Hard adaptation in pet environment management involves physical modifications like installing climate control systems or durable shelters to protect pets from extreme weather. Soft adaptation focuses on behavioral adjustments and routine changes, such as altering feeding schedules or increasing indoor activities to reduce stress. Balancing hard and soft adaptation strategies ensures pets remain comfortable and healthy amid environmental fluctuations.
Table of Comparison
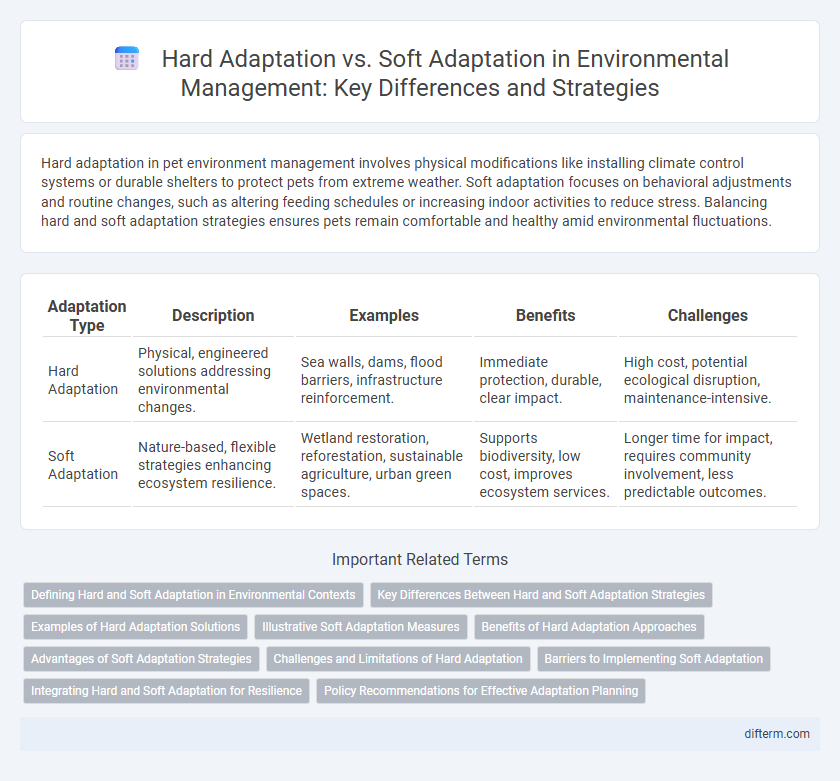
| Adaptation Type | Description | Examples | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Adaptation | Physical, engineered solutions addressing environmental changes. | Sea walls, dams, flood barriers, infrastructure reinforcement. | Immediate protection, durable, clear impact. | High cost, potential ecological disruption, maintenance-intensive. |
| Soft Adaptation | Nature-based, flexible strategies enhancing ecosystem resilience. | Wetland restoration, reforestation, sustainable agriculture, urban green spaces. | Supports biodiversity, low cost, improves ecosystem services. | Longer time for impact, requires community involvement, less predictable outcomes. |
Defining Hard and Soft Adaptation in Environmental Contexts
Hard adaptation in environmental contexts involves structural, often engineering-based solutions such as seawalls, dams, and infrastructure reinforcement to withstand climate impacts. Soft adaptation emphasizes ecosystem-based approaches and policy measures, including habitat restoration, community engagement, and flexible management strategies to enhance resilience. Differentiating these approaches is essential for optimizing climate response strategies and balancing ecological, social, and economic outcomes.
Key Differences Between Hard and Soft Adaptation Strategies
Hard adaptation strategies involve engineered solutions such as seawalls, dams, and infrastructure reinforcement designed to withstand environmental stressors, focusing on physical resilience and immediate protection. Soft adaptation strategies emphasize ecosystem-based approaches like reforestation, wetland restoration, and sustainable land management, promoting long-term ecological balance and enhancing natural adaptive capacity. The key differences lie in implementation scale, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the impact on biodiversity, with hard strategies often being capital-intensive and rigid, while soft strategies offer sustainable, scalable benefits by integrating with natural processes.
Examples of Hard Adaptation Solutions
Hard adaptation solutions in environmental management often involve large-scale infrastructure projects such as building seawalls, flood barriers, and dams designed to protect coastal and urban areas from rising sea levels and extreme weather events. Other examples include the construction of desalination plants to secure freshwater supplies in arid regions and the installation of advanced irrigation systems to ensure agricultural productivity under changing climate conditions. These engineered interventions provide immediate and measurable protection but require significant capital investment and ongoing maintenance.
Illustrative Soft Adaptation Measures
Soft adaptation measures in environmental management emphasize flexible, nature-based solutions such as restoring wetlands, enhancing green infrastructure, and promoting sustainable agriculture practices to improve ecosystem resilience. These approaches prioritize ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, and community participation to mitigate climate impacts while supporting livelihoods. By integrating adaptive management and local knowledge, soft adaptation fosters long-term sustainability and reduces vulnerability to climate change.
Benefits of Hard Adaptation Approaches
Hard adaptation approaches offer robust, engineered solutions such as sea walls, dams, and flood barriers that provide immediate and tangible protection against extreme weather events and rising sea levels. These measures reduce vulnerability by physically altering environments to withstand climate impacts, ensuring infrastructure and communities remain secure. Their durability and effectiveness in high-risk areas contribute significantly to safeguarding human lives and economic assets from climate-related damages.
Advantages of Soft Adaptation Strategies
Soft adaptation strategies in environmental management prioritize flexibility and ecosystem-based approaches, enhancing resilience in the face of climate variability. These strategies promote sustainable resource use by integrating social and ecological systems, thereby reducing vulnerability without extensive infrastructure costs. Emphasizing community participation, soft adaptation fosters adaptive capacity and long-term environmental stewardship.
Challenges and Limitations of Hard Adaptation
Hard adaptation strategies in environmental management face significant challenges including high financial costs, long implementation timelines, and potential ecological disruption. Such measures often require extensive infrastructure changes or engineered solutions that may not be flexible under evolving climate scenarios. Limitations also arise from socio-political resistance and difficulties in maintaining these structures over time amid unpredictable environmental stresses.
Barriers to Implementing Soft Adaptation
Barriers to implementing soft adaptation include institutional inertia, limited funding, and lack of stakeholder engagement, which hinder flexible risk management and ecosystem-based approaches. Complex governance structures often create coordination challenges among agencies, while insufficient awareness and capacity-building reduce local community participation. Overcoming these obstacles requires integrated policy frameworks, enhanced communication strategies, and targeted investment in adaptive capacity.
Integrating Hard and Soft Adaptation for Resilience
Integrating hard adaptation measures, such as constructing flood barriers and seawalls, with soft adaptation strategies like ecosystem restoration and community-based planning enhances overall resilience to climate change impacts. Hard adaptations provide immediate physical protection, while soft adaptations offer flexible, sustainable solutions that improve social and ecological systems' capacity to absorb shocks. Combining these approaches creates a synergistic effect, reducing vulnerability and promoting long-term environmental stability.
Policy Recommendations for Effective Adaptation Planning
Policy recommendations for effective adaptation planning emphasize integrating both hard and soft adaptation strategies to enhance climate resilience. Hard adaptation involves infrastructure investments such as seawalls and flood barriers, while soft adaptation focuses on ecosystem-based approaches and community engagement. Prioritizing flexible policies that support innovation, cross-sector collaboration, and continuous monitoring ensures adaptive management aligns with evolving environmental risks.
hard adaptation vs soft adaptation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com