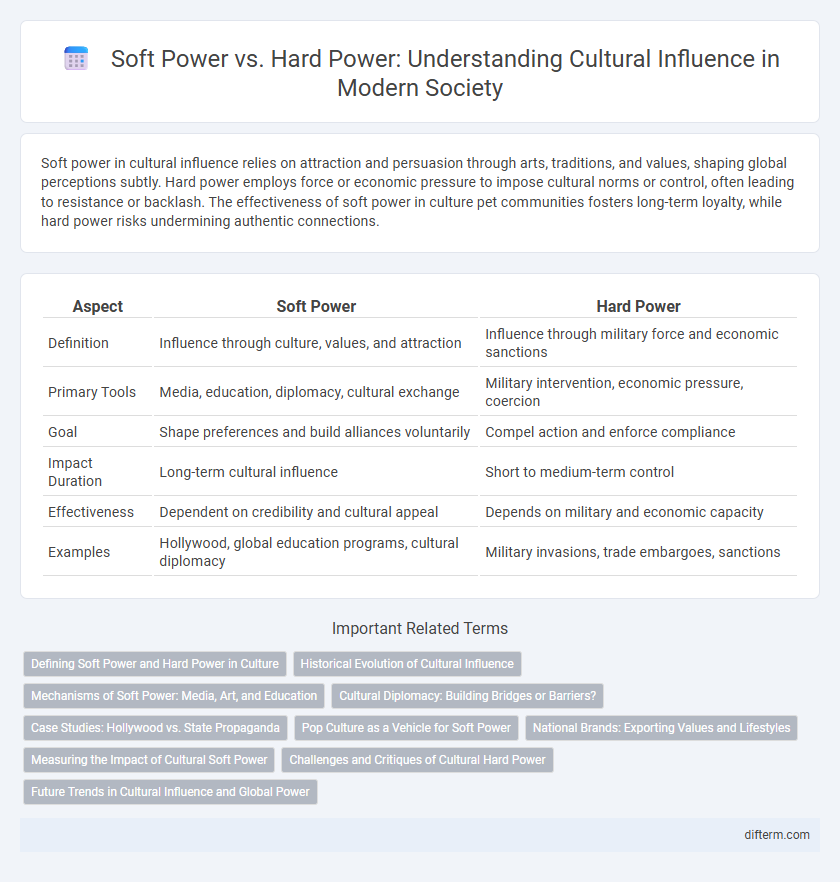
Soft power in cultural influence relies on attraction and persuasion through arts, traditions, and values, shaping global perceptions subtly. Hard power employs force or economic pressure to impose cultural norms or control, often leading to resistance or backlash. The effectiveness of soft power in culture pet communities fosters long-term loyalty, while hard power risks undermining authentic connections.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Soft Power | Hard Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Influence through culture, values, and attraction | Influence through military force and economic sanctions |
| Primary Tools | Media, education, diplomacy, cultural exchange | Military intervention, economic pressure, coercion |
| Goal | Shape preferences and build alliances voluntarily | Compel action and enforce compliance |
| Impact Duration | Long-term cultural influence | Short to medium-term control |
| Effectiveness | Dependent on credibility and cultural appeal | Depends on military and economic capacity |
| Examples | Hollywood, global education programs, cultural diplomacy | Military invasions, trade embargoes, sanctions |
Defining Soft Power and Hard Power in Culture
Soft power in culture is the ability of a nation or group to attract and co-opt others through cultural appeal, values, and ideologies, influencing global perceptions and behaviors without force or coercion. Hard power involves direct influence through military, economic, or political means to compel or coerce behavior from others. While soft power relies on cultural diplomacy, media, education, and shared values, hard power emphasizes tangible control mechanisms like sanctions, military presence, and political pressure.
Historical Evolution of Cultural Influence
Cultural influence has evolved from hard power tactics like colonization and military conquest to the strategic use of soft power through media, education, and diplomacy. Historical shifts show nations leveraging cultural exports such as language, arts, and technology to shape global perceptions and forge alliances without coercion. This transition underscores the growing importance of cultural attractiveness in international relations and global influence.
Mechanisms of Soft Power: Media, Art, and Education
Media, art, and education serve as primary mechanisms of soft power by shaping perceptions and values across global audiences. Cultural exports such as films, music, and literature create emotional connections that enhance a nation's attractiveness without coercion. Educational exchanges and academic collaborations foster long-term relationships and mutual understanding, reinforcing cultural influence at a foundational level.
Cultural Diplomacy: Building Bridges or Barriers?
Cultural diplomacy leverages soft power by promoting mutual understanding and shared values through art, education, and exchange programs, fostering cooperation between nations. Hard power approaches in cultural influence often impose specific ideologies or restrict cultural expressions, creating resistance and barriers instead of dialogue. Effective cultural diplomacy balances these strategies to build bridges that facilitate global partnerships and peaceful interactions.
Case Studies: Hollywood vs. State Propaganda
Hollywood's global dominance in film and television exemplifies soft power, shaping cultural values and public opinion through entertainment that promotes ideas of freedom and individualism. State propaganda relies on hard power tactics by controlling media content and disseminating ideological messages to reinforce government authority and national unity. Comparative case studies reveal Hollywood's persuasive appeal produces more sustainable cultural influence, while state propaganda often triggers resistance and skepticism.
Pop Culture as a Vehicle for Soft Power
Pop culture serves as a powerful vehicle for soft power by shaping global perceptions and values through music, film, fashion, and digital media. Nations leveraging pop culture exports, such as K-pop from South Korea or Hollywood movies from the United States, enhance their cultural appeal and influence without coercion. This form of cultural diplomacy fosters international goodwill, facilitates cross-cultural exchange, and strengthens a country's global standing more effectively than hard power tactics like military or economic force.
National Brands: Exporting Values and Lifestyles
National brands leverage soft power by exporting values and lifestyles that shape global perceptions and consumer behavior, fostering cultural affinity without coercion. Unlike hard power, which relies on military or economic force, cultural influence through branding promotes long-term relationships and ideological alignment across borders. This strategic use of cultural capital enhances a nation's global image, boosting economic and diplomatic leverage.
Measuring the Impact of Cultural Soft Power
Measuring the impact of cultural soft power involves analyzing indicators such as international public opinion, cultural exports, and global media influence to assess a nation's ability to shape preferences and attract cooperation. Metrics include the popularity of cultural products, the reach of language and education programs, and the effectiveness of diplomacy in promoting national values. Quantitative data from cultural exchange participation and qualitative assessments of cultural resonance reveal the nuanced effectiveness of soft power compared to traditional hard power approaches.
Challenges and Critiques of Cultural Hard Power
Cultural hard power faces challenges such as resistance from local populations who perceive imposed values as cultural imperialism, leading to backlash instead of influence. Critics argue that coercive tactics undermine genuine cultural exchange and fail to foster long-term respect or understanding. The reliance on economic or military pressure to enforce cultural norms often generates ethical concerns and diminishes legitimacy in international relations.
Future Trends in Cultural Influence and Global Power
Future trends in cultural influence suggest a growing emphasis on soft power as global interconnectedness increases and digital media expands cultural reach. Nations leveraging cultural diplomacy, creative industries, and educational exchanges are expected to shape global power dynamics more effectively than traditional hard power tactics. This shift highlights the rising importance of cultural narratives and values in international relations and global leadership.
Soft power vs hard power (in cultural influence) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com