A longitudinal engine is mounted with the crankshaft parallel to the vehicle's length, often enhancing balance and allowing for easier integration with rear-wheel or all-wheel drive systems. In contrast, a transverse engine is positioned with the crankshaft perpendicular to the vehicle's length, which maximizes space efficiency and is commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. Choosing between these engine layouts impacts vehicle dynamics, packaging, and drivetrain configuration.
Table of Comparison
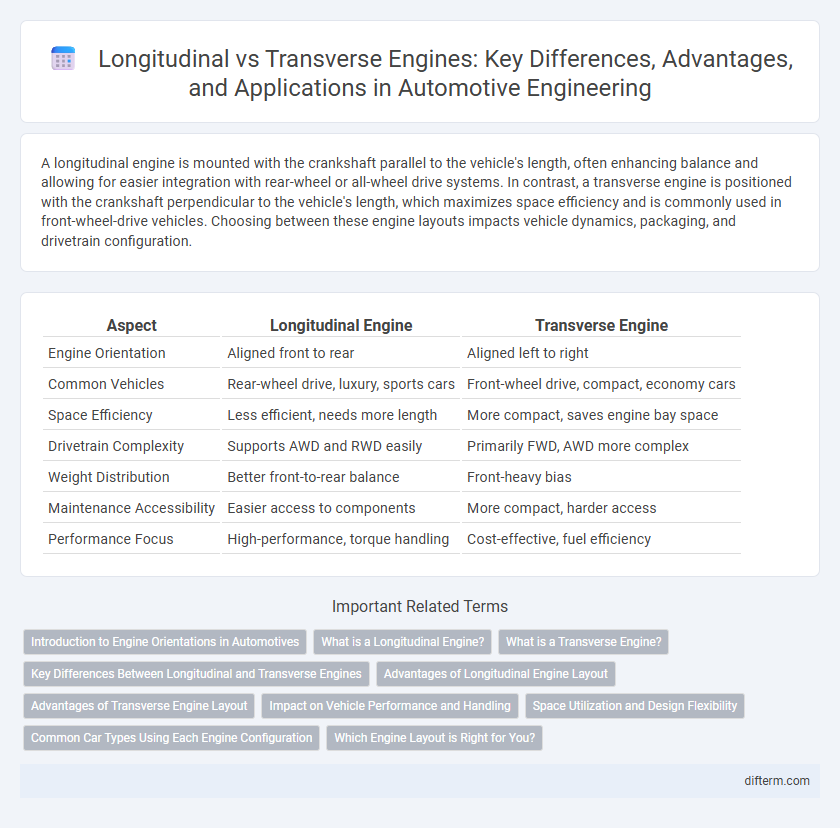
| Aspect | Longitudinal Engine | Transverse Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Orientation | Aligned front to rear | Aligned left to right |
| Common Vehicles | Rear-wheel drive, luxury, sports cars | Front-wheel drive, compact, economy cars |
| Space Efficiency | Less efficient, needs more length | More compact, saves engine bay space |
| Drivetrain Complexity | Supports AWD and RWD easily | Primarily FWD, AWD more complex |
| Weight Distribution | Better front-to-rear balance | Front-heavy bias |
| Maintenance Accessibility | Easier access to components | More compact, harder access |
| Performance Focus | High-performance, torque handling | Cost-effective, fuel efficiency |
Introduction to Engine Orientations in Automotives
Longitudinal engines are aligned with the vehicle's length, typically found in rear-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive cars, enhancing balance and power delivery. Transverse engines, positioned perpendicular to the vehicle's length, are common in front-wheel-drive vehicles, optimizing space efficiency and reducing drivetrain complexity. Understanding these engine orientations is crucial for automotive design, affecting performance, packaging, and handling characteristics.
What is a Longitudinal Engine?
A longitudinal engine is positioned with its crankshaft aligned parallel to the vehicle's length, running from the front to the rear of the car. This configuration is commonly found in rear-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, allowing for better weight distribution and improved handling dynamics. It facilitates easier integration with transmission systems that power the rear wheels, making it a preferred choice for performance and luxury cars.
What is a Transverse Engine?
A transverse engine is an internal combustion engine mounted perpendicular to the vehicle's direction of travel, typically in front-wheel-drive cars. This layout optimizes space by allowing a more compact engine bay, improving interior room and weight distribution. Transverse engines simplify drivetrain design by directly connecting to the front axle, enhancing fuel efficiency and handling.
Key Differences Between Longitudinal and Transverse Engines
Longitudinal engines are mounted parallel to the vehicle's length, promoting better weight distribution and suitability for rear-wheel or all-wheel-drive configurations. Transverse engines are positioned perpendicular to the vehicle's length, optimizing space efficiency and commonly used in front-wheel-drive platforms. Key differences include drivetrain layout impact, vehicle packaging, and cooling system design, influencing overall performance and handling characteristics.
Advantages of Longitudinal Engine Layout
Longitudinal engine layouts offer superior power delivery and balance for rear-wheel-drive vehicles, enhancing overall driving dynamics and handling precision. They enable easier integration with sophisticated transmission systems, such as dual-clutch or manual gearboxes, often resulting in better performance and cooling efficiency. This configuration also simplifies maintenance and allows for larger engine sizes, making it ideal for luxury cars, sports cars, and trucks.
Advantages of Transverse Engine Layout
The transverse engine layout offers improved space efficiency by allowing more compact engine bay designs, which creates increased cabin space and better weight distribution for front-wheel-drive vehicles. This configuration simplifies the drivetrain by reducing the length of the driveshaft, resulting in lower production costs and improved fuel efficiency. Additionally, transverse engines often provide better handling characteristics in urban driving due to their lighter front-end weight and optimized packaging.
Impact on Vehicle Performance and Handling
Longitudinal engines, typically found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, provide better weight distribution along the vehicle's length, enhancing handling stability and allowing for higher power output. Transverse engines, common in front-wheel-drive cars, offer compact packaging that improves interior space and fuel efficiency but may lead to understeer due to front-heavy weight distribution. The choice between longitudinal and transverse engine layouts directly impacts torque delivery, vehicle balance, and cornering dynamics, influencing overall driving performance.
Space Utilization and Design Flexibility
Longitudinal engines provide better balance and allow for easier integration with rear-wheel-drive systems, optimizing under-hood space for performance components but requiring more lengthwise space. Transverse engines maximize cabin and cargo space by orienting the powertrain perpendicularly, which enhances design flexibility for front-wheel-drive vehicles and allows for more compact engine bays. The choice between longitudinal and transverse layouts significantly impacts overall vehicle packaging, affecting drivetrain complexity and interior volume optimization.
Common Car Types Using Each Engine Configuration
Longitudinal engines are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles and luxury sedans such as the BMW 3 Series and Mercedes-Benz C-Class, where balanced weight distribution and performance are prioritized. Transverse engines dominate front-wheel-drive cars like the Honda Civic and Toyota Corolla, optimizing space efficiency and compact design for economy and daily commuting. Each engine layout caters to different vehicle architectures, influencing drivetrain configuration, interior space, and handling characteristics.
Which Engine Layout is Right for You?
Choosing between a longitudinal engine and a transverse engine depends on your vehicle's intended use and performance preferences. Longitudinal engines, typically found in rear-wheel-drive cars, offer better weight distribution and are ideal for performance and towing. Transverse engines, common in front-wheel-drive vehicles, provide compact design, improved fuel efficiency, and maximize interior space.
Longitudinal Engine vs Transverse Engine Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com