Public communication involves sharing information openly with a large audience, often through media platforms or speeches, ensuring transparency and broad reach. Private communication occurs in a more controlled, intimate setting, such as one-on-one conversations or small group discussions, allowing for confidentiality and personalized interaction. Understanding the distinct dynamics of public versus private communication helps tailor messages effectively to different audiences and contexts.
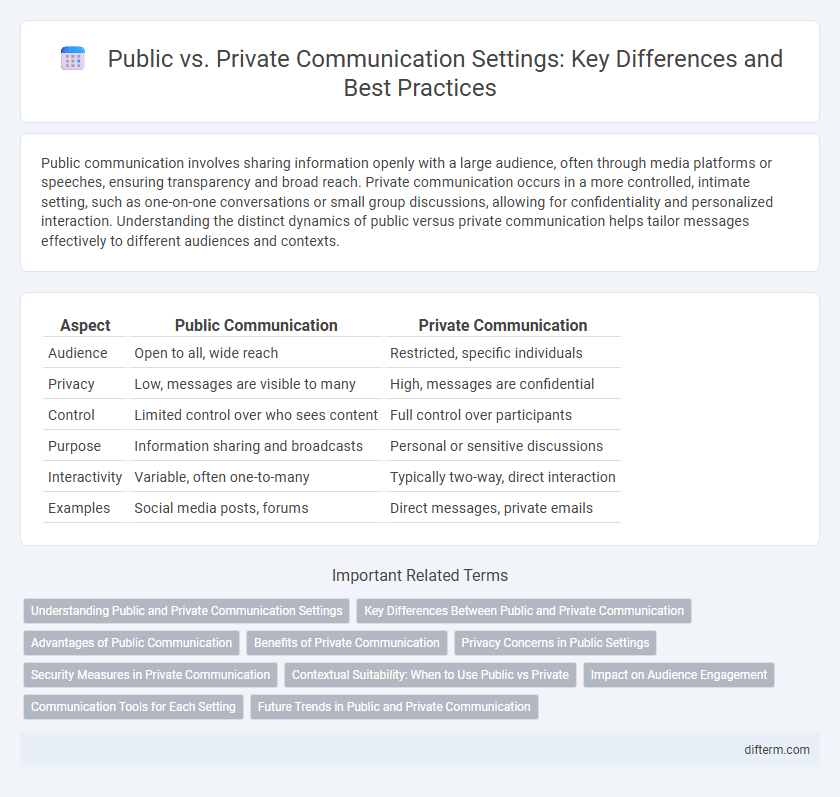
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Communication | Private Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Audience | Open to all, wide reach | Restricted, specific individuals |
| Privacy | Low, messages are visible to many | High, messages are confidential |
| Control | Limited control over who sees content | Full control over participants |
| Purpose | Information sharing and broadcasts | Personal or sensitive discussions |
| Interactivity | Variable, often one-to-many | Typically two-way, direct interaction |
| Examples | Social media posts, forums | Direct messages, private emails |
Understanding Public and Private Communication Settings
Public communication occurs in open, accessible environments where messages reach broad audiences, such as social media platforms or public speeches. Private communication takes place in restricted, intimate settings like personal conversations or encrypted messaging apps, ensuring confidentiality and selective sharing. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize message delivery based on audience scope and privacy requirements.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Communication
Public communication involves transmitting messages to large, diverse audiences in open settings such as speeches, broadcasts, or social media platforms, prioritizing clarity, formality, and broad appeal. Private communication occurs in intimate or restricted environments, including personal conversations, emails, or group chats, emphasizing confidentiality, personalization, and emotional expression. Key differences include audience size, level of formality, and the degree of message control and feedback immediacy.
Advantages of Public Communication
Public communication enhances message reach by allowing information to be shared with a broader audience, increasing awareness and engagement. It fosters transparency and accountability, essential in organizational and governmental contexts. The interactive nature of public communication encourages feedback and diverse perspectives, improving message effectiveness and community involvement.
Benefits of Private Communication
Private communication fosters trust and openness by providing a secure environment where individuals feel safe to express honest thoughts and emotions. It enhances confidentiality, reducing the risk of sensitive information being exposed or misinterpreted. This setting promotes deeper connections and personalized feedback, leading to more effective problem-solving and conflict resolution.
Privacy Concerns in Public Settings
Public communication settings pose significant privacy concerns due to the increased risk of unauthorized information exposure and eavesdropping. In these environments, sensitive data can be intercepted by unintended recipients, compromising confidentiality and personal security. Strategies such as encryption, awareness of surroundings, and selective information sharing are essential to mitigate privacy risks in public interactions.
Security Measures in Private Communication
Private communication employs robust encryption protocols such as end-to-end encryption to safeguard messages from unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication systems enhance identity verification, reducing the risk of impersonation in confidential exchanges. Secure communication platforms often implement data loss prevention techniques and strict access controls to maintain message integrity and confidentiality.
Contextual Suitability: When to Use Public vs Private
Public communication suits announcements, presentations, or marketing where broad reach and transparency are essential, fostering community engagement and brand awareness. Private communication is ideal for sensitive topics, confidential information, or personalized feedback, ensuring privacy and trust between parties. Evaluating the context, audience, and message sensitivity determines the optimal setting for effective and appropriate communication.
Impact on Audience Engagement
Public communication settings foster broad audience engagement through transparency and inclusivity, allowing diverse perspectives to be shared and debated. Private communication settings enable tailored interactions that build trust and deepen relationships by addressing specific audience needs and concerns. Understanding these dynamics enhances strategic message delivery for effective audience connection and influence.
Communication Tools for Each Setting
Public communication tools often include social media platforms, public forums, and broadcast channels designed to reach large, diverse audiences efficiently. Private communication settings rely on encrypted messaging apps, email, and secure video calls to ensure confidentiality and direct interaction among selected participants. Choosing the right tool depends on the desired level of privacy, audience size, and the communication objective.
Future Trends in Public and Private Communication
Future trends in public communication emphasize immersive technologies such as augmented reality and AI-driven content personalization to enhance audience engagement and real-time interaction. Private communication is increasingly secured through advanced encryption methods and decentralized platforms, prioritizing user privacy and data sovereignty. Integration of AI-powered analytics in both settings will optimize message delivery and tailor communication strategies to evolving user behaviors.
public vs private (communication settings) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com