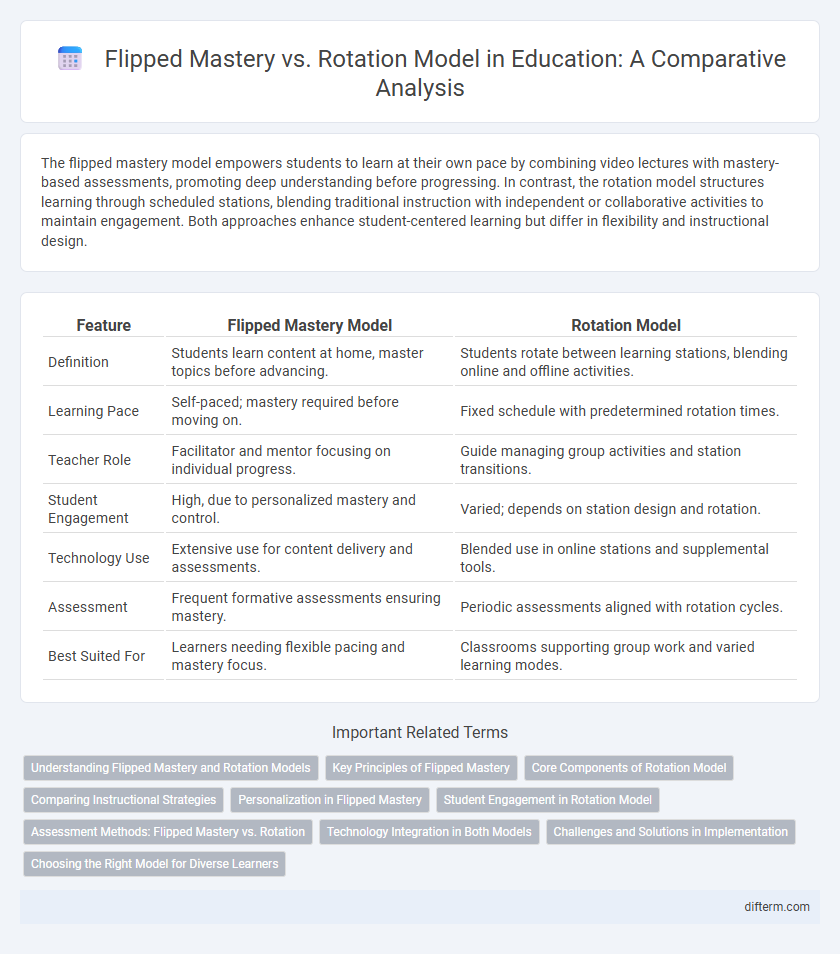
The flipped mastery model empowers students to learn at their own pace by combining video lectures with mastery-based assessments, promoting deep understanding before progressing. In contrast, the rotation model structures learning through scheduled stations, blending traditional instruction with independent or collaborative activities to maintain engagement. Both approaches enhance student-centered learning but differ in flexibility and instructional design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flipped Mastery Model | Rotation Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students learn content at home, master topics before advancing. | Students rotate between learning stations, blending online and offline activities. |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced; mastery required before moving on. | Fixed schedule with predetermined rotation times. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and mentor focusing on individual progress. | Guide managing group activities and station transitions. |
| Student Engagement | High, due to personalized mastery and control. | Varied; depends on station design and rotation. |
| Technology Use | Extensive use for content delivery and assessments. | Blended use in online stations and supplemental tools. |
| Assessment | Frequent formative assessments ensuring mastery. | Periodic assessments aligned with rotation cycles. |
| Best Suited For | Learners needing flexible pacing and mastery focus. | Classrooms supporting group work and varied learning modes. |
Understanding Flipped Mastery and Rotation Models
Flipped Mastery emphasizes personalized learning by allowing students to progress at their own pace, mastering each concept before moving on, which enhances comprehension and retention. The Rotation Model structures learning through scheduled rotations between different modalities such as online learning, group projects, and individual assignments, promoting varied and balanced engagement. Both models leverage technology to increase student autonomy and tailor instruction to diverse learning needs.
Key Principles of Flipped Mastery
Flipped Mastery centers on student-paced learning where mastery of concepts is demonstrated before progression, emphasizing personalized instruction and competency-based assessment. This model requires students to engage with digital content independently, allowing classroom time to be dedicated to individualized support and active learning. The core principles involve continuous feedback, self-directed study, and flexible pacing to ensure thorough understanding and skill acquisition.
Core Components of Rotation Model
The Rotation Model in education is characterized by structured cycles of learning activities, including station rotation, lab rotation, and individual rotation, ensuring students rotate through various modalities such as online learning and face-to-face instruction. Core components emphasize personalized pacing, direct teacher interaction, and collaborative learning environments that enhance student engagement and mastery. This model leverages technology to facilitate differentiated instruction while maintaining consistent teacher oversight to support diverse learning needs.
Comparing Instructional Strategies
Flipped mastery emphasizes self-paced learning through pre-recorded lectures, allowing students to achieve mastery before moving on, while the rotation model incorporates structured station rotations combining teacher-led instruction, collaborative work, and online activities. The flipped mastery model prioritizes individualized assessment and mastery checks, promoting deeper understanding, whereas the rotation model balances varied learning modalities to cater to diverse student needs in a scheduled format. Data shows flipped mastery can accelerate learning for motivated students, whereas the rotation model supports consistent engagement across different skill levels.
Personalization in Flipped Mastery
Flipped Mastery enhances personalization by allowing students to progress at their own pace, revisiting concepts until mastery is achieved, unlike the Rotation model that follows a fixed schedule. This approach tailors learning experiences to individual needs, promoting deeper understanding and skill retention. Personalized feedback and self-directed learning are core to Flipped Mastery, creating an adaptive and student-centered educational environment.
Student Engagement in Rotation Model
The Rotation Model enhances student engagement by allowing learners to interact with diverse activities such as online learning, collaborative projects, and teacher-led instruction within a structured schedule. This variety keeps students motivated and attentive, catering to different learning styles and pacing. Data shows that student participation rates increase in classrooms using the Rotation Model due to its dynamic and interactive nature.
Assessment Methods: Flipped Mastery vs. Rotation
Flipped Mastery employs continuous formative assessments allowing students to demonstrate mastery at their own pace before advancing, emphasizing personalized feedback and individualized learning checkpoints. The Rotation model incorporates scheduled formative and summative assessments aligned with distinct learning stations, promoting varied evaluation through collaborative, online, and direct instruction tasks. Both models prioritize frequent assessment but differ in pacing and structure, with Flipped Mastery focusing on mastery-based progression and Rotation emphasizing time-based rotation through diverse learning activities.
Technology Integration in Both Models
Flipped mastery and rotation models both leverage technology to personalize learning, with flipped mastery emphasizing self-paced video lessons accessed online, enabling students to control the timing and depth of content engagement. The rotation model integrates educational software and digital assessments within scheduled station rotations, allowing for varied instructional modes such as teacher-led sessions and collaborative work. Both models rely on technology platforms to track student progress and provide real-time data analytics, enhancing differentiated instruction and mastery-based outcomes.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Flipped mastery and rotation models face challenges such as varied student pacing and resource-intensive lesson planning, which can hinder personalized learning effectiveness. Solutions include leveraging adaptive technology platforms to track progress and facilitate tailored instruction, alongside providing professional development for educators to manage diverse classroom dynamics efficiently. Integrating data analytics helps identify struggling students early, enabling timely interventions that support mastery learning goals.
Choosing the Right Model for Diverse Learners
Flipped Mastery empowers students to learn at their own pace by allowing them to master concepts before progressing, making it ideal for personalized learning in diverse classrooms. The Rotation Model combines various instructional methods, such as station rotation and computer labs, providing structured variety that supports multiple learning styles. Selecting the right model depends on classroom resources, student readiness for self-directed learning, and the need for flexibility in instructional delivery.
Flipped mastery vs Rotation model Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com