Naturally aspirated engines provide linear power delivery and simpler mechanics, resulting in reliable performance with minimal maintenance. Forced induction, such as turbocharging or supercharging, increases engine efficiency and power output by compressing air intake, enhancing acceleration and overall speed. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance of power, efficiency, and engine complexity in automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
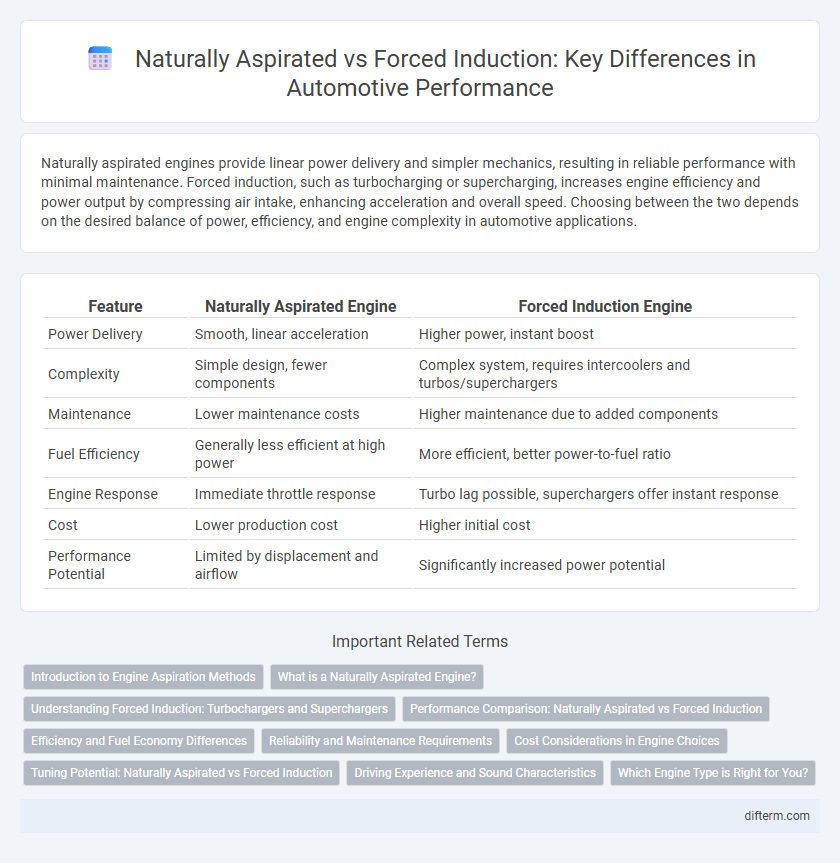
| Feature | Naturally Aspirated Engine | Forced Induction Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Smooth, linear acceleration | Higher power, instant boost |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | Complex system, requires intercoolers and turbos/superchargers |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs | Higher maintenance due to added components |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally less efficient at high power | More efficient, better power-to-fuel ratio |
| Engine Response | Immediate throttle response | Turbo lag possible, superchargers offer instant response |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher initial cost |
| Performance Potential | Limited by displacement and airflow | Significantly increased power potential |
Introduction to Engine Aspiration Methods
Engine aspiration methods significantly impact automotive performance and efficiency, with naturally aspirated engines relying on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, offering simpler design and linear throttle response. Forced induction systems, including turbochargers and superchargers, compress incoming air to increase oxygen density, resulting in higher power output and improved fuel efficiency. Understanding these differing approaches is essential for optimizing engine tuning, fuel consumption, and emission control in modern vehicles.
What is a Naturally Aspirated Engine?
A naturally aspirated engine relies on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber without the use of turbochargers or superchargers. This type of engine delivers immediate throttle response and linear power delivery but generally produces less horsepower compared to forced induction systems. Commonly found in performance and everyday vehicles, naturally aspirated engines are valued for their mechanical simplicity and consistent reliability.
Understanding Forced Induction: Turbochargers and Superchargers
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, increase engine power by compressing incoming air, allowing more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber for enhanced fuel combustion. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine, while superchargers rely on a belt-driven compressor directly connected to the engine. Both technologies improve engine efficiency and performance by significantly boosting horsepower and torque compared to naturally aspirated engines.
Performance Comparison: Naturally Aspirated vs Forced Induction
Naturally aspirated engines deliver linear throttle response and high-revving performance, benefiting from simpler design and reduced turbo lag. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, significantly increase power output and torque by compressing intake air, enhancing engine efficiency and acceleration. Performance metrics show forced induction engines typically produce 30-50% more horsepower and torque than their naturally aspirated counterparts of the same displacement.
Efficiency and Fuel Economy Differences
Naturally aspirated engines offer simpler designs with fewer components, resulting in lower parasitic losses and often better fuel economy at steady, low-load conditions. Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged units, provide higher power density by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, which can improve efficiency during high-load scenarios but may increase fuel consumption under partial throttle due to boost demand. Overall, forced induction optimizes power output and can reduce engine displacement for better highway fuel efficiency, whereas naturally aspirated engines excel in consistent low-load fuel economy and reliability.
Reliability and Maintenance Requirements
Naturally aspirated engines generally offer greater reliability due to their simpler design, with fewer components that are prone to failure compared to forced induction systems. Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged variants, require more frequent maintenance, including regular inspection of intercoolers, turbochargers, and higher quality lubricants to prevent wear and overheating. The increased thermal and mechanical stress in forced induction setups often leads to shorter service intervals and higher maintenance costs.
Cost Considerations in Engine Choices
Naturally aspirated engines typically have lower upfront costs and simpler designs, reducing maintenance expenses and enhancing long-term reliability. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, increase initial investment due to complex components and potential for higher repair costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing these factors against performance benefits and fuel efficiency gains in automotive applications.
Tuning Potential: Naturally Aspirated vs Forced Induction
Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged systems, typically offer greater tuning potential due to their ability to increase air intake and boost power output without major engine modifications. Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure, limiting power gains primarily to internal modifications like camshaft upgrades or increased displacement. Consequently, forced induction setups provide more flexible and cost-effective pathways for significant horsepower improvements in automotive tuning.
Driving Experience and Sound Characteristics
Naturally aspirated engines deliver a linear throttle response and a raw, mechanical sound that enhances the driving experience with immediate feedback and a pure engine note. Forced induction systems, including turbochargers and superchargers, provide increased power and torque at lower RPMs, producing a distinctive turbo spool or supercharger whine that adds a dynamic and aggressive auditory presence. Enthusiasts often prefer naturally aspirated engines for their spontaneous engine revs, while forced induction appeals to those seeking exhilarating acceleration and a sportier sound profile.
Which Engine Type is Right for You?
Naturally aspirated engines offer linear power delivery and lower complexity, making them ideal for drivers valuing reliability and smooth throttle response. Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged setups, provide significantly higher power and torque by increasing air intake pressure, suitable for performance enthusiasts seeking acceleration and efficiency. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize consistent driveability and maintenance or enhanced performance and fuel economy under demanding conditions.
naturally aspirated vs forced induction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com