Rituals are formalized and symbolic actions performed with specific meanings and often tied to religious or spiritual beliefs, while customs are habitual practices shared by a community that shape everyday life and social interactions. Rituals tend to follow a prescribed set of steps and carry deeper cultural significance, whereas customs evolve organically and may vary widely within different groups. Both play crucial roles in preserving cultural identity, but rituals emphasize intentionality and symbolism, contrasting with the flexible, adaptive nature of customs.
Table of Comparison
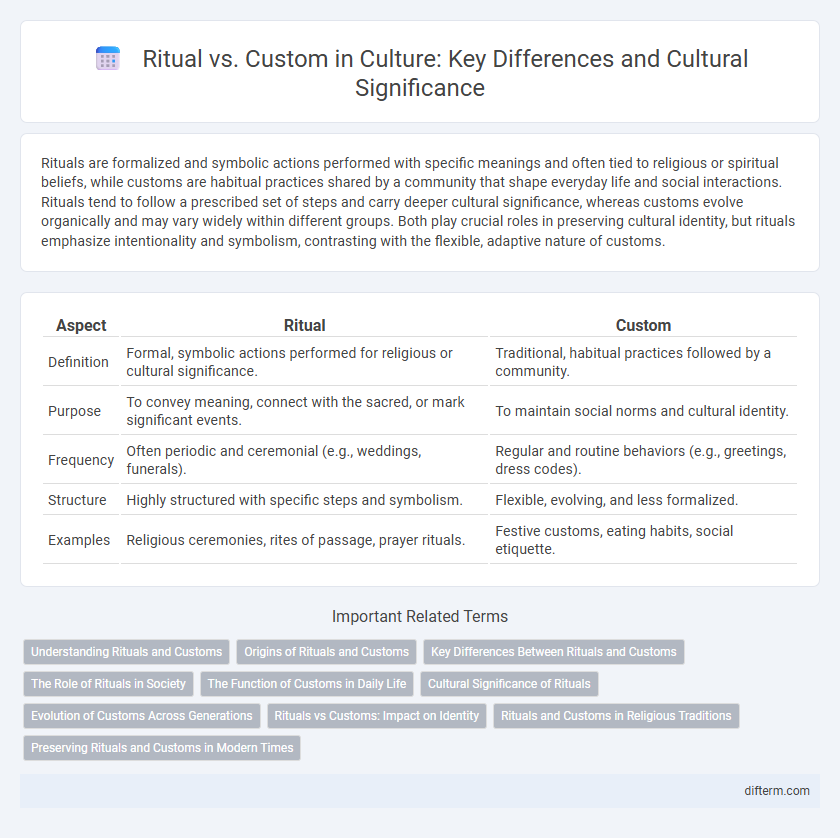
| Aspect | Ritual | Custom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal, symbolic actions performed for religious or cultural significance. | Traditional, habitual practices followed by a community. |
| Purpose | To convey meaning, connect with the sacred, or mark significant events. | To maintain social norms and cultural identity. |
| Frequency | Often periodic and ceremonial (e.g., weddings, funerals). | Regular and routine behaviors (e.g., greetings, dress codes). |
| Structure | Highly structured with specific steps and symbolism. | Flexible, evolving, and less formalized. |
| Examples | Religious ceremonies, rites of passage, prayer rituals. | Festive customs, eating habits, social etiquette. |
Understanding Rituals and Customs
Rituals are formalized actions performed in a specific order, often imbued with symbolic meaning and spiritual significance within a culture, while customs are habitual practices shared by a group that may not hold deep symbolic value. Understanding rituals involves recognizing their role in reinforcing community beliefs and spiritual connections, whereas understanding customs requires grasping everyday social behaviors that define cultural identity. Both rituals and customs shape cultural continuity by fostering shared experiences and collective memory.
Origins of Rituals and Customs
Rituals originate from deeply rooted religious or spiritual beliefs, often involving prescribed actions that symbolize connection to a higher power or community identity. Customs develop from habitual social practices passed down through generations, reflecting cultural norms and collective experiences. Both play crucial roles in shaping societal structure and reinforcing shared values within cultural groups.
Key Differences Between Rituals and Customs
Rituals are formal, symbolic actions performed in a specific sequence, often with spiritual or cultural significance, while customs are habitual practices developed over time within a community. Rituals usually involve prescribed ceremonies and are often tied to religious or cultural rites, whereas customs are more flexible social behaviors that reflect a group's identity and everyday traditions. Understanding the key differences highlights how rituals convey meaning through intentional actions, whereas customs serve as a reflection of collective social norms and values.
The Role of Rituals in Society
Rituals serve as structured practices that reinforce cultural identity and social cohesion, often marked by symbolic actions performed in a prescribed order. These ceremonies provide individuals with a sense of belonging and continuity, connecting communities across generations. Unlike customs, which are habitual and informal behaviors, rituals carry profound spiritual or societal significance, shaping collective values and social norms.
The Function of Customs in Daily Life
Customs serve as essential frameworks guiding daily behavior, reinforcing social norms, and fostering community cohesion by establishing predictable patterns of interaction. These shared practices transmit cultural values, promote social harmony, and provide individuals with a sense of identity and belonging within their group. Unlike rituals, which often carry ceremonial or symbolic significance, customs primarily facilitate practical, everyday social order and continuity.
Cultural Significance of Rituals
Rituals hold deep cultural significance as they embody collective beliefs, values, and social identities passed down through generations, often marked by symbolic actions or ceremonies. Unlike customs, which are habitual practices, rituals are intentionally structured and imbued with meaning, fostering community cohesion and reinforcing cultural continuity. The performative nature of rituals serves to connect individuals to their heritage, reinforcing shared narratives and cultural heritage within societies.
Evolution of Customs Across Generations
Rituals often originate from deeply rooted spiritual or religious practices, maintaining consistent forms across generations, while customs evolve dynamically, adapting to social changes and technological advancements. The transmission of customs reflects shifting values and collective experiences, highlighting cultural resilience and identity transformation. This evolution underscores how communities continuously reinterpret traditions to remain relevant in contemporary contexts.
Rituals vs Customs: Impact on Identity
Rituals reinforce collective identity through formalized, symbolic actions that connect individuals to shared cultural values and traditions. Customs, as habitual practices passed down through generations, shape everyday behaviors and social norms, fostering a sense of belonging within a community. The interplay between rituals and customs creates a dynamic framework for cultural identity, blending structured ceremonies with routine social practices.
Rituals and Customs in Religious Traditions
Rituals in religious traditions are structured ceremonies with symbolic actions performed in specific sequences to convey spiritual meanings, often reinforcing communal beliefs and values. Customs represent habitual practices or social norms observed by adherents, reflecting the cultural heritage and everyday life within the religious community. Understanding the distinction between rituals and customs helps illuminate how faith is both formally expressed and informally lived.
Preserving Rituals and Customs in Modern Times
Preserving rituals and customs in modern times involves balancing traditional practices with contemporary lifestyles, ensuring cultural heritage remains vibrant and meaningful. Rituals often carry deep symbolic significance and structured ceremonies, while customs tend to be habitual behaviors reflecting communal values. Efforts such as cultural festivals, oral history projects, and educational programs play critical roles in maintaining these practices amidst rapid social change and globalization.
Ritual vs Custom Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com