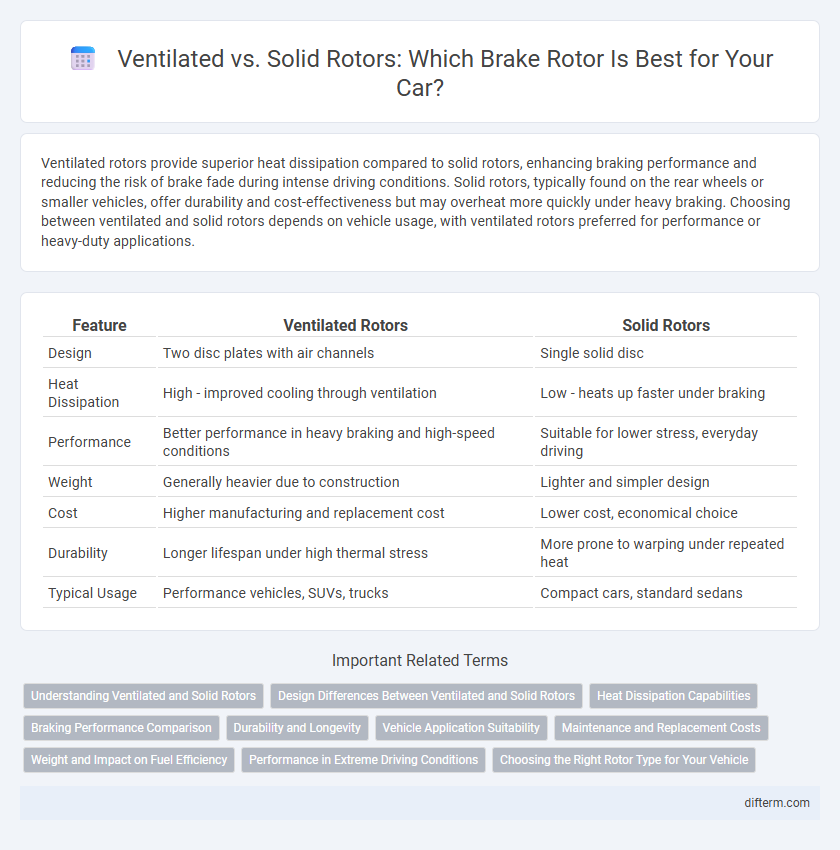
Ventilated rotors provide superior heat dissipation compared to solid rotors, enhancing braking performance and reducing the risk of brake fade during intense driving conditions. Solid rotors, typically found on the rear wheels or smaller vehicles, offer durability and cost-effectiveness but may overheat more quickly under heavy braking. Choosing between ventilated and solid rotors depends on vehicle usage, with ventilated rotors preferred for performance or heavy-duty applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ventilated Rotors | Solid Rotors |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Two disc plates with air channels | Single solid disc |
| Heat Dissipation | High - improved cooling through ventilation | Low - heats up faster under braking |
| Performance | Better performance in heavy braking and high-speed conditions | Suitable for lower stress, everyday driving |
| Weight | Generally heavier due to construction | Lighter and simpler design |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing and replacement cost | Lower cost, economical choice |
| Durability | Longer lifespan under high thermal stress | More prone to warping under repeated heat |
| Typical Usage | Performance vehicles, SUVs, trucks | Compact cars, standard sedans |
Understanding Ventilated and Solid Rotors
Ventilated rotors feature internal vanes that enhance airflow, improving heat dissipation and reducing brake fade during intense braking conditions. Solid rotors are a single piece of metal that provide consistent braking performance but tend to retain more heat, leading to potential overheating in high-stress situations. Understanding the difference in cooling efficiency and thermal management between ventilated and solid rotors is crucial for optimal brake system performance and safety.
Design Differences Between Ventilated and Solid Rotors
Ventilated rotors feature an internal air channel between two rotor faces, enhancing heat dissipation and reducing brake fade during intense driving conditions, while solid rotors consist of a single solid disc that provides basic braking performance. The design of ventilated rotors incorporates vanes that draw air through the rotor to cool the braking system more effectively compared to the compact structure of solid rotors. This structural difference directly impacts the rotor's weight, thermal management, and overall braking efficiency in automotive applications.
Heat Dissipation Capabilities
Ventilated rotors feature internal channels designed to increase air circulation, significantly enhancing heat dissipation compared to solid rotors, which lack these cooling pathways. Effective heat dissipation in ventilated rotors reduces brake fade and extends rotor lifespan during high-performance or heavy-duty automotive applications. Solid rotors, typically found in lower-performance or lighter vehicles, dissipate heat more slowly, potentially compromising braking efficiency under prolonged or intense use.
Braking Performance Comparison
Ventilated rotors offer superior braking performance compared to solid rotors by efficiently dissipating heat during heavy braking, which reduces brake fade and maintains consistent stopping power. The enhanced cooling capability of ventilated rotors minimizes the risk of thermal deformation, ensuring better brake pad contact and longer rotor life. Solid rotors, while simpler and more cost-effective, are prone to overheating under high-stress conditions, resulting in diminished braking efficiency and faster wear.
Durability and Longevity
Ventilated rotors offer superior durability and longevity compared to solid rotors due to their enhanced heat dissipation capabilities, which reduce the risk of warping and brake fade under heavy use. The internal vanes in ventilated rotors efficiently channel air, maintaining optimal operating temperatures and extending the lifespan of brake components. Solid rotors, while simpler and less expensive, are more prone to overheating and cracking, leading to faster wear and the need for more frequent replacements in demanding driving conditions.
Vehicle Application Suitability
Ventilated rotors offer superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications that require enhanced braking efficiency and reduced fade. Solid rotors are better suited for smaller, lighter vehicles with less aggressive braking demands, providing adequate stopping power at a lower cost. Choosing the appropriate rotor depends on vehicle weight, usage intensity, and driving conditions to ensure optimal braking performance and longevity.
Maintenance and Replacement Costs
Ventilated rotors generally have higher maintenance and replacement costs compared to solid rotors due to their complex design and increased susceptibility to wear from heat dissipation efficiency requirements. Solid rotors, while typically less expensive to replace, may experience more frequent overheating and warping, leading to increased long-term maintenance expenses. Choosing between ventilated and solid rotors involves balancing upfront replacement costs with durability and heat management to optimize overall brake system lifecycle expenses.
Weight and Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Ventilated rotors are typically heavier than solid rotors due to their dual-disc design with internal cooling vanes, which can slightly increase a vehicle's unsprung weight. The added weight from ventilated rotors can marginally reduce fuel efficiency by increasing rolling resistance and overall vehicle weight. However, their improved heat dissipation enhances braking performance and longevity, partially offsetting the fuel consumption impact over time.
Performance in Extreme Driving Conditions
Ventilated rotors significantly enhance braking performance in extreme driving conditions by dissipating heat faster than solid rotors, reducing brake fade and maintaining consistent stopping power under high stress. Their design, featuring internal vanes, promotes airflow and cooling, which is crucial for high-speed or aggressive driving scenarios such as track racing or steep descents. Solid rotors, while durable, tend to overheat quickly, risking decreased braking efficiency and increased wear in intense performance environments.
Choosing the Right Rotor Type for Your Vehicle
Ventilated rotors provide superior heat dissipation and improved braking performance, making them ideal for heavy-duty vehicles or those frequently exposed to high-stress driving conditions. Solid rotors, typically lighter and more affordable, suit everyday driving with less intense braking demands. Selecting the right rotor depends on factors such as vehicle weight, driving style, and brake system requirements to ensure optimal safety and efficiency.
ventilated rotors vs solid rotors Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com