Formal norms in culture consist of written rules and laws that dictate appropriate behavior, ensuring social order and consistency. Informal norms, though unwritten, govern everyday interactions through shared expectations and social cues that promote cohesion within communities. Both formal and informal norms shape cultural identity by influencing how individuals communicate, behave, and maintain relationships.
Table of Comparison
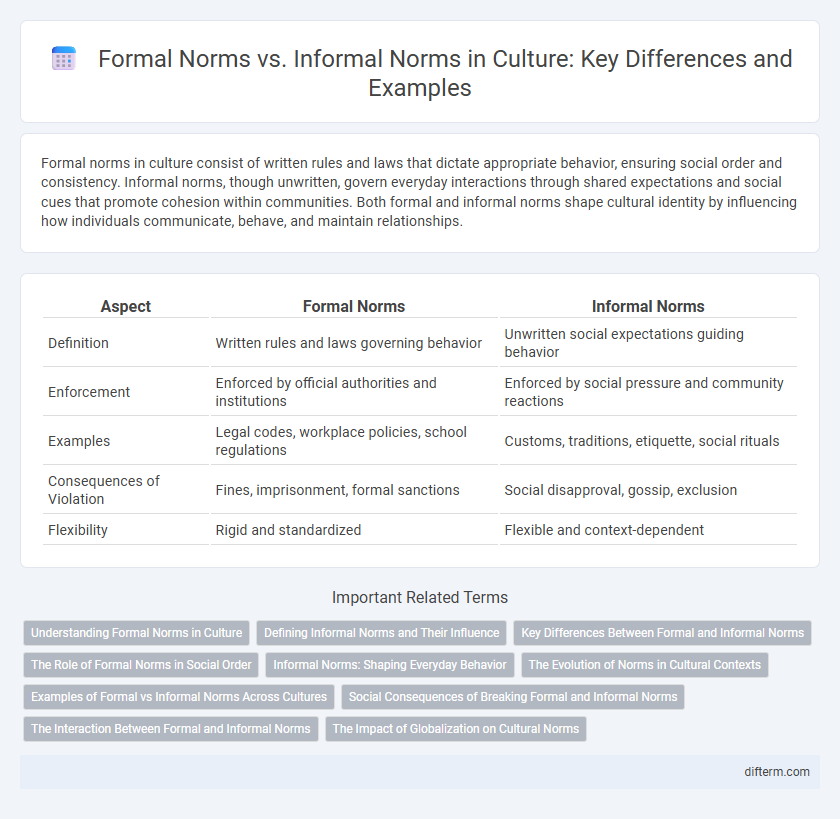
| Aspect | Formal Norms | Informal Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Written rules and laws governing behavior | Unwritten social expectations guiding behavior |
| Enforcement | Enforced by official authorities and institutions | Enforced by social pressure and community reactions |
| Examples | Legal codes, workplace policies, school regulations | Customs, traditions, etiquette, social rituals |
| Consequences of Violation | Fines, imprisonment, formal sanctions | Social disapproval, gossip, exclusion |
| Flexibility | Rigid and standardized | Flexible and context-dependent |
Understanding Formal Norms in Culture
Formal norms in culture consist of established rules and laws enforced by official institutions, guiding acceptable behavior in structured settings. These norms are explicit, documented, and often come with specific sanctions for violations, ensuring social order and predictability. Understanding formal norms helps individuals navigate legal systems, workplace protocols, and educational standards within a cultural context.
Defining Informal Norms and Their Influence
Informal norms are unwritten, socially shared rules that guide everyday behavior within cultural groups, influencing interactions without formal enforcement mechanisms. These norms dictate acceptable dress codes, language use, and social rituals, shaping group identity and cohesion through shared expectations. Their influence extends to workplace dynamics, peer relationships, and community practices, often reinforcing cultural continuity and social order informally.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Norms
Formal norms are codified rules established by authorities, including laws, regulations, and company policies, which carry explicit sanctions for non-compliance. Informal norms consist of unwritten social expectations, such as customs, traditions, and etiquette, guiding everyday behavior without official enforcement. The key difference lies in formal norms being documented and officially enforced, while informal norms rely on social approval and peer pressure for adherence.
The Role of Formal Norms in Social Order
Formal norms, such as laws and regulations, play a critical role in establishing clear expectations and consequences within society, thereby maintaining social order. These codified rules are enforced by authorized institutions to ensure compliance and resolve conflicts systematically. By providing stability and predictability, formal norms help coordinate behavior across diverse groups and prevent chaos.
Informal Norms: Shaping Everyday Behavior
Informal norms play a crucial role in shaping everyday behavior by guiding social interactions through unspoken rules and shared expectations within a community. These norms influence manners, dress codes, and communication styles without formal enforcement, often reflecting cultural values and social cohesion. Understanding informal norms enhances social harmony and reduces conflicts by fostering implicit mutual understanding among individuals.
The Evolution of Norms in Cultural Contexts
Formal norms in cultural contexts are codified rules such as laws and official regulations that govern behavior, while informal norms consist of unwritten social expectations shaped by customs and traditions. The evolution of norms reflects shifting values, technological advancements, and intercultural interactions, leading to dynamic adaptations in both formal and informal guidelines. Understanding the interplay between these evolving norms is crucial for analyzing social cohesion and cultural change across diverse societies.
Examples of Formal vs Informal Norms Across Cultures
Formal norms, such as laws against theft in the United States or traffic regulations in Germany, are codified rules enforced by official institutions, ensuring societal order. Informal norms vary culturally and include practices like bowing as a greeting in Japan or the casual dress code often seen at social gatherings in Brazil, reflecting underlying social expectations and values. These distinctions highlight how formal norms maintain structured compliance, whereas informal norms guide everyday interpersonal interactions differently across cultures.
Social Consequences of Breaking Formal and Informal Norms
Breaking formal norms such as laws often results in legal penalties, including fines, imprisonment, or community service, reflecting society's investment in maintaining order and safety. Violating informal norms, like dress codes or etiquette, typically leads to social sanctions such as ostracism, gossip, or loss of reputation, which can impact personal relationships and social standing. The severity of consequences from formal versus informal norm violations depends on cultural context and the specific norms breached, influencing social cohesion and individual behavior within a community.
The Interaction Between Formal and Informal Norms
Formal norms consist of codified rules and regulations established by institutions, while informal norms are unwritten social expectations shaped by cultural practices and daily interactions. Their interaction influences behavior by balancing legal requirements with social acceptance, often leading to the emergence of hybrid norms in workplaces, communities, and organizations. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for analyzing how social order and compliance evolve in different cultural contexts.
The Impact of Globalization on Cultural Norms
Globalization accelerates the blending of formal norms, such as laws and regulations, across cultures, promoting uniformity in business and legal practices worldwide. Informal norms, including social customs and everyday behaviors, adapt more fluidly, reflecting a fusion of traditions influenced by international media, migration, and technology. This dynamic reshapes cultural identities, challenging traditional boundaries while fostering cross-cultural understanding and hybrid social practices.
formal norms vs informal norms Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com