Appropriation refers to the legal authorization granted by the government to allocate funds for specific purposes, setting limits on the total amount available for expenditure. Allocation involves the detailed distribution of these appropriated funds to various departments or projects for operational use. Understanding the distinction between appropriation and allocation is crucial for ensuring proper budget management and compliance within government entities.
Table of Comparison
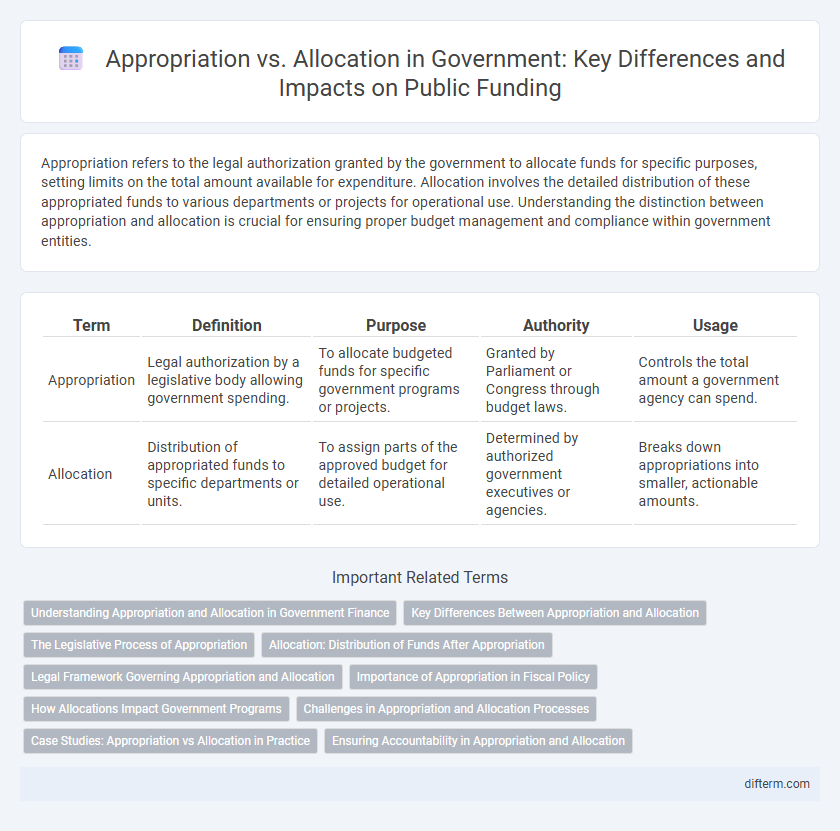
| Term | Definition | Purpose | Authority | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appropriation | Legal authorization by a legislative body allowing government spending. | To allocate budgeted funds for specific government programs or projects. | Granted by Parliament or Congress through budget laws. | Controls the total amount a government agency can spend. |
| Allocation | Distribution of appropriated funds to specific departments or units. | To assign parts of the approved budget for detailed operational use. | Determined by authorized government executives or agencies. | Breaks down appropriations into smaller, actionable amounts. |
Understanding Appropriation and Allocation in Government Finance
Appropriation in government finance refers to the legal authorization granted by the legislature to allocate specific funds for designated purposes within a fiscal year. Allocation involves the distribution and management of these appropriated funds across various departments or projects to ensure efficient utilization. Understanding the distinction between appropriation as the approved budget authority and allocation as the operational distribution is crucial for effective public financial management.
Key Differences Between Appropriation and Allocation
Appropriation refers to the legal authorization granted by a legislative body allowing government entities to incur obligations and make expenditures from the treasury for specific purposes. Allocation, on the other hand, involves the distribution or assignment of appropriated funds among various departments, projects, or programs within the authorized limits. The key difference lies in appropriation establishing the legal limit of spending, while allocation deals with how the approved funds are divided and utilized across government sectors.
The Legislative Process of Appropriation
The legislative process of appropriation involves the formal approval of specific government expenditures by the legislature, which grants legal authority to allocate public funds. Appropriation bills specify how much money will be spent and on what purposes, creating a legally binding limit on government spending. Allocation refers to the distribution of those appropriated funds among government agencies or programs, ensuring that resources are directed according to legislative priorities.
Allocation: Distribution of Funds After Appropriation
Allocation in government finance refers to the specific distribution of funds following the approval of an appropriation bill by the legislature. This process involves assigning budgeted resources to various departments, programs, or projects based on priorities and established guidelines. Precise allocation ensures that authorized funds are directed efficiently towards intended public services and government operations.
Legal Framework Governing Appropriation and Allocation
The legal framework governing appropriation mandates that legislative bodies authorize specific budget amounts for government expenditures, ensuring fiscal accountability and adherence to statutory limits. Allocation refers to the administrative process of distributing appropriated funds to various departments or programs, guided by government policies and regulatory guidelines to optimize resource utilization. Statutes such as the Anti-Deficiency Act and Financial Management Acts establish clear boundaries and procedures for appropriation and allocation within public financial management systems.
Importance of Appropriation in Fiscal Policy
Appropriation is a critical component of fiscal policy as it legally authorizes government spending, ensuring funds are designated for specific programs and priorities established by the legislature. This mechanism enables effective budget control, transparency, and accountability in the use of public resources. Appropriation directly impacts the execution of economic policies by aligning financial resources with policy objectives, promoting fiscal discipline and economic stability.
How Allocations Impact Government Programs
Allocations determine the specific distribution of funds within government programs, directly influencing their operational efficiency and scope. Precise allocation ensures targeted resource use, enabling programs to meet their strategic objectives and deliver public services effectively. Misallocation can lead to underfunded initiatives and reduced program impact, affecting overall government performance and public trust.
Challenges in Appropriation and Allocation Processes
Challenges in government appropriation and allocation processes often include budgetary constraints, bureaucratic delays, and misalignment between policy goals and fund distribution. Ensuring transparency and accountability remains difficult due to complex regulatory frameworks and competing stakeholder interests. These issues frequently hinder efficient public resource management and affect the timely execution of government programs.
Case Studies: Appropriation vs Allocation in Practice
Case studies in government finance reveal that appropriation refers to the legal authorization of funds by the legislature, while allocation involves the distribution of those funds to specific departments or projects. For instance, in the 2022 U.S. federal budget, Congress enacted appropriations totaling $1.7 trillion, which the Office of Management and Budget then allocated across defense, education, and healthcare sectors. These practical examples highlight how appropriation establishes the funding ceiling, whereas allocation directs the operational use of resources within that framework.
Ensuring Accountability in Appropriation and Allocation
Ensuring accountability in appropriation involves legally authorizing specific funds through legislation, which sets clear spending limits and purposes for government entities. Allocation focuses on distributing these appropriated funds to various departments or projects with transparent criteria and monitoring to prevent misuse and ensure compliance with budgetary goals. Effective oversight mechanisms, including audits and reporting, are critical to maintaining fiscal responsibility and public trust in both appropriation and allocation processes.
Appropriation vs Allocation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com