Technocracy emphasizes decision-making by experts based on technical knowledge and data, aiming to improve efficiency and innovation within government operations. Bureaucracy relies on standardized procedures and hierarchical structures to maintain order and consistency in public administration. Balancing technocracy's focus on expertise with bureaucracy's institutional stability is crucial for effective governance.
Table of Comparison
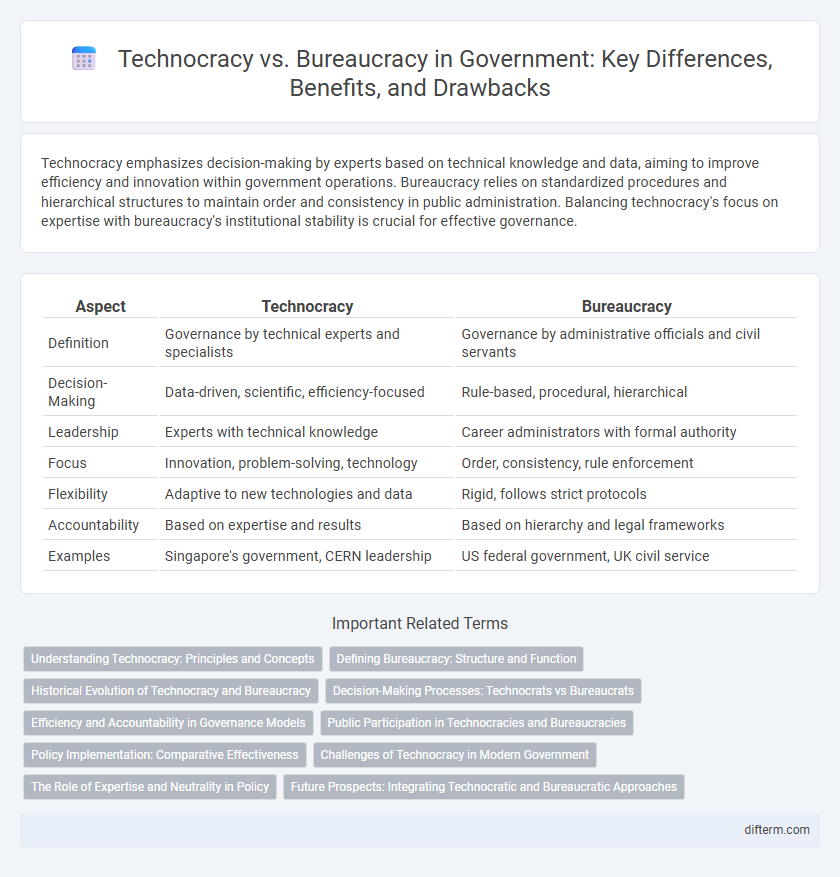
| Aspect | Technocracy | Bureaucracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance by technical experts and specialists | Governance by administrative officials and civil servants |
| Decision-Making | Data-driven, scientific, efficiency-focused | Rule-based, procedural, hierarchical |
| Leadership | Experts with technical knowledge | Career administrators with formal authority |
| Focus | Innovation, problem-solving, technology | Order, consistency, rule enforcement |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to new technologies and data | Rigid, follows strict protocols |
| Accountability | Based on expertise and results | Based on hierarchy and legal frameworks |
| Examples | Singapore's government, CERN leadership | US federal government, UK civil service |
Understanding Technocracy: Principles and Concepts
Technocracy is a system of governance where decision-makers are selected based on their expertise, particularly in science, engineering, and technology, rather than political affiliation. It prioritizes data-driven policies, emphasizing efficiency, technical competence, and empirical evidence in public administration. This approach contrasts with traditional bureaucracy, which relies on hierarchical, rule-based procedures and political appointment, often leading to slower decision-making processes.
Defining Bureaucracy: Structure and Function
Bureaucracy in government refers to a hierarchical organization characterized by standardized procedures, formal rules, and clear division of labor to ensure efficient policy implementation and public administration. Its structure typically includes multiple levels of authority, specialized departments, and a rigid chain of command designed to maintain order and accountability. The primary function of bureaucracy is to translate legislative directives into practical, day-to-day government operations, balancing consistency with adherence to established regulations.
Historical Evolution of Technocracy and Bureaucracy
Technocracy emerged in the early 20th century as a response to industrial complexity, advocating for governance by technical experts and engineers, while bureaucracy has roots in ancient civilizations, evolving through Weberian principles of hierarchical organization and rule-based administration. During the Progressive Era, technocratic ideas gained momentum, emphasizing efficiency and scientific management within government institutions. Bureaucratic systems solidified in modern states through codified regulations and merit-based civil services, contrasting with technocracy's focus on technical expertise driving policy decisions.
Decision-Making Processes: Technocrats vs Bureaucrats
Technocrats rely on specialized knowledge, data-driven analysis, and empirical evidence to guide decision-making processes, ensuring policies are technically sound and efficient. Bureaucrats often emphasize adherence to established rules, procedures, and hierarchical structures, which can slow decision-making but promote consistency and accountability. The balance between technocratic expertise and bureaucratic protocol shapes governmental effectiveness and policy implementation outcomes.
Efficiency and Accountability in Governance Models
Technocracy prioritizes expertise-driven decision-making, enhancing efficiency by utilizing specialized knowledge and data analytics for policy formulation. Bureaucracy emphasizes structured procedures and hierarchical accountability, which can slow responsiveness but ensures consistent regulatory oversight. Balancing technocratic efficiency with bureaucratic accountability remains a critical challenge in contemporary governance models.
Public Participation in Technocracies and Bureaucracies
Public participation in technocracies is often limited due to the emphasis on expert knowledge and decision-making by specialized professionals, which can reduce direct citizen involvement. Bureaucracies, while structured around formal procedures and hierarchical organization, provide more established mechanisms for public input through consultations, hearings, and feedback channels. Both systems face challenges balancing efficiency with democratic engagement, but bureaucracies tend to offer greater opportunities for citizen participation in policy processes.
Policy Implementation: Comparative Effectiveness
Technocracy ensures policy implementation through expert-driven decision-making, leading to technically efficient and innovative solutions tailored to complex problems. Bureaucracy emphasizes rule-based procedures and hierarchical structures, which promote consistency and accountability but may slow responsiveness. Comparative studies show technocratic systems excel in specialized policy areas, while bureaucracies provide stable governance across diverse policy domains.
Challenges of Technocracy in Modern Government
Technocracy in modern government faces challenges such as balancing expert-driven decision-making with democratic accountability and public participation. The reliance on specialized knowledge can create barriers to transparency and inclusiveness, leading to potential disconnects between technocrats and the general populace. Furthermore, bureaucratic systems may resist technocratic reforms due to institutional inertia and vested interests, complicating effective implementation.
The Role of Expertise and Neutrality in Policy
Technocracy emphasizes the role of specialized expertise and evidence-based decision-making in government policy, prioritizing technical knowledge over political considerations. Bureaucracy relies on established rules, procedures, and hierarchical authority to ensure consistency, neutrality, and impartiality in administrative functions. The balance between technocratic expert input and bureaucratic process safeguards democratic accountability while enhancing policy effectiveness through informed and unbiased implementation.
Future Prospects: Integrating Technocratic and Bureaucratic Approaches
Future governance models emphasize integrating technocratic expertise with bureaucratic structures to enhance policy efficiency and accountability. Leveraging data-driven decision-making alongside established administrative protocols can address complex societal challenges more effectively. This hybrid approach facilitates adaptive governance, improving responsiveness to technological advancements and evolving public needs.
technocracy vs bureaucracy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com