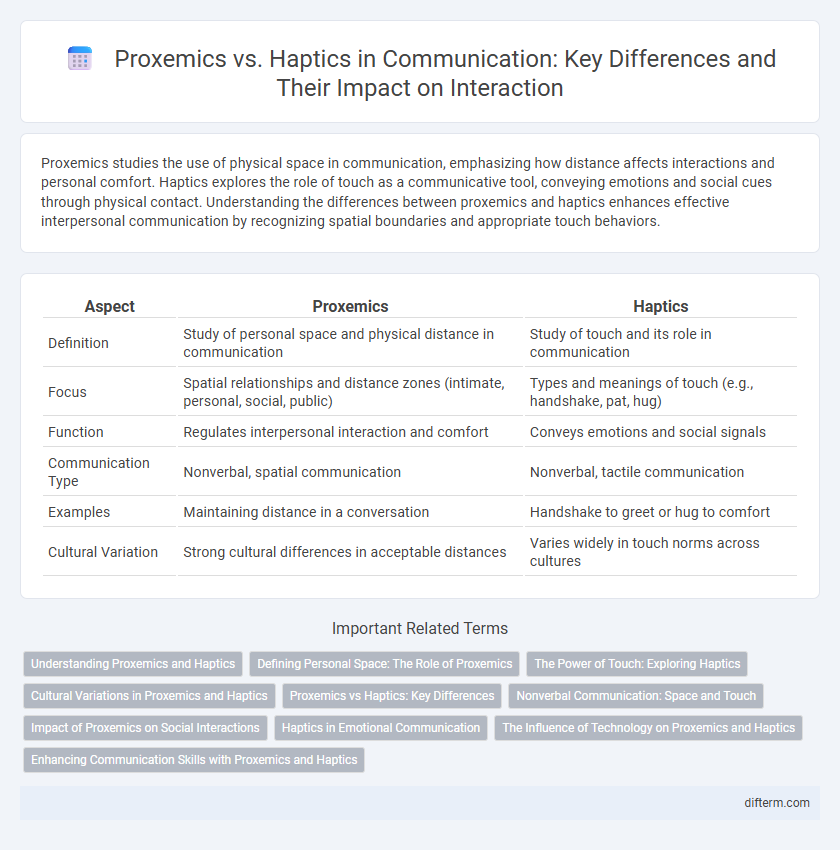
Proxemics studies the use of physical space in communication, emphasizing how distance affects interactions and personal comfort. Haptics explores the role of touch as a communicative tool, conveying emotions and social cues through physical contact. Understanding the differences between proxemics and haptics enhances effective interpersonal communication by recognizing spatial boundaries and appropriate touch behaviors.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Proxemics | Haptics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of personal space and physical distance in communication | Study of touch and its role in communication |
| Focus | Spatial relationships and distance zones (intimate, personal, social, public) | Types and meanings of touch (e.g., handshake, pat, hug) |
| Function | Regulates interpersonal interaction and comfort | Conveys emotions and social signals |
| Communication Type | Nonverbal, spatial communication | Nonverbal, tactile communication |
| Examples | Maintaining distance in a conversation | Handshake to greet or hug to comfort |
| Cultural Variation | Strong cultural differences in acceptable distances | Varies widely in touch norms across cultures |
Understanding Proxemics and Haptics
Proxemics studies the use of personal space and physical distance in communication, revealing how spatial behavior influences social interactions and cultural norms. Haptics examines touch as a form of nonverbal communication, emphasizing its role in expressing emotions, establishing relationships, and conveying authority. Understanding proxemics and haptics enhances the interpretation of nonverbal cues, improving interpersonal communication and social awareness.
Defining Personal Space: The Role of Proxemics
Proxemics studies personal space and physical distance in communication, influencing how individuals perceive comfort and boundaries during interactions. This field defines spatial zones--intimate, personal, social, and public distances--that regulate nonverbal cues and social behavior. Unlike haptics, which centers on touch, proxemics emphasizes the significance of spatial relationships in conveying messages and maintaining personal comfort.
The Power of Touch: Exploring Haptics
Haptics, the study of touch communication, plays a crucial role in conveying emotions and establishing connections beyond verbal language. Unlike proxemics, which centers on spatial relationships and personal distance, haptics leverages tactile interactions such as handshakes, hugs, and pats to express empathy, support, and intimacy. Research shows that touch can significantly enhance trust, reduce stress, and facilitate social bonding, underscoring its power in effective communication.
Cultural Variations in Proxemics and Haptics
Cultural variations in proxemics and haptics profoundly affect interpersonal communication, with different societies exhibiting distinct spatial boundaries and tactile behaviors. For example, Latin American and Middle Eastern cultures often prefer closer personal distances and frequent physical touch, whereas Northern European and East Asian cultures maintain greater personal space and limited touch. Understanding these cultural nuances in proxemics and haptics enhances effective communication and helps avoid misunderstandings in cross-cultural interactions.
Proxemics vs Haptics: Key Differences
Proxemics studies the use of personal space and physical distance in communication, whereas haptics focuses on the role of touch and tactile interactions. Proxemic zones, such as intimate, personal, social, and public distances, influence comfort and message interpretation, while haptic cues like handshakes, hugs, and pats convey emotions and relational dynamics. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective nonverbal communication across cultures and social settings.
Nonverbal Communication: Space and Touch
Proxemics studies the use of physical space in communication, highlighting how distance influences interpersonal interactions and conveys social meanings. Haptics examines touch as a nonverbal cue, revealing emotional states and establishing relational dynamics through different types and intensities of contact. Both proxemics and haptics are critical in understanding nonverbal communication, affecting perceptions of intimacy, power, and cultural norms.
Impact of Proxemics on Social Interactions
Proxemics, the study of personal space and distance in communication, significantly impacts social interactions by influencing comfort levels and perceived intimacy among individuals. Spatial boundaries vary across cultures, affecting how people interpret social cues and engage in conversations. Unlike haptics, which focuses on touch, proxemics primarily shapes nonverbal communication through physical distance, managing social norms and relational dynamics.
Haptics in Emotional Communication
Haptics, the study of touch in communication, plays a crucial role in conveying emotions through physical contact such as hugs, handshakes, or pats on the back. Touch can express empathy, comfort, affection, and support more effectively than verbal communication, often triggering emotional responses and strengthening interpersonal bonds. Unlike proxemics, which focuses on spatial distance, haptics directly engages the sensory experience, making it indispensable in emotional communication.
The Influence of Technology on Proxemics and Haptics
Technology has transformed proxemics by expanding virtual communication spaces, allowing people to maintain social distance through video calls and digital interactions. Haptics has evolved with the integration of tactile feedback in smartphones, wearables, and VR devices, enabling users to experience touch remotely and enhancing emotional connection. These technological advances blur traditional physical boundaries, reshaping social norms regarding personal space and touch in modern communication.
Enhancing Communication Skills with Proxemics and Haptics
Mastering proxemics and haptics deepens understanding of nonverbal cues, significantly enhancing interpersonal communication. Effective use of personal space and touch facilitates stronger emotional connections and clearer message delivery. Training in these areas improves social awareness, leading to more impactful and empathetic interactions.
proxemics vs haptics Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com