Experiential learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by engaging students in hands-on activities that connect theory to real-world applications. Rote learning emphasizes memorization and repetition, often neglecting deeper understanding and long-term retention. Prioritizing experiential methods enhances knowledge retention and prepares learners for practical challenges beyond the classroom.
Table of Comparison
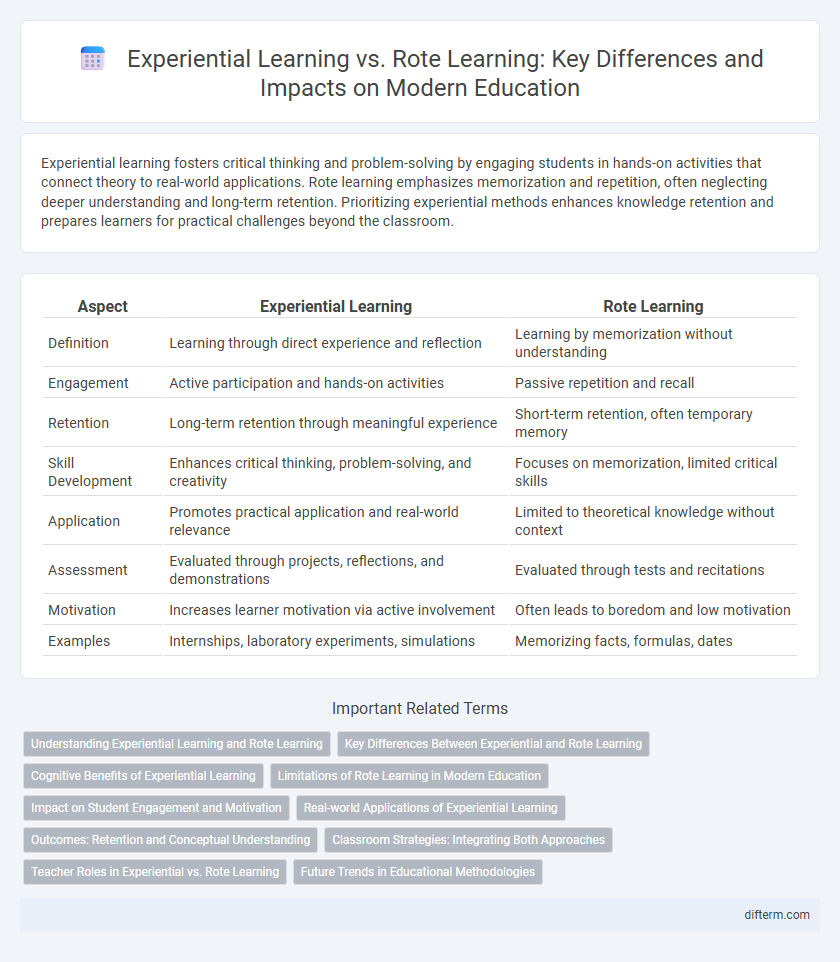
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Rote Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Learning by memorization without understanding |
| Engagement | Active participation and hands-on activities | Passive repetition and recall |
| Retention | Long-term retention through meaningful experience | Short-term retention, often temporary memory |
| Skill Development | Enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity | Focuses on memorization, limited critical skills |
| Application | Promotes practical application and real-world relevance | Limited to theoretical knowledge without context |
| Assessment | Evaluated through projects, reflections, and demonstrations | Evaluated through tests and recitations |
| Motivation | Increases learner motivation via active involvement | Often leads to boredom and low motivation |
| Examples | Internships, laboratory experiments, simulations | Memorizing facts, formulas, dates |
Understanding Experiential Learning and Rote Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement through hands-on activities, critical thinking, and real-world problem solving, leading to deeper comprehension and long-term retention. Rote learning relies on repetition and memorization, often resulting in short-term recall without true understanding or application of knowledge. Studies show experiential methods improve cognitive development and learner motivation compared to traditional rote approaches.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Rote Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement and practical application, allowing learners to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world experiences. In contrast, rote learning relies on memorization and repetition, often leading to short-term recall without deep understanding or the ability to apply knowledge in varied contexts. Key differences include the focus on understanding and skill development in experiential learning versus the emphasis on retention and recall in rote learning.
Cognitive Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on activities that promote active mental processing and real-world application. This approach increases memory retention and deepens understanding, contrasting with rote learning, which emphasizes memorization without contextual comprehension. Cognitive benefits include improved adaptability, creativity, and the ability to transfer knowledge across diverse situations.
Limitations of Rote Learning in Modern Education
Rote learning in modern education often leads to limited critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students memorize information without understanding underlying concepts. This approach hinders long-term retention and fails to foster creativity or adaptability, essential for success in rapidly changing environments. Educational research emphasizes the need for experiential learning methods that promote active engagement and deeper comprehension.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Experiential learning enhances student engagement and motivation by involving hands-on activities that encourage critical thinking and real-world problem solving. In contrast, rote learning often leads to passive memorization, resulting in lower retention and decreased interest among students. Research shows that experiential methods improve long-term understanding and intrinsic motivation, fostering deeper cognitive connections.
Real-world Applications of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes real-world applications by engaging students in hands-on activities that mimic actual challenges, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach contrasts with rote learning, which primarily focuses on memorization without understanding, often leading to limited knowledge retention. Studies show that experiential learning improves long-term comprehension and better prepares students for practical scenarios in professional environments.
Outcomes: Retention and Conceptual Understanding
Experiential learning significantly enhances retention and deepens conceptual understanding by engaging learners in active problem-solving and real-world application, which strengthens neural connections. In contrast, rote learning often leads to superficial memorization with limited long-term retention and poor transfer of knowledge to practical situations. Research indicates that students involved in experiential methods demonstrate higher academic performance and more meaningful mastery of concepts compared to those relying solely on repetitive memorization techniques.
Classroom Strategies: Integrating Both Approaches
Classroom strategies that integrate experiential learning with rote learning enhance student engagement and knowledge retention by combining hands-on activities and memorization techniques. Utilizing project-based tasks alongside traditional drills fosters critical thinking and reinforces foundational facts, creating a balanced learning environment. This dual approach addresses diverse learning styles and promotes deeper comprehension across subjects.
Teacher Roles in Experiential vs. Rote Learning
Teachers in experiential learning environments act as facilitators and mentors, guiding students through hands-on activities and real-world problem solving to enhance critical thinking and engagement. In contrast, rote learning positions teachers primarily as information transmitters, emphasizing memorization and repetition over deeper understanding. Effective educators balance these roles by fostering active participation while providing structured knowledge acquisition.
Future Trends in Educational Methodologies
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving, fostering critical thinking and adaptability essential for future workforce demands. Rote learning, based on memorization without context, is becoming less effective as education shifts towards skills like creativity and collaboration. Emerging trends highlight the integration of technology and personalized learning paths to enhance experiential methodologies and prepare students for evolving global challenges.
experiential learning vs rote learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com