Wet liners in automotive engines provide superior cooling by being in direct contact with the coolant, which enhances engine durability and performance. Dry liners, while easier to replace and install, rely on indirect cooling through the cylinder block, potentially leading to higher operating temperatures. Choosing between wet and dry liners depends on factors like engine design, maintenance preferences, and thermal management requirements.
Table of Comparison
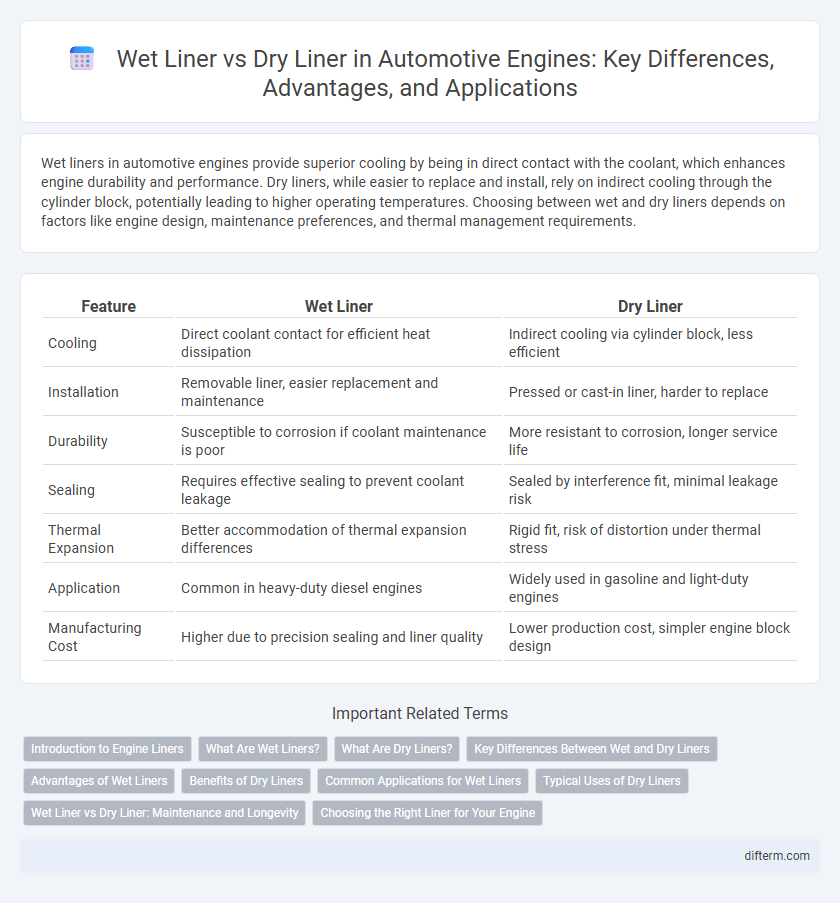
| Feature | Wet Liner | Dry Liner |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling | Direct coolant contact for efficient heat dissipation | Indirect cooling via cylinder block, less efficient |
| Installation | Removable liner, easier replacement and maintenance | Pressed or cast-in liner, harder to replace |
| Durability | Susceptible to corrosion if coolant maintenance is poor | More resistant to corrosion, longer service life |
| Sealing | Requires effective sealing to prevent coolant leakage | Sealed by interference fit, minimal leakage risk |
| Thermal Expansion | Better accommodation of thermal expansion differences | Rigid fit, risk of distortion under thermal stress |
| Application | Common in heavy-duty diesel engines | Widely used in gasoline and light-duty engines |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher due to precision sealing and liner quality | Lower production cost, simpler engine block design |
Introduction to Engine Liners
Engine liners are critical components in internal combustion engines, serving as the cylindrical sleeves where pistons move to create combustion pressure. Wet liners are surrounded directly by coolant, enhancing heat dissipation and simplifying replacement, while dry liners fit tightly into the engine block without direct coolant contact, offering structural rigidity. Selecting between wet and dry liners influences engine durability, maintenance complexity, and thermal management in automotive design.
What Are Wet Liners?
Wet liners are engine cylinder liners directly exposed to the engine coolant, allowing efficient heat dissipation and improved thermal management. These liners form a crucial part of the cooling system in automotive engines by maintaining optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating. Their design facilitates better sealing and easier replacement compared to dry liners, enhancing engine durability and maintenance.
What Are Dry Liners?
Dry liners in automotive engines are cylindrical sleeves installed into the engine block without direct contact with the coolant, providing a robust wear-resistant surface for piston movement. Unlike wet liners, dry liners rely on the engine block for heat dissipation, which often results in a lighter engine design and simplified maintenance. Their durability and ease of replacement make them a preferred choice in high-performance and heavy-duty engines.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Liners
Wet liners have direct contact with engine coolant, allowing efficient heat transfer but requiring robust sealing to prevent leaks, while dry liners are surrounded by the engine block metal, offering simplified maintenance and enhanced structural integrity. Wet liners typically facilitate better engine cooling and are often used in heavy-duty or high-performance engines, whereas dry liners provide easier replacement and better resistance to coolant corrosion. The choice between wet and dry liners impacts engine durability, maintenance complexity, and thermal management.
Advantages of Wet Liners
Wet liners offer superior cooling efficiency by allowing direct contact between the coolant and the cylinder walls, which helps prevent overheating and enhances engine durability. They facilitate easier maintenance and replacement, reducing downtime for repairs in heavy-duty automotive engines. Additionally, wet liners provide better sealing performance, minimizing the risk of coolant leakage and improving overall engine reliability.
Benefits of Dry Liners
Dry liners offer improved heat dissipation due to direct contact with the engine block, enhancing overall thermal efficiency. They reduce coolant contamination risks by preventing coolant-lubricant mixing, thereby increasing engine longevity and reliability. Maintenance and replacement processes are simplified with dry liners, minimizing engine downtime and repair costs.
Common Applications for Wet Liners
Wet liners are commonly used in heavy-duty diesel engines, marine engines, and industrial machinery where efficient cooling and ease of replacement are critical. These liners allow direct contact with engine coolant, which improves heat dissipation and engine temperature management. Their widespread application in large bore engines ensures durability and cost-effective maintenance in demanding operating conditions.
Typical Uses of Dry Liners
Dry liners are commonly used in high-performance engines and heavy-duty applications due to their durability and ease of replacement without requiring engine block modification. They provide better heat transfer management and improved wear resistance compared to wet liners, making them ideal for diesel engines and racing vehicles. Their typical uses include motorsports, commercial trucks, and industrial engines where enhanced maintenance and extended engine life are critical.
Wet Liner vs Dry Liner: Maintenance and Longevity
Wet liners offer superior cooling and easier replacement, reducing engine overheating risks and simplifying maintenance tasks compared to dry liners. Dry liners, integrated directly into the engine block, provide increased structural rigidity but generally require more complex procedures for servicing and cylinder replacement. Wet liners typically extend engine lifespan by improving heat dissipation and minimizing wear, while dry liners may face challenges in thermal expansion and corrosion over time.
Choosing the Right Liner for Your Engine
Selecting the appropriate engine liner is crucial for optimal performance and longevity, with wet liners providing superior cooling due to direct coolant contact, making them ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty engines. Dry liners, being integrated with the engine block, offer easier manufacturing and replacement, suitable for standard passenger vehicles with moderate performance demands. Understanding your engine's cooling requirements and maintenance preferences helps determine whether a wet or dry liner will best support engine durability and efficiency.
wet liner vs dry liner Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com