Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members openly show support for candidates, fostering in-depth discussions and grassroots engagement. Primaries are statewide voting processes that function like general elections, offering a straightforward and private way to select party nominees. Understanding the differences between caucus and primary systems helps clarify how candidates secure government party nominations.
Table of Comparison
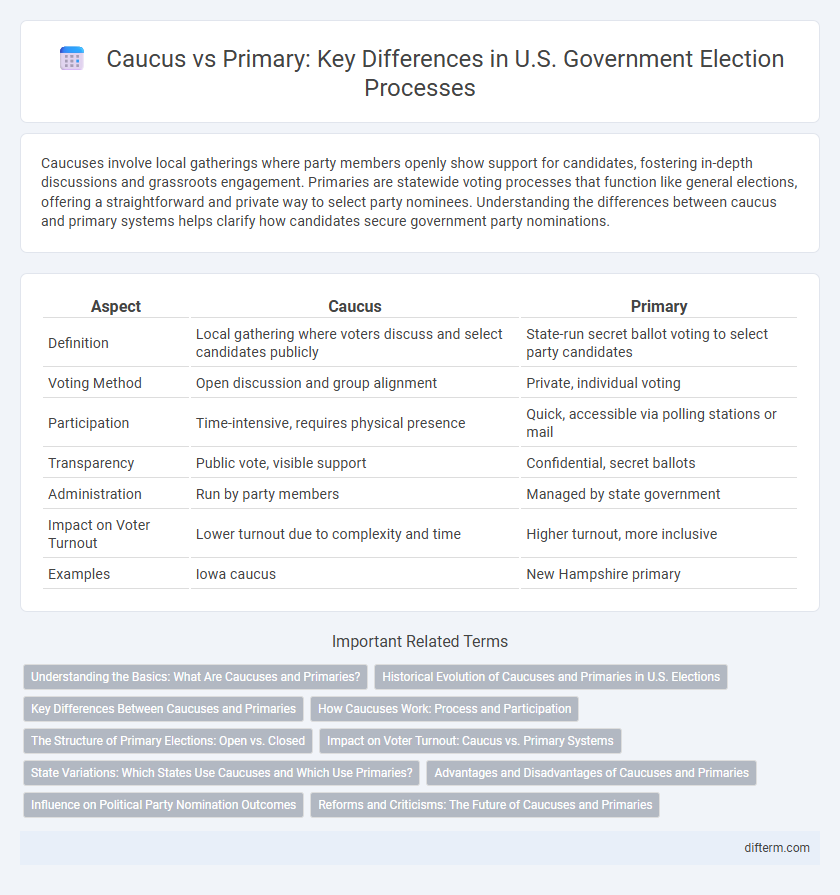
| Aspect | Caucus | Primary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Local gathering where voters discuss and select candidates publicly | State-run secret ballot voting to select party candidates |
| Voting Method | Open discussion and group alignment | Private, individual voting |
| Participation | Time-intensive, requires physical presence | Quick, accessible via polling stations or mail |
| Transparency | Public vote, visible support | Confidential, secret ballots |
| Administration | Run by party members | Managed by state government |
| Impact on Voter Turnout | Lower turnout due to complexity and time | Higher turnout, more inclusive |
| Examples | Iowa caucus | New Hampshire primary |
Understanding the Basics: What Are Caucuses and Primaries?
Caucuses and primaries are both methods used by political parties in the United States to select their candidates for general elections. Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members discuss and vote for their preferred candidate through a public, often debate-driven process, promoting active participation. Primaries function like standard elections, allowing registered voters to cast private ballots for their favored candidate, providing a more straightforward and accessible voting experience.
Historical Evolution of Caucuses and Primaries in U.S. Elections
Caucuses originated in the early 19th century as local gatherings where party members met to discuss and select candidates, emphasizing grassroots participation and deliberation. Primaries emerged in the early 20th century, starting with Wisconsin's 1905 primary law, as a reform to democratize candidate selection by allowing direct, private voting from the electorate. Over time, the shift toward primaries reflects a broader trend in U.S. elections favoring more inclusive and standardized processes, reducing party leadership's influence in candidate nomination.
Key Differences Between Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members discuss and vote publicly to select candidates, emphasizing community engagement and deliberation, whereas primaries are state-level elections where voters cast secret ballots to choose their preferred candidates directly. Caucuses typically have lower turnout due to time and participation commitments, while primaries tend to attract higher voter participation with straightforward voting procedures. The timing and rules for caucuses vary significantly by state and party, whereas primaries often follow standardized rules governed by state election laws.
How Caucuses Work: Process and Participation
Caucuses operate through local gatherings where registered party members discuss and vote openly for their preferred candidates, emphasizing active participation and community involvement. Unlike primaries, caucuses often require attendees to physically remain at the location for extended periods, engaging in debates and aligning their support in multiple rounds of voting. This process fosters a grassroots approach to candidate selection, influencing delegate allocation based on participants' collective decisions.
The Structure of Primary Elections: Open vs. Closed
Primary elections vary primarily between open and closed structures, impacting voter participation and party control. Open primaries allow any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation, fostering broader inclusivity but potentially diluting party influence. Closed primaries restrict voting to registered party members, ensuring candidates reflect party preferences while limiting crossover voting.
Impact on Voter Turnout: Caucus vs. Primary Systems
Caucus systems typically result in lower voter turnout due to time-intensive and often complex participation requirements, limiting accessibility for many voters. Primaries, by offering a straightforward secret ballot similar to general elections, significantly increase voter engagement and turnout. Data from states using primaries consistently show higher participation rates compared to those relying on caucuses, highlighting accessibility as a key factor influencing voter involvement.
State Variations: Which States Use Caucuses and Which Use Primaries?
States vary significantly in their use of caucuses and primaries to select party nominees; Iowa and Nevada are well-known for their caucus systems, while larger states like California and New York primarily utilize primaries. Caucuses generally involve local gatherings where party members discuss and vote, emphasizing grassroots participation, whereas primaries are statewide elections with secret ballots that mirror general election procedures. This state-level variation impacts voter turnout, candidate strategies, and the timing of delegate allocation in presidential nomination contests.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses promote direct voter engagement through in-person discussions, fostering community involvement and deeper candidate understanding but they often result in lower turnout due to time commitments and accessibility issues. Primaries provide a more straightforward, private voting process with higher participation rates and broader representation, though they can be costlier and more susceptible to influence from party elites or external groups. Both systems impact candidate selection by balancing grassroots input with voter accessibility and operational efficiency.
Influence on Political Party Nomination Outcomes
Caucuses tend to favor candidates with strong grassroots support due to their in-person, time-intensive format, often benefiting well-organized, deeply engaged party members. Primaries allow broader voter participation through secret ballots, increasing the influence of moderate or widely appealing candidates on party nomination outcomes. The structural differences between caucuses and primaries significantly impact the strategic approaches candidates must adopt to secure a party's nomination.
Reforms and Criticisms: The Future of Caucuses and Primaries
Reforms in caucuses aim to increase accessibility by adopting more inclusive voting methods, such as ranked-choice ballots and extended voting hours, addressing criticisms of low participation and complexity. Primaries face scrutiny over high financial costs and influence of party elites, prompting calls for open primaries and public funding reforms to enhance fairness and voter engagement. The future of caucuses and primaries depends on balancing transparency, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness to strengthen democratic processes within government elections.
caucus vs primary Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com