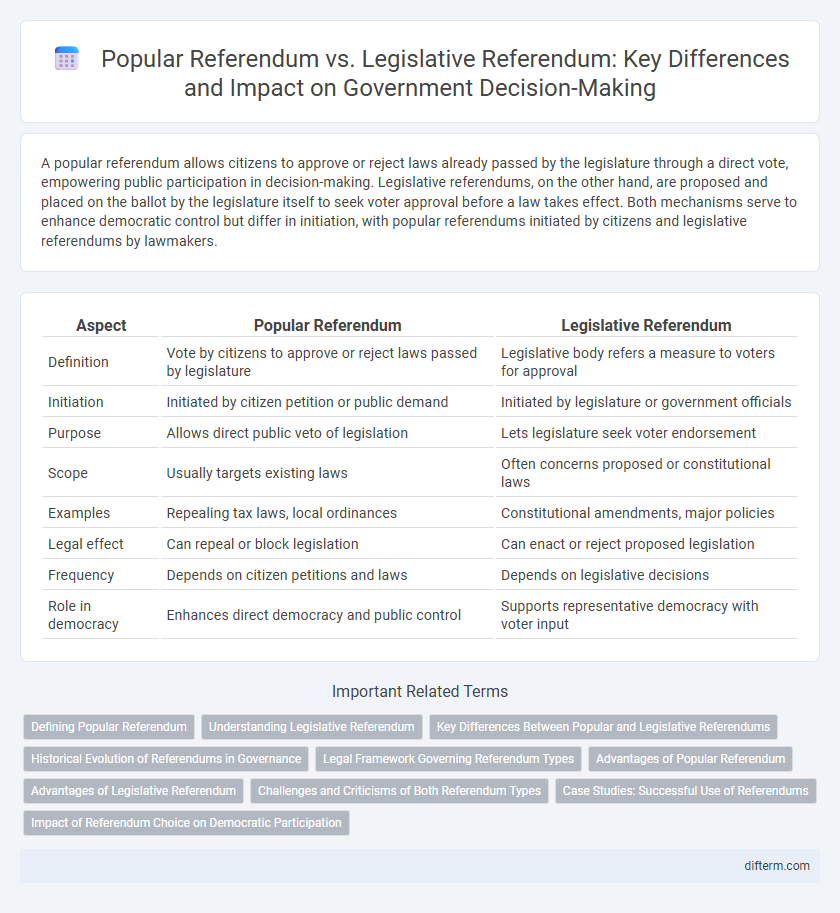
A popular referendum allows citizens to approve or reject laws already passed by the legislature through a direct vote, empowering public participation in decision-making. Legislative referendums, on the other hand, are proposed and placed on the ballot by the legislature itself to seek voter approval before a law takes effect. Both mechanisms serve to enhance democratic control but differ in initiation, with popular referendums initiated by citizens and legislative referendums by lawmakers.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Popular Referendum | Legislative Referendum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vote by citizens to approve or reject laws passed by legislature | Legislative body refers a measure to voters for approval |
| Initiation | Initiated by citizen petition or public demand | Initiated by legislature or government officials |
| Purpose | Allows direct public veto of legislation | Lets legislature seek voter endorsement |
| Scope | Usually targets existing laws | Often concerns proposed or constitutional laws |
| Examples | Repealing tax laws, local ordinances | Constitutional amendments, major policies |
| Legal effect | Can repeal or block legislation | Can enact or reject proposed legislation |
| Frequency | Depends on citizen petitions and laws | Depends on legislative decisions |
| Role in democracy | Enhances direct democracy and public control | Supports representative democracy with voter input |
Defining Popular Referendum
A Popular Referendum is a democratic mechanism enabling citizens to challenge and approve or reject laws passed by the legislature through a direct vote, thereby providing a check on legislative power. Unlike a Legislative Referendum, which is initiated by the government or legislature to seek public approval for proposed statutes or amendments, the Popular Referendum is typically driven by a petition from the electorate. This form of direct democracy enhances political participation by empowering voters to overturn or affirm legislative decisions outside the usual electoral process.
Understanding Legislative Referendum
Legislative referendum is a process where the legislature refers a proposed law or constitutional amendment to the electorate for approval, ensuring direct public participation in key decisions. This type of referendum differs from a popular referendum, which is typically initiated by citizens through petitions to challenge or approve existing laws. Understanding legislative referendums involves recognizing their role in balancing representative democracy with direct voter input on significant legislative actions.
Key Differences Between Popular and Legislative Referendums
Popular referendums allow citizens to directly approve or reject laws through signature collection and voting, ensuring direct public participation in legislative decisions. Legislative referendums are initiated by legislative bodies to seek voter approval on laws or constitutional amendments, reflecting a representative approach within democratic processes. The key difference lies in the origin of the referendum--popular referendums are citizen-driven while legislative referendums are government-initiated.
Historical Evolution of Referendums in Governance
The historical evolution of referendums in governance reveals distinct paths for popular and legislative referendums, with popular referendums emerging as a tool for direct citizen intervention to repeal or challenge existing laws, while legislative referendums enable lawmakers to seek public approval on specific bills. Swiss governance pioneered the popular referendum system in the 19th century, embedding direct democracy mechanisms that influenced numerous democratic countries worldwide. Legislative referendums have roots in representative democracies where parliaments submit critical or contentious legislation for voter validation, reflecting an evolving balance between representative authority and popular sovereignty.
Legal Framework Governing Referendum Types
The legal framework governing referendum types distinguishes popular referendums as mechanisms allowing citizens to repeal existing laws through direct vote, while legislative referendums involve the electorate approving or rejecting laws previously passed by the legislature. Popular referendums typically require a petition with a specified number of signatures within a set timeframe to qualify for the ballot, as outlined by constitutional or statutory provisions. Legislative referendums are often mandatory or optional under law, depending on the jurisdiction, and are initiated by legislative bodies to seek voter consent on specific legislative acts or constitutional amendments.
Advantages of Popular Referendum
Popular referendums empower citizens by allowing direct voting on specific laws, enhancing democratic participation and accountability. This mechanism ensures that legislation reflects the public's will more accurately than legislative referendums, which are limited to decisions made by elected representatives. By facilitating grassroots involvement, popular referendums increase transparency and can prevent unpopular or controversial laws from being enacted without public consent.
Advantages of Legislative Referendum
Legislative referendum allows elected representatives to propose laws, providing a more informed and organized approach to lawmaking compared to popular referendums driven by general public initiatives. This mechanism enhances the quality and complexity of legislation by leveraging expert knowledge and political experience, reducing the risk of populism and hasty decisions. It also fosters greater political stability and accountability by involving institutional checks and balances before laws are put to a direct vote.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Referendum Types
Popular referendums often face challenges such as the risk of populism, misinformation, and low voter turnout, which can undermine informed decision-making and democratic legitimacy. Legislative referendums may attract criticism for limited citizen participation and potential political manipulation, as elected officials can control the agenda and limit referendum topics. Both types struggle with ensuring comprehensive public debate and addressing complex policy issues in a simplified voting format, raising concerns about the effectiveness and fairness of direct democracy mechanisms.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Referendums
Popular referendums allow citizens to directly approve or reject laws, exemplified by Switzerland's frequent use for policy decisions on immigration and healthcare reforms, resulting in high civic engagement and policy legitimacy. Legislative referendums, initiated by parliaments, have been effectively used in Italy and Ireland to confirm constitutional amendments, ensuring democratic oversight within representative institutions. Case studies show popular referendums often lead to increased public participation, while legislative referendums provide structured, law-based validation of key legislative changes.
Impact of Referendum Choice on Democratic Participation
Popular referendums empower citizens by enabling them to directly propose or repeal laws, significantly enhancing grassroots democratic participation and civic engagement. Legislative referendums, initiated by elected bodies, tend to reinforce representative democracy but may limit direct public influence on policy decisions. The choice between popular and legislative referendums fundamentally shapes voter turnout, public trust, and the overall responsiveness of democratic institutions to citizen demands.
Popular Referendum vs Legislative Referendum Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com