The Shadow Cabinet is composed of opposition party members who scrutinize and challenge the policies of the current government, acting as a government-in-waiting by mirroring the roles of official ministers. The Inner Cabinet, also known as the Cabinet, consists of key government ministers responsible for core decision-making and policy implementation within the ruling party. Understanding the distinction between these groups highlights the mechanisms of parliamentary democracy and the balance of power.
Table of Comparison
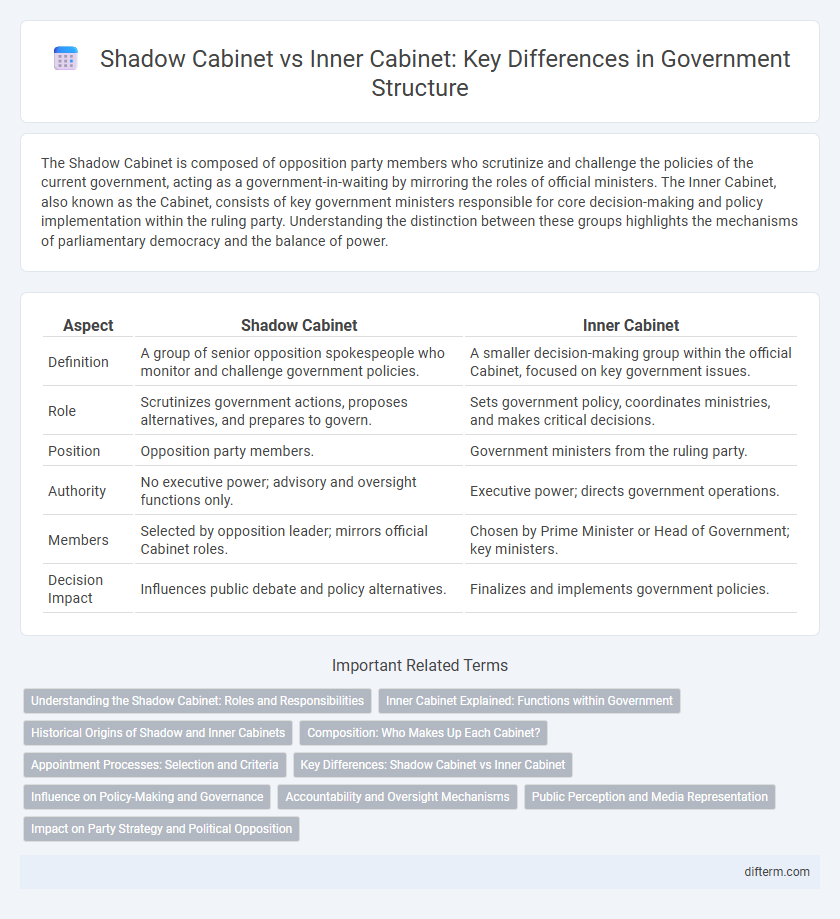
| Aspect | Shadow Cabinet | Inner Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of senior opposition spokespeople who monitor and challenge government policies. | A smaller decision-making group within the official Cabinet, focused on key government issues. |
| Role | Scrutinizes government actions, proposes alternatives, and prepares to govern. | Sets government policy, coordinates ministries, and makes critical decisions. |
| Position | Opposition party members. | Government ministers from the ruling party. |
| Authority | No executive power; advisory and oversight functions only. | Executive power; directs government operations. |
| Members | Selected by opposition leader; mirrors official Cabinet roles. | Chosen by Prime Minister or Head of Government; key ministers. |
| Decision Impact | Influences public debate and policy alternatives. | Finalizes and implements government policies. |
Understanding the Shadow Cabinet: Roles and Responsibilities
The Shadow Cabinet consists of senior opposition party members tasked with scrutinizing government policies and presenting alternative strategies, acting as a government-in-waiting. Each Shadow Cabinet member mirrors a specific government minister, focusing on holding their counterparts accountable and developing policy expertise in designated sectors. This structure enhances democratic transparency and ensures ongoing policy debate, preparing the opposition to assume office effectively when required.
Inner Cabinet Explained: Functions within Government
The Inner Cabinet consists of senior government ministers who hold key portfolios, making critical decisions on national policy and strategy. This core executive group coordinates cross-departmental initiatives and advises the Prime Minister on pressing issues. Their functions include setting government priorities, managing crises, and ensuring cohesive implementation of policies across departments.
Historical Origins of Shadow and Inner Cabinets
The concept of the Shadow Cabinet originated in 19th-century British parliamentary politics as a formalized opposition team mirroring the government's Inner Cabinet to provide effective checks and balances. The Inner Cabinet, evolving from the early 18th-century British Cabinet system, comprises a small group of senior ministers commanding major departments and key policy decisions, shaping executive governance. Both structures historically reflect the development of responsible government, where the Inner Cabinet coordinates executive policy while the Shadow Cabinet offers structured accountability from the opposition.
Composition: Who Makes Up Each Cabinet?
The Shadow Cabinet consists mainly of senior members from the main opposition party, each mirroring a specific government minister and tasked with scrutinizing their policies and actions. The Inner Cabinet, also known as the Cabinet Committee or Core Cabinet, comprises the most influential ministers, including the Prime Minister, Chancellor, Foreign Secretary, and Home Secretary, responsible for making key executive decisions. This composition reflects the Inner Cabinet's role as the central decision-making group, while the Shadow Cabinet functions as a structured opposition team ready to assume power.
Appointment Processes: Selection and Criteria
The appointment process for the Shadow Cabinet involves opposition party leaders selecting members based on expertise and party loyalty to scrutinize government policies effectively. In contrast, the Inner Cabinet appointments are made by the Prime Minister or President, prioritizing seniority, political strategy, and alignment with government agendas. Both processes emphasize political experience, but the Inner Cabinet requires formal approval or swearing-in procedures, reflecting their executive authority.
Key Differences: Shadow Cabinet vs Inner Cabinet
The Shadow Cabinet consists of opposition party members who scrutinize and challenge the policies of the ruling party, each shadow minister mirroring a specific government department, while the Inner Cabinet is composed of senior government ministers who make crucial decisions and set policy agendas. The Inner Cabinet operates within the executive branch, holding actual administrative power, whereas the Shadow Cabinet functions as a political watchdog without formal authority. The key difference lies in their roles: the Inner Cabinet shapes and implements government policy, and the Shadow Cabinet provides accountability and prepares alternative governance plans.
Influence on Policy-Making and Governance
The Shadow Cabinet plays a crucial role in shaping opposition policy frameworks, providing alternative proposals that influence public debate and government decisions. The Inner Cabinet, composed of senior ministers, holds direct authority over policy-making and governance, enabling swift implementation and coordination of governmental strategies. While the Inner Cabinet executes and refines policies, the Shadow Cabinet's scrutiny pressures the ruling government to maintain transparency and effectiveness in governance.
Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms
The Shadow Cabinet serves as a critical accountability mechanism by shadowing each member of the Inner Cabinet, scrutinizing government policies and decisions to ensure transparency and effectiveness. While the Inner Cabinet holds executive authority and implements policy, the Shadow Cabinet functions primarily as an opposition body, providing oversight through questioning, debate, and policy alternatives. This dynamic fosters a balanced governance structure where oversight mechanisms enhance democratic accountability and prevent unilateral decision-making.
Public Perception and Media Representation
The Shadow Cabinet often receives focused media attention as a key opposition force, shaping public perception by scrutinizing government policies and offering alternative solutions. In contrast, the Inner Cabinet, comprising senior government ministers, gains portrayal as the central decision-making body, influencing public trust through policy effectiveness and leadership visibility. Media representation tends to frame the Shadow Cabinet as a government-in-waiting, while the Inner Cabinet is viewed as the actual implementer of power, impacting the public's confidence and political engagement.
Impact on Party Strategy and Political Opposition
The Shadow Cabinet shapes party strategy by formulating policies that challenge the ruling government, enabling the opposition to present clear alternatives and scrutinize decisions effectively. The Inner Cabinet, composed of senior government officials, drives policymaking and strategic governance, impacting how the party manages internal alignment and public messaging. This dynamic between the Shadow Cabinet and Inner Cabinet intensifies political opposition, influencing voter perception and party cohesion during election cycles.
Shadow Cabinet vs Inner Cabinet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com