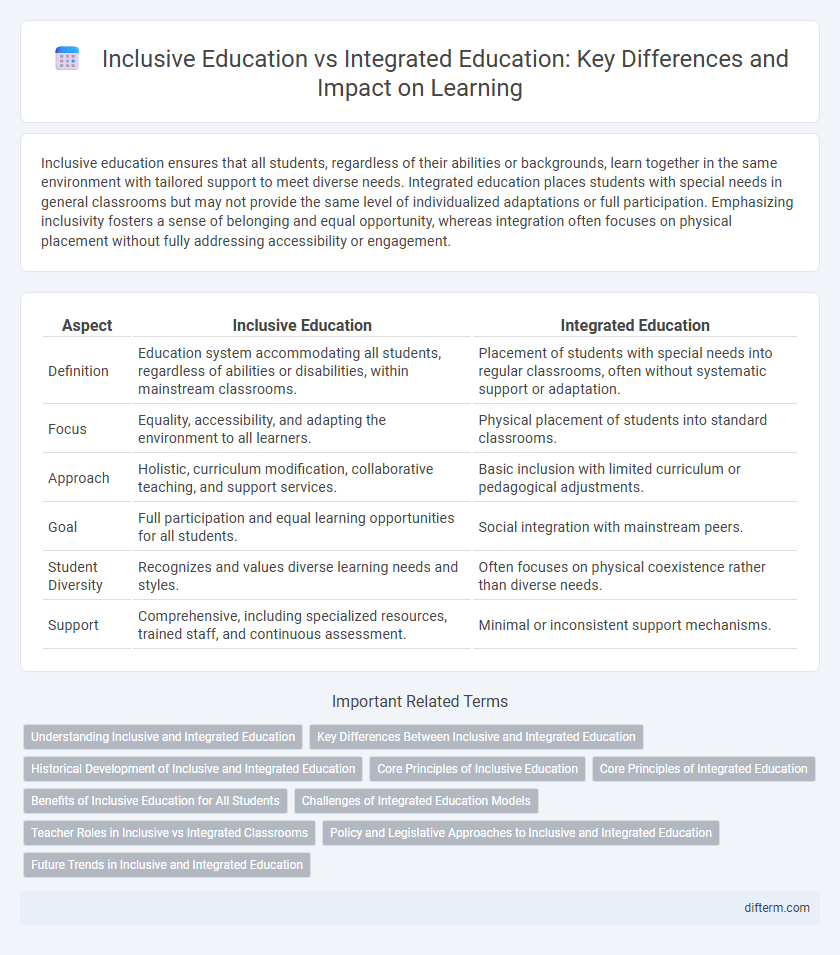
Inclusive education ensures that all students, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, learn together in the same environment with tailored support to meet diverse needs. Integrated education places students with special needs in general classrooms but may not provide the same level of individualized adaptations or full participation. Emphasizing inclusivity fosters a sense of belonging and equal opportunity, whereas integration often focuses on physical placement without fully addressing accessibility or engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Inclusive Education | Integrated Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education system accommodating all students, regardless of abilities or disabilities, within mainstream classrooms. | Placement of students with special needs into regular classrooms, often without systematic support or adaptation. |
| Focus | Equality, accessibility, and adapting the environment to all learners. | Physical placement of students into standard classrooms. |
| Approach | Holistic, curriculum modification, collaborative teaching, and support services. | Basic inclusion with limited curriculum or pedagogical adjustments. |
| Goal | Full participation and equal learning opportunities for all students. | Social integration with mainstream peers. |
| Student Diversity | Recognizes and values diverse learning needs and styles. | Often focuses on physical coexistence rather than diverse needs. |
| Support | Comprehensive, including specialized resources, trained staff, and continuous assessment. | Minimal or inconsistent support mechanisms. |
Understanding Inclusive and Integrated Education
Inclusive education ensures all students, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, learn together in mainstream classrooms with tailored support to meet diverse needs. Integrated education typically places students with disabilities in regular classes but may lack the comprehensive adaptations and collaboration fundamental to inclusion. Understanding these distinctions helps educators design environments that promote equity, participation, and personalized learning for every student.
Key Differences Between Inclusive and Integrated Education
Inclusive education emphasizes adapting the learning environment to meet diverse student needs, ensuring full participation and equal access for all learners regardless of their abilities or backgrounds. Integrated education typically involves placing students with special needs into regular classrooms but may not fully address individual learning requirements or promote active engagement. Key differences include the scope of support, with inclusive education fostering a supportive culture and tailored teaching strategies, while integrated education focuses primarily on physical placement within mainstream settings.
Historical Development of Inclusive and Integrated Education
Inclusive education emerged from the civil rights movements of the 1960s and 1970s, emphasizing equal access to education for all students regardless of disabilities. Integrated education originated earlier, in the mid-20th century, focusing primarily on placing students with disabilities alongside their non-disabled peers in regular classrooms. Over time, inclusive education has evolved to promote full participation and tailored support within diverse learning environments, surpassing the integration model's emphasis on physical placement.
Core Principles of Inclusive Education
Inclusive education centers on the core principles of equity, accessibility, and participation, ensuring all students, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, receive meaningful learning opportunities. It emphasizes adapting teaching methods and curricula to accommodate diverse needs, fostering a supportive environment that values diversity and promotes social interaction among all learners. This contrasts with integrated education, which often places students with disabilities in mainstream settings without necessarily providing tailored support or modifications to fully engage them.
Core Principles of Integrated Education
Integrated education prioritizes placing students with special needs in mainstream classrooms to promote social interaction and equality. Core principles include collaboration among educators, individualized support plans, and adaptation of curricula to meet diverse learning needs. This approach fosters an inclusive environment by valuing diversity and ensuring all students participate actively in the learning process.
Benefits of Inclusive Education for All Students
Inclusive education fosters a supportive learning environment where students with diverse abilities learn together, promoting empathy, collaboration, and social development for all. It enhances academic outcomes by providing individualized support and adaptive teaching strategies that address varied learning needs. Research shows inclusive settings improve peer relationships and reduce stigma, benefiting both students with disabilities and their typically developing classmates.
Challenges of Integrated Education Models
Integrated education models face challenges such as insufficient teacher training to handle diverse learning needs and a lack of tailored resources that support all students equitably. Physical accessibility and social acceptance within mainstream classrooms often hinder effective inclusion, limiting full participation for students with disabilities. Addressing these obstacles requires systemic changes in policy, infrastructure, and professional development to create genuinely inclusive educational environments.
Teacher Roles in Inclusive vs Integrated Classrooms
Teachers in inclusive classrooms adapt instruction to meet diverse needs, fostering collaboration and differentiated learning to support students with and without disabilities together. In integrated classrooms, teachers primarily modify existing curricula to accommodate students with disabilities, often focusing on physical placement rather than full participation. Effective teacher roles in inclusive settings involve proactive planning, individualized support strategies, and cultivating an environment of acceptance and equity.
Policy and Legislative Approaches to Inclusive and Integrated Education
Policy and legislative approaches to inclusive education emphasize the removal of barriers and the provision of equal opportunities for all students by adapting curricula, teaching methods, and learning environments to accommodate diverse needs. Integrated education policies often focus on physically placing students with disabilities in mainstream classrooms but may lack comprehensive support systems essential for true inclusivity. Effective legislation for inclusive education incorporates individualized support, anti-discrimination measures, and funding allocations to ensure accessibility and participation for learners with disabilities in all educational settings.
Future Trends in Inclusive and Integrated Education
Future trends in inclusive and integrated education emphasize personalized learning technologies and universal design for learning (UDL) to accommodate diverse student needs. Increased use of AI-driven adaptive learning platforms supports real-time assessment and tailored instruction, fostering equitable access and participation. Collaboration between educators, families, and policymakers is expected to strengthen, promoting systemic changes that embed inclusivity and integration as standard educational practices.
Inclusive education vs integrated education Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com