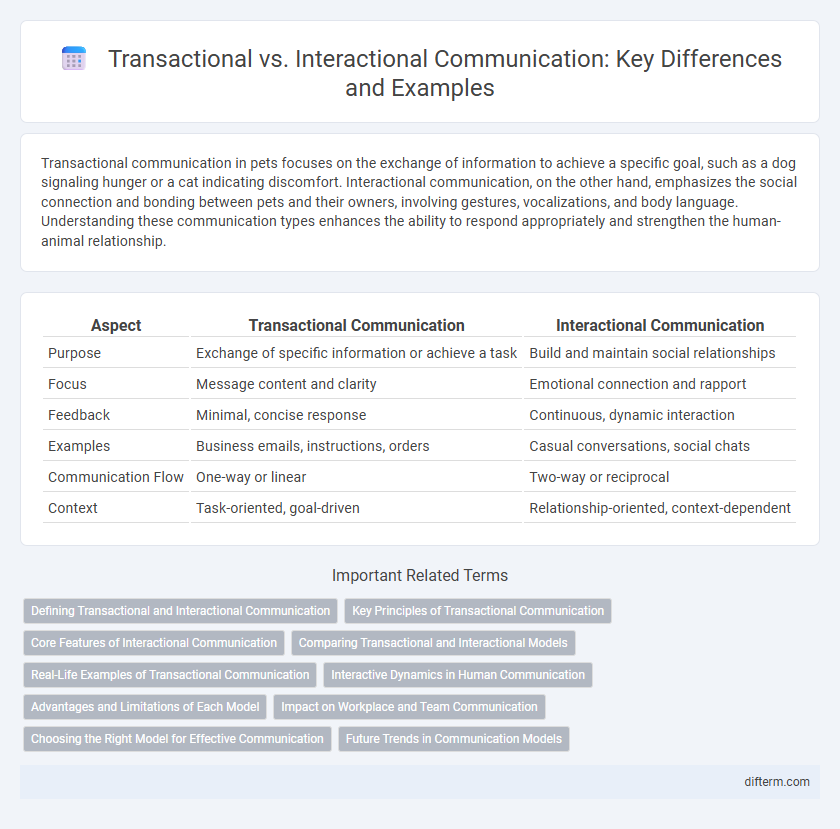
Transactional communication in pets focuses on the exchange of information to achieve a specific goal, such as a dog signaling hunger or a cat indicating discomfort. Interactional communication, on the other hand, emphasizes the social connection and bonding between pets and their owners, involving gestures, vocalizations, and body language. Understanding these communication types enhances the ability to respond appropriately and strengthen the human-animal relationship.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transactional Communication | Interactional Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Exchange of specific information or achieve a task | Build and maintain social relationships |
| Focus | Message content and clarity | Emotional connection and rapport |
| Feedback | Minimal, concise response | Continuous, dynamic interaction |
| Examples | Business emails, instructions, orders | Casual conversations, social chats |
| Communication Flow | One-way or linear | Two-way or reciprocal |
| Context | Task-oriented, goal-driven | Relationship-oriented, context-dependent |
Defining Transactional and Interactional Communication
Transactional communication involves the exchange of information with a specific goal, emphasizing sender and receiver roles simultaneously to create shared meaning. Interactional communication focuses on social interactions that build relationships and maintain social bonds through reciprocal feedback. Understanding these communication types enhances effective message delivery in both professional and personal contexts.
Key Principles of Transactional Communication
Transactional communication is characterized by the simultaneous sending and receiving of messages, emphasizing the dynamic and continuous exchange between participants. Key principles include the mutual influence of communicators, context shaping the interaction, and the shared creation of meaning through verbal and nonverbal cues. This model highlights the importance of feedback and adaptability to ensure effective and meaningful communication in interpersonal and organizational settings.
Core Features of Interactional Communication
Interactional communication emphasizes mutual exchange and social connection, characterized by continuous feedback loops, shared context, and relational dynamics. This form of communication prioritizes understanding, empathy, and the negotiation of meaning between participants, fostering stronger interpersonal relationships. Core features include bidirectional message flow, adaptability to social cues, and a focus on maintaining interpersonal bonds rather than simply transmitting information.
Comparing Transactional and Interactional Models
Transactional models of communication emphasize simultaneous sending and receiving of messages, highlighting the dynamic exchange between participants, whereas interactional models focus on sequential communication with defined roles of sender and receiver. Transactional communication integrates feedback as an ongoing process, enhancing mutual understanding in real-time, while interactional communication treats feedback as a discrete, separate response. The transactional approach better captures the complexity of communication contexts where messages are influenced by multiple simultaneous factors, making it more effective for analyzing modern interpersonal exchanges.
Real-Life Examples of Transactional Communication
Transactional communication occurs in settings like customer service calls where clear exchange of information and problem resolution are the main goals. Examples include ordering food at a restaurant, where the customer communicates their order and the server confirms it, ensuring efficient service. In professional environments, transactional communication is evident in meetings where instructions are given and feedback is directly exchanged to complete specific tasks.
Interactive Dynamics in Human Communication
Transactional communication emphasizes the exchange of messages where both sender and receiver simultaneously influence each other, highlighting the dynamic and continuous nature of human interaction. Interactional communication focuses on the social and relational aspects, where feedback and mutual understanding are essential to maintain dialogue and build connections. Analyzing interactive dynamics reveals how context, nonverbal cues, and feedback loops shape effective communication outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Model
Transactional communication models emphasize simultaneous sending and receiving of messages, allowing real-time feedback that enhances clarity and mutual understanding. However, these models may overlook individual interpretations and internal thought processes, limiting their effectiveness in complex or emotionally nuanced exchanges. Interactional models highlight the back-and-forth nature of communication with feedback loops, supporting relationship building and context consideration, but can be slower and less efficient for quick information transfer.
Impact on Workplace and Team Communication
Transactional communication drives efficiency in workplace exchanges by focusing on clear, goal-oriented messages that minimize misunderstandings and accelerate task completion. Interactional communication fosters stronger team cohesion through feedback loops, emotional expression, and collaborative dialogue, enhancing trust and morale. Balancing both approaches optimizes productivity and cultivates a supportive, adaptive work environment.
Choosing the Right Model for Effective Communication
Selecting the appropriate communication model depends on the context and goals; transactional communication emphasizes continuous, simultaneous exchange of messages, fostering dynamic feedback and mutual understanding in real-time conversations. Interactional communication, while still involving feedback, typically follows a more linear, turn-taking process suitable for structured dialogues or information transfer. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize message clarity and relationship building by aligning communication strategies with situational requirements.
Future Trends in Communication Models
Future trends in communication models emphasize a shift from transactional to interactional frameworks, highlighting the importance of dynamic, reciprocal exchanges over one-way information transfer. Emerging technologies like AI-driven platforms and real-time analytics enhance engagement by facilitating adaptive, context-aware interactions. This evolution supports more personalized, collaborative communication experiences, aligning with growing demands for immersive and responsive digital environments.
transactional vs interactional Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com