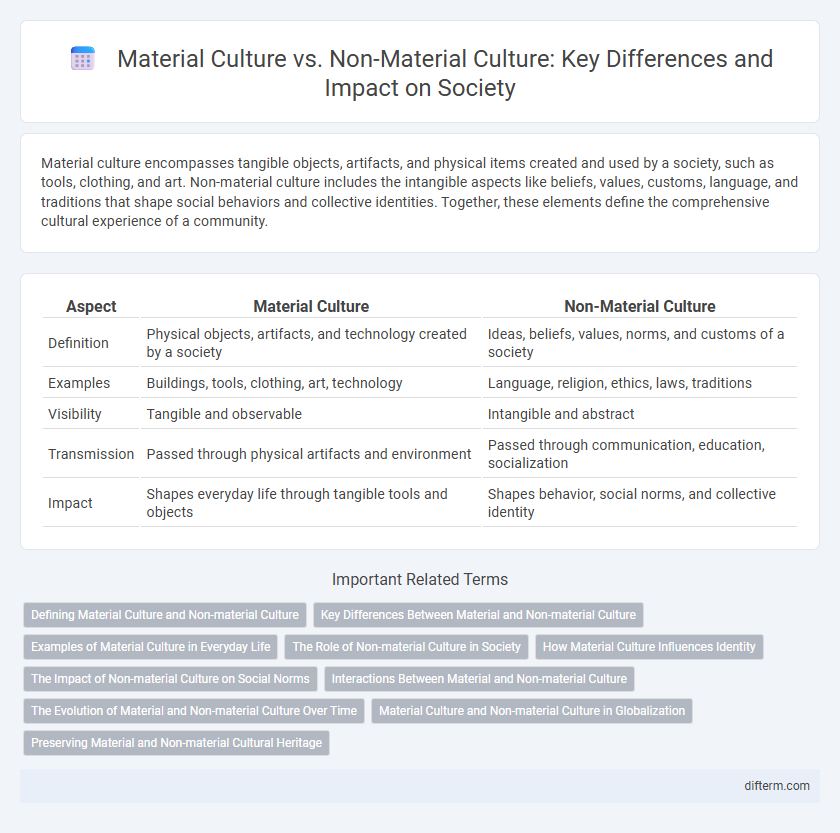
Material culture encompasses tangible objects, artifacts, and physical items created and used by a society, such as tools, clothing, and art. Non-material culture includes the intangible aspects like beliefs, values, customs, language, and traditions that shape social behaviors and collective identities. Together, these elements define the comprehensive cultural experience of a community.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Material Culture | Non-Material Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical objects, artifacts, and technology created by a society | Ideas, beliefs, values, norms, and customs of a society |
| Examples | Buildings, tools, clothing, art, technology | Language, religion, ethics, laws, traditions |
| Visibility | Tangible and observable | Intangible and abstract |
| Transmission | Passed through physical artifacts and environment | Passed through communication, education, socialization |
| Impact | Shapes everyday life through tangible tools and objects | Shapes behavior, social norms, and collective identity |
Defining Material Culture and Non-material Culture
Material culture encompasses the physical objects, artifacts, and technology created and used by a society, such as tools, clothing, buildings, and art. Non-material culture refers to the intangible aspects including beliefs, values, customs, language, and social norms that shape a group's way of life. Understanding the distinction between these two components is essential for analyzing how culture influences human behavior and social organization.
Key Differences Between Material and Non-material Culture
Material culture consists of physical objects, artifacts, and technological tools created and used by society, reflecting tangible aspects of human life. Non-material culture encompasses intangible elements such as beliefs, values, norms, language, and customs that shape social behavior and identity. The key difference lies in material culture's physical presence, whereas non-material culture exists in ideas and practices transmitted through socialization.
Examples of Material Culture in Everyday Life
Material culture encompasses tangible objects created and used by a society, such as clothing, tools, architecture, and artwork. Everyday examples include smartphones, kitchen utensils, vehicles, and furniture, which reflect technological advancement and cultural values. These physical artifacts provide insight into the lifestyle, economic activities, and social norms of a community.
The Role of Non-material Culture in Society
Non-material culture encompasses beliefs, values, norms, language, and customs that shape social behavior and collective identity within a society. It plays a crucial role in guiding interpersonal interactions, ensuring social cohesion, and transmitting cultural heritage across generations. Unlike material culture, which consists of physical objects, non-material culture influences attitudes and social structures, underpinning the meaning and purpose of community life.
How Material Culture Influences Identity
Material culture, encompassing physical objects like clothing, architecture, and technology, shapes individual and collective identity by providing tangible symbols of cultural heritage and social belonging. These artifacts influence self-expression and group affiliation, reinforcing societal norms and values embedded within a community. Non-material culture, including beliefs, traditions, and language, interacts with material culture to create a comprehensive framework for identity formation and cultural continuity.
The Impact of Non-material Culture on Social Norms
Non-material culture, encompassing beliefs, values, and norms, significantly shapes social behavior by influencing unwritten rules and expectations within a society. These intangible elements guide interpersonal interactions, moral judgments, and community cohesion more profoundly than physical artifacts alone. Understanding non-material culture is essential for analyzing the formation and evolution of social norms across different cultural contexts.
Interactions Between Material and Non-material Culture
Material culture, consisting of physical objects such as tools, clothing, and technology, directly influences non-material culture by shaping beliefs, values, and social norms. Non-material culture, including traditions, language, and customs, guides the creation, use, and symbolic meaning of material artifacts, reflecting cultural identity and societal priorities. The dynamic interaction between these two forms of culture drives cultural evolution and facilitates the adaptation of societies to changing environments.
The Evolution of Material and Non-material Culture Over Time
Material culture, encompassing physical objects like tools, clothing, and artifacts, evolves through technological advances that reshape everyday life and societal functions. Non-material culture, including beliefs, values, and customs, transforms with changing social norms, ideologies, and collective experiences, often driving shifts in material culture itself. The interplay between these two cultural dimensions reflects dynamic human adaptation and cultural continuity across historical epochs.
Material Culture and Non-material Culture in Globalization
Material culture encompasses physical objects, artifacts, and technology that shape everyday life, such as clothing, architecture, and tools, which are increasingly exchanged and adapted across global societies. Non-material culture includes intangible elements like beliefs, values, norms, and customs that influence social behavior and identity, often evolving through cross-cultural interactions and global communication. Globalization accelerates the diffusion of both material and non-material cultural components, creating hybrid cultures and impacting cultural preservation and transformation worldwide.
Preserving Material and Non-material Cultural Heritage
Preserving material culture involves safeguarding physical artifacts like monuments, artworks, and traditional crafts that embody historical and cultural significance. Non-material cultural heritage includes intangible elements such as oral traditions, performing arts, rituals, and knowledge systems that require documentation, transmission, and community engagement for their survival. Effective conservation strategies integrate digital archiving, education programs, and international cooperation to ensure both tangible and intangible cultural assets endure for future generations.
Material culture vs Non-material culture Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com