Scaffolding provides tailored support that gradually diminishes as learners gain mastery, fostering independent problem-solving skills in education. Modeling demonstrates expert behaviors or processes, allowing students to observe and imitate successful strategies for learning and task completion. Both techniques enhance understanding by combining direct guidance with active participation, promoting deeper cognitive development.
Table of Comparison
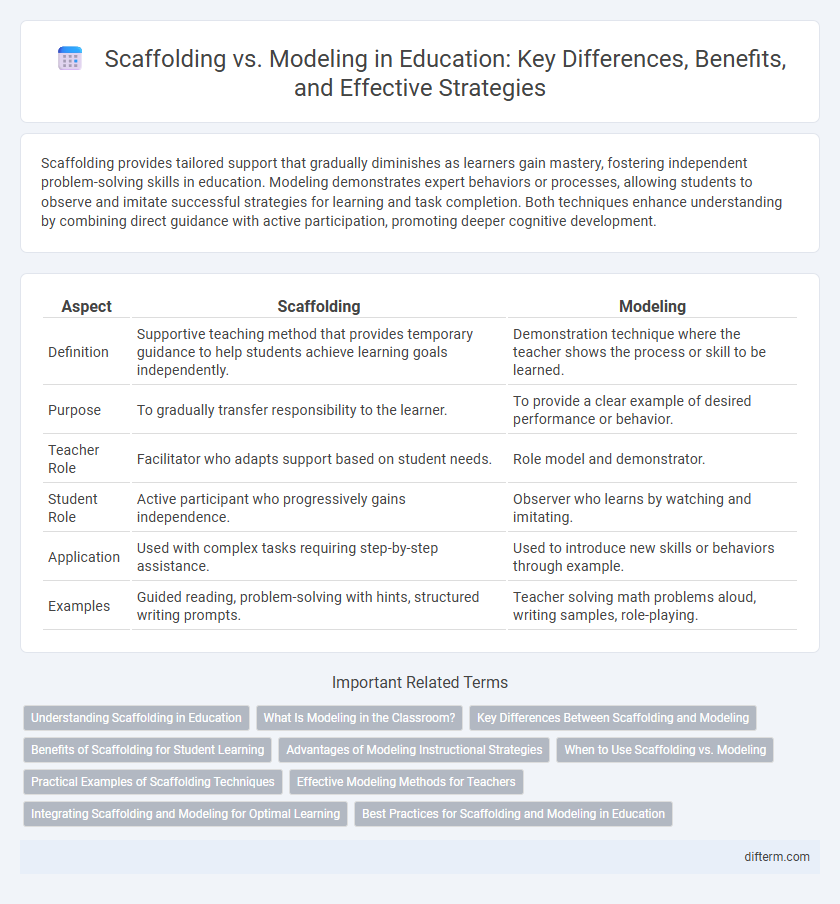
| Aspect | Scaffolding | Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supportive teaching method that provides temporary guidance to help students achieve learning goals independently. | Demonstration technique where the teacher shows the process or skill to be learned. |
| Purpose | To gradually transfer responsibility to the learner. | To provide a clear example of desired performance or behavior. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator who adapts support based on student needs. | Role model and demonstrator. |
| Student Role | Active participant who progressively gains independence. | Observer who learns by watching and imitating. |
| Application | Used with complex tasks requiring step-by-step assistance. | Used to introduce new skills or behaviors through example. |
| Examples | Guided reading, problem-solving with hints, structured writing prompts. | Teacher solving math problems aloud, writing samples, role-playing. |
Understanding Scaffolding in Education
Scaffolding in education refers to the strategic support provided by teachers to help students progress toward stronger understanding and greater independence in the learning process. This method involves breaking down complex tasks into manageable parts, offering guidance and resources tailored to individual learner needs. Effective scaffolding enhances cognitive development by gradually shifting responsibility from teacher to student, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
What Is Modeling in the Classroom?
Modeling in the classroom involves the teacher demonstrating specific skills, processes, or behaviors to guide student learning and understanding. This technique provides a clear example that students can observe and emulate, enhancing comprehension and skill acquisition. Effective modeling supports students by making abstract concepts tangible and actionable through step-by-step demonstration.
Key Differences Between Scaffolding and Modeling
Scaffolding involves providing temporary support and gradually removing assistance as learners gain independence, emphasizing guided practice and tailored feedback. Modeling demonstrates specific skills or behaviors for students to observe and imitate, focusing on clear examples and expectations. The key difference lies in scaffolding's adaptive support throughout the learning process, while modeling centers on showcasing desired outcomes for learners to replicate.
Benefits of Scaffolding for Student Learning
Scaffolding enhances student learning by providing tailored support that gradually shifts responsibility to the learner, fostering independence and confidence in problem-solving. It promotes deeper understanding through guided practice, enabling students to connect new knowledge with prior experiences. This approach increases engagement and motivation, leading to improved academic outcomes and long-term retention.
Advantages of Modeling Instructional Strategies
Modeling instructional strategies enhance learners' comprehension by providing clear, concrete examples of desired skills or behaviors, facilitating observational learning. This approach supports cognitive development through demonstration, allowing students to internalize processes and replicate them independently. Research indicates modeling increases engagement and retention, particularly in complex or abstract subject areas, by bridging theory and practice effectively.
When to Use Scaffolding vs. Modeling
Use scaffolding when learners need structured support to progressively build skills and knowledge through guided practice and tailored prompts. Modeling is most effective for demonstrating specific techniques or processes, allowing students to observe and internalize expert performance before attempting tasks independently. Scaffolding is ideal during early acquisition stages, while modeling suits skill acquisition requiring clear examples and repeated observations.
Practical Examples of Scaffolding Techniques
Scaffolding techniques in education include breaking complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps, providing hints or prompts, and using visual aids such as graphic organizers to support student understanding. For example, teachers may guide students through a math problem by demonstrating each stage before gradually reducing assistance. Another practical approach is prompting students with questions to encourage critical thinking while allowing them to construct knowledge independently.
Effective Modeling Methods for Teachers
Effective modeling methods for teachers include demonstrating thought processes aloud, using clear and explicit examples, and gradually increasing task complexity to support student understanding. Incorporating visual aids and real-life applications enhances comprehension and retention, fostering deeper engagement with the material. Regularly assessing student responses allows teachers to adjust their modeling strategies, ensuring alignment with diverse learning needs.
Integrating Scaffolding and Modeling for Optimal Learning
Integrating scaffolding and modeling in education enhances students' comprehension and skill acquisition by providing step-by-step support alongside clear examples of expert performance. Scaffolding breaks complex tasks into manageable parts, enabling learners to gradually develop independence, while modeling demonstrates effective strategies and problem-solving processes for learners to emulate. Combining these instructional techniques fosters deeper understanding and retention, leading to more effective and autonomous learning outcomes.
Best Practices for Scaffolding and Modeling in Education
Effective scaffolding in education involves gradually releasing responsibility to students by providing tailored support that adapts to their evolving skill levels and encourages active problem-solving. Modeling best practices include demonstrating cognitive and metacognitive strategies explicitly, making thinking processes visible to learners through clear, step-by-step examples. Combining these techniques fosters deeper understanding and skill acquisition by first guiding learners through tasks and then enabling independent application.
Scaffolding vs Modeling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com