Culture pet explores the distinctions between gender roles and gender norms, highlighting how gender roles refer to the socially expected behaviors assigned to individuals based on their perceived gender. Gender norms, on the other hand, encompass the broader societal rules and standards that dictate what is considered acceptable or typical for each gender. Analyzing these concepts reveals how cultural practices shape identities and influence social dynamics within communities.
Table of Comparison
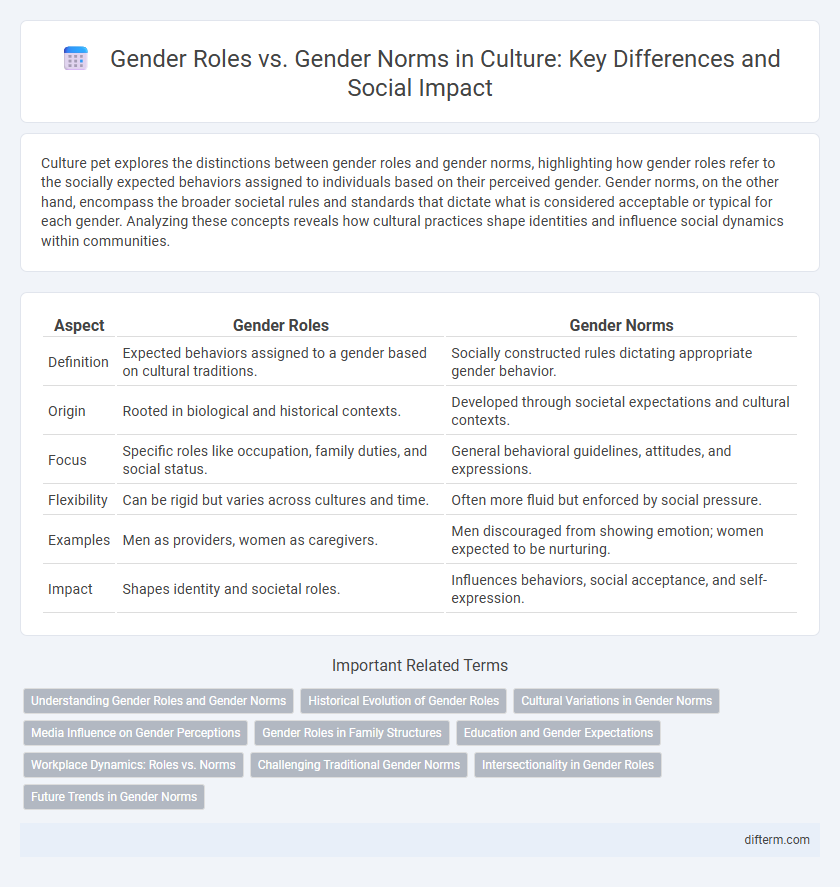
| Aspect | Gender Roles | Gender Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expected behaviors assigned to a gender based on cultural traditions. | Socially constructed rules dictating appropriate gender behavior. |
| Origin | Rooted in biological and historical contexts. | Developed through societal expectations and cultural contexts. |
| Focus | Specific roles like occupation, family duties, and social status. | General behavioral guidelines, attitudes, and expressions. |
| Flexibility | Can be rigid but varies across cultures and time. | Often more fluid but enforced by social pressure. |
| Examples | Men as providers, women as caregivers. | Men discouraged from showing emotion; women expected to be nurturing. |
| Impact | Shapes identity and societal roles. | Influences behaviors, social acceptance, and self-expression. |
Understanding Gender Roles and Gender Norms
Understanding gender roles involves recognizing the societal expectations assigned to individuals based on their perceived gender, which shape behaviors, responsibilities, and opportunities. Gender norms refer to the deeply ingrained cultural standards that dictate acceptable expressions, attire, and interactions for different genders, often reinforced through media, education, and family structures. Examining the distinction between gender roles and gender norms highlights how cultural constructs influence identity formation and social dynamics.
Historical Evolution of Gender Roles
Historical evolution of gender roles reveals a significant transformation influenced by economic, social, and political changes across centuries. In agrarian societies, rigid gender roles centered on division of labor based on physical ability, while industrialization introduced more fluid expectations, enabling women's entry into the workforce. Contemporary cultures increasingly challenge traditional gender norms, promoting equality and diverse gender identities through legal reforms and social movements.
Cultural Variations in Gender Norms
Cultural variations in gender norms reflect diverse societal frameworks shaping expectations for behavior, roles, and identities across different communities. In some cultures, rigid gender roles dictate specific responsibilities and status, while others embrace fluid or multiple gender identities, challenging binary conceptions. Understanding these cultural distinctions highlights the importance of context in analyzing gender dynamics and promotes a more inclusive perspective on identity and equality.
Media Influence on Gender Perceptions
Media significantly shapes gender perceptions by reinforcing traditional gender roles and norms through repeated portrayals in television, film, and advertising. Stereotypical depictions often present men as dominant and women as nurturing, influencing public attitudes and expectations regarding gender behavior. These portrayals contribute to the persistence of rigid gender norms, impacting individual identity formation and societal power dynamics.
Gender Roles in Family Structures
Gender roles in family structures define specific responsibilities and behaviors expected from individuals based on their gender, deeply influencing decision-making, caregiving, and economic contributions. Traditional gender roles often assign men as breadwinners and women as caregivers, shaping household dynamics and power distribution. These roles impact cultural identity, socialization processes, and intergenerational relationships within families across diverse societies.
Education and Gender Expectations
Gender roles in education shape students' experiences by reinforcing traditional gender norms, often steering girls toward humanities and boys toward STEM fields. These expectations limit individual potential and perpetuate gender disparities in academic achievement and career opportunities. Challenging conventional gender norms in educational settings promotes equity and encourages diverse skill development regardless of gender.
Workplace Dynamics: Roles vs. Norms
Gender roles in workplace dynamics refer to traditional expectations assigned to men and women based on societal beliefs, often dictating job types and leadership opportunities. Gender norms, however, encompass broader cultural standards influencing daily workplace behavior, interaction, and accepted professional conduct beyond specific job functions. Understanding the distinction helps organizations develop inclusive policies that challenge stereotypes and promote equity in career advancement and workplace participation.
Challenging Traditional Gender Norms
Challenging traditional gender norms reshapes cultural expectations by promoting equality and fluidity in gender roles, allowing individuals to express identities beyond binary definitions. This shift encourages dismantling stereotypes that restrict behavior, opportunities, and self-perception based on gender. Embracing diverse gender expressions fosters inclusivity and advances social progress within both family and workplace settings.
Intersectionality in Gender Roles
Gender roles are socially constructed behaviors and expectations assigned to individuals based on their perceived sex, while gender norms encompass the broader societal standards dictating conformity to these roles. Intersectionality highlights how overlapping identities such as race, class, ethnicity, and sexuality influence the experience and expression of gender roles, revealing the complexity beyond binary classifications. Understanding intersectionality in gender roles is essential for addressing diverse and nuanced challenges faced by marginalized groups within cultural contexts.
Future Trends in Gender Norms
Emerging future trends in gender norms emphasize increased fluidity and inclusivity, challenging traditional gender roles that have long dictated behavior and societal expectations. Advances in education, media representation, and policy reforms are driving a cultural shift towards recognizing non-binary and diverse gender identities. This evolution promotes greater equality and diminishes rigid stereotypes, fostering a more accepting and dynamic understanding of gender in global societies.
gender roles vs gender norms Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com