Clean energy refers specifically to energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro that produce little to no pollution or greenhouse gases during generation. Clean technology encompasses a broader range of innovations designed to reduce environmental impact, including energy-efficient appliances, waste management systems, and sustainable manufacturing processes. Prioritizing clean energy is essential for decarbonizing power production, while clean technology integrates solutions across industries to promote environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
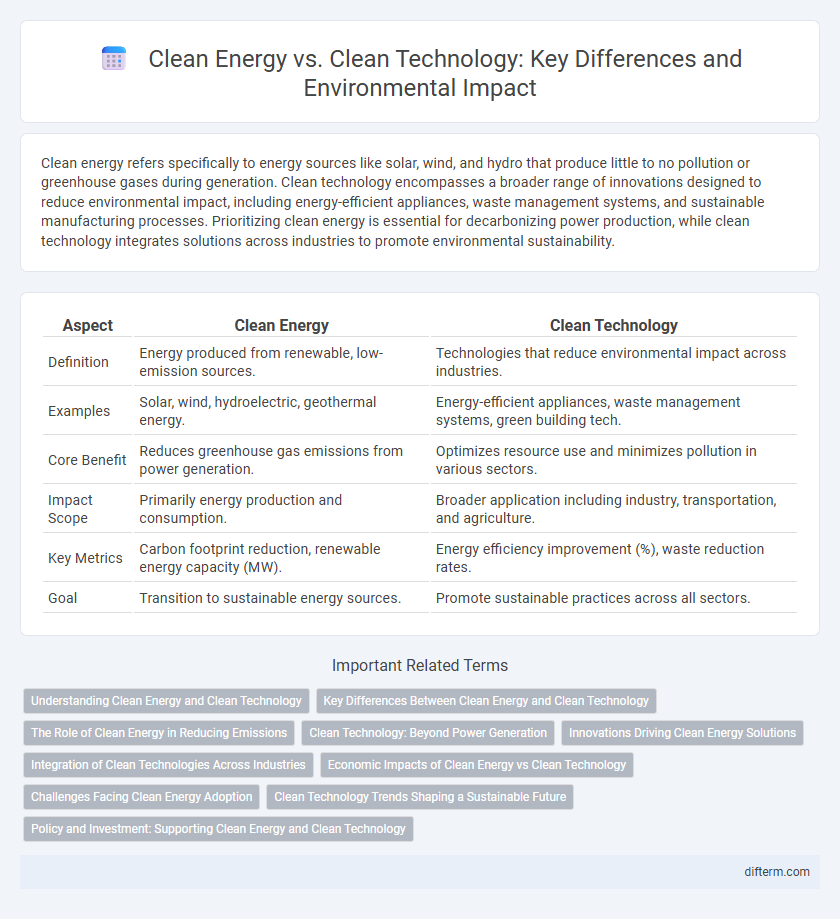
| Aspect | Clean Energy | Clean Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy produced from renewable, low-emission sources. | Technologies that reduce environmental impact across industries. |
| Examples | Solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal energy. | Energy-efficient appliances, waste management systems, green building tech. |
| Core Benefit | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. | Optimizes resource use and minimizes pollution in various sectors. |
| Impact Scope | Primarily energy production and consumption. | Broader application including industry, transportation, and agriculture. |
| Key Metrics | Carbon footprint reduction, renewable energy capacity (MW). | Energy efficiency improvement (%), waste reduction rates. |
| Goal | Transition to sustainable energy sources. | Promote sustainable practices across all sectors. |
Understanding Clean Energy and Clean Technology
Clean energy refers to energy produced from renewable sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal that generate power with minimal environmental impact and zero greenhouse gas emissions. Clean technology encompasses a broader range of innovations and processes designed to reduce pollution, enhance energy efficiency, and promote sustainable resource management, including advancements in clean energy systems, electric vehicles, and waste treatment solutions. Understanding the distinction between clean energy and clean technology is essential for developing holistic environmental strategies that address both energy production and sustainable technological innovation.
Key Differences Between Clean Energy and Clean Technology
Clean energy specifically refers to energy sources that produce minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. Clean technology encompasses a broader range of innovations designed to reduce environmental impact, including energy-efficient appliances, pollution control systems, and sustainable manufacturing processes. The key difference lies in clean energy being a subset focused solely on renewable energy generation, while clean technology covers all environmentally friendly technological solutions.
The Role of Clean Energy in Reducing Emissions
Clean energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power play a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation. The scalability and increasing cost-effectiveness of renewable energy technologies enable significant carbon footprint reduction across industrial, residential, and transportation sectors. Integrating clean energy into power grids accelerates the transition to low-carbon economies and supports global climate targets.
Clean Technology: Beyond Power Generation
Clean technology encompasses innovations that improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact across various sectors, not limited to power generation. It integrates advanced materials, smart grids, and sustainable resource management to optimize industrial processes and urban infrastructure. By advancing clean technology, industries can achieve significant carbon footprint reductions while promoting economic growth and environmental resilience.
Innovations Driving Clean Energy Solutions
Innovations in clean energy solutions emphasize advanced solar photovoltaics, wind turbine efficiency, and energy storage technologies that reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Breakthroughs in clean technology, such as smart grids and carbon capture systems, enhance energy distribution and minimize greenhouse gas emissions. These developments accelerate the transition to sustainable energy ecosystems while promoting environmental resilience.
Integration of Clean Technologies Across Industries
Integration of clean technologies across industries accelerates the transition to renewable energy sources, enhancing efficiency and reducing carbon footprints. Innovations such as advanced solar panels, energy storage systems, and smart grids enable seamless adoption of clean energy solutions in manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture. This holistic approach supports sustainable development goals by promoting resource optimization and minimizing environmental impact.
Economic Impacts of Clean Energy vs Clean Technology
Clean energy investments stimulate job creation by expanding renewable power industries, while clean technology innovations drive productivity gains across multiple sectors. Economic impacts of clean energy center on reducing fossil fuel dependency and stabilizing energy prices, whereas clean technology fosters diversified market growth through efficiency improvements and new product development. Both contribute to long-term economic resilience by lowering environmental costs and enhancing sustainable industrial competitiveness.
Challenges Facing Clean Energy Adoption
Clean energy adoption faces significant challenges including high initial investment costs, limited infrastructure, and intermittent energy supply from sources like solar and wind. Regulatory hurdles and inconsistent policy support further slow the transition, while clean technology development struggles with scalability and integration into existing grids. Overcoming these issues requires coordinated efforts in innovation, financing, and policy frameworks to ensure reliable and affordable clean energy solutions.
Clean Technology Trends Shaping a Sustainable Future
Clean technology innovations, such as advanced energy storage systems and smart grid solutions, drive the transition toward a sustainable future by optimizing renewable energy integration and reducing carbon emissions. Breakthroughs in green hydrogen production and carbon capture utilization highlight the rapid evolution of clean technology applications beyond traditional clean energy sources. These trends accelerate global efforts to achieve net-zero targets, enhance resource efficiency, and promote circular economy principles in environmental management.
Policy and Investment: Supporting Clean Energy and Clean Technology
Policy frameworks promoting renewable energy adoption and innovation in clean technology significantly influence investment flows, driving the transition to a sustainable economy. Government incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, enhance the financial viability of wind, solar, and battery storage projects, attracting private sector investment. Targeted funding for research and development accelerates breakthroughs in energy efficiency and carbon capture technologies, aligning economic growth with climate goals.
clean energy vs clean technology Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com