Crossplane cranks deliver smoother power and better torque at lower RPMs, making them ideal for everyday driving and muscle cars. Flatplane cranks offer higher rev capability and a more aggressive exhaust note, favored in high-performance and racing engines. The choice between the two affects engine sound, vibration, and overall driving experience.
Table of Comparison
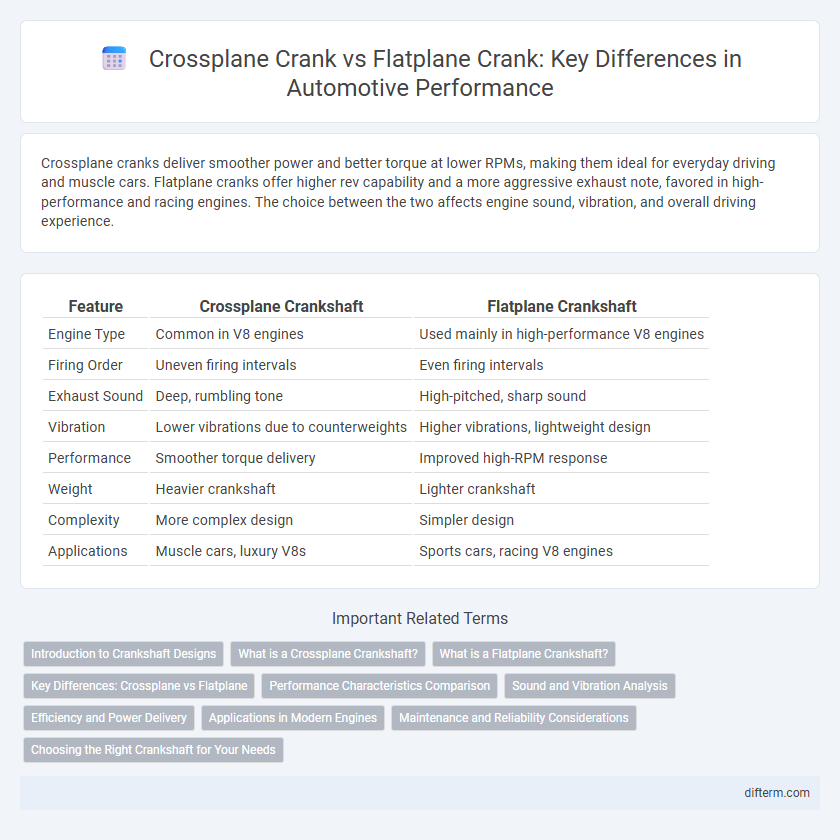
| Feature | Crossplane Crankshaft | Flatplane Crankshaft |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Type | Common in V8 engines | Used mainly in high-performance V8 engines |
| Firing Order | Uneven firing intervals | Even firing intervals |
| Exhaust Sound | Deep, rumbling tone | High-pitched, sharp sound |
| Vibration | Lower vibrations due to counterweights | Higher vibrations, lightweight design |
| Performance | Smoother torque delivery | Improved high-RPM response |
| Weight | Heavier crankshaft | Lighter crankshaft |
| Complexity | More complex design | Simpler design |
| Applications | Muscle cars, luxury V8s | Sports cars, racing V8 engines |
Introduction to Crankshaft Designs
Crossplane crankshafts feature a 90-degree offset between crank pins, enhancing engine balance and producing a distinctive exhaust note favored in V8 engines. Flatplane crankshafts, with crank pins positioned at 180 degrees, reduce rotational inertia, allowing higher engine RPMs and quicker throttle response typical in high-performance sports cars. Each design impacts engine characteristics, influencing vibration, sound, and power delivery.
What is a Crossplane Crankshaft?
A crossplane crankshaft features crankpins set at 90-degree intervals, creating a distinctive firing order used primarily in V8 engines to enhance torque and reduce vibrations. This design balances engine forces more effectively than flatplane crankshafts, contributing to smoother operation and improved low-end power delivery. Crossplane cranks are favored in production cars for their superior refinement and characteristic exhaust note.
What is a Flatplane Crankshaft?
A flatplane crankshaft features crank pins arranged at 180-degree intervals, allowing for a straightforward firing order and reduced rotational inertia. This design enhances engine responsiveness and high-rev performance by minimizing crankshaft mass and improving exhaust pulse timing. Commonly found in high-performance V8 engines, flatplane crankshafts deliver sharp throttle response and a distinctive exhaust note compared to crossplane counterparts.
Key Differences: Crossplane vs Flatplane
Crossplane crankshafts feature a 90-degree crankpin arrangement that reduces torsional vibrations and produces a distinctive exhaust sound, commonly used in V8 engines for smoother power delivery. Flatplane crankshafts have crankpins positioned at 180 degrees, offering a lighter rotating assembly, higher revving capability, and more aggressive exhaust note favored in performance and racing applications. The main differences lie in vibration characteristics, engine sound, rev range, and power delivery, impacting vehicle performance and driving experience.
Performance Characteristics Comparison
Crossplane crankshafts offer smoother power delivery and reduced vibration due to their 90-degree crankpin arrangement, enhancing low-end torque and overall drivability in V8 engines. Flatplane crankshafts feature a 180-degree design that allows for quicker engine response and higher revving capability, resulting in improved top-end performance and a distinct exhaust note. The choice between crossplane and flatplane crankshafts significantly impacts the engine's balance, sound characteristics, and torque curve in high-performance automotive applications.
Sound and Vibration Analysis
Crossplane cranks produce a distinctive, deep rumbling sound due to uneven firing intervals, enhancing the engine's auditory appeal in V8 configurations. Flatplane cranks generate a higher-pitched, sharper exhaust note with more consistent firing pulses, resulting in reduced low-frequency vibration but increased high-frequency vibration. Vibration analysis shows crossplane cranks typically require balance shafts or counterweights to minimize vibrations, while flatplane cranks exhibit inherent primary balance but may produce more secondary vibrations.
Efficiency and Power Delivery
Crossplane crankshafts enhance power delivery by reducing vibration and improving torque output at low RPMs, making them ideal for smoother drivability and efficiency in everyday automotive applications. Flatplane crankshafts offer higher efficiency at high RPMs due to reduced rotational mass and improved exhaust scavenging, resulting in increased horsepower and quicker throttle response. Optimizing engine design with either crank type directly impacts fuel efficiency and performance characteristics tailored to specific driving demands.
Applications in Modern Engines
Crossplane cranks dominate V8 engines in muscle cars and luxury sedans for their smoother idle and enhanced low-end torque, improving drivability and refinement. Flatplane cranks are prevalent in high-performance sports cars and racing applications due to their lighter weight and higher revving capabilities, which optimize power output and throttle response. Modern engine designs often pair crossplane cranks with advanced balancing techniques and variable valve timing to reduce vibrations while maximizing efficiency and performance.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Crossplane crankshafts offer smoother engine operation with reduced vibrations, leading to lower wear and longer maintenance intervals compared to flatplane cranks. Flatplane crankshafts, favored in high-performance applications, require more frequent inspections due to higher stress and increased vibrations that can accelerate component fatigue. Overall, crossplane designs typically provide enhanced reliability and lower maintenance demands for everyday automotive use.
Choosing the Right Crankshaft for Your Needs
Selecting the right crankshaft depends on performance goals and engine characteristics; crossplane cranks offer smoother power delivery and reduced vibrations ideal for muscle cars and V8 engines, while flatplane cranks provide higher revving capabilities and a more aggressive exhaust note suited for sports cars and racing applications. Crossplane crankshafts deliver better low-end torque and a distinctive rumble favored in American muscle engines, whereas flatplane designs promote quicker throttle response and lighter rotating mass, enhancing high RPM efficiency. Understanding these differences enables optimized engine tuning and vehicle performance tailored to specific driving styles and automotive purposes.
crossplane crank vs flatplane crank Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com