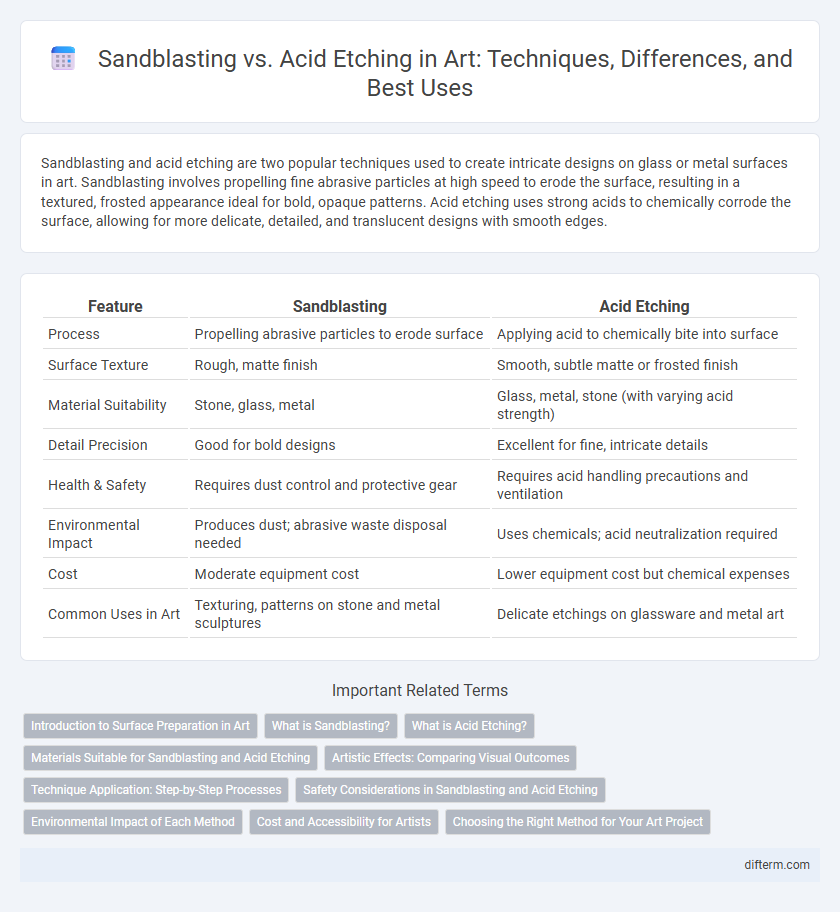
Sandblasting and acid etching are two popular techniques used to create intricate designs on glass or metal surfaces in art. Sandblasting involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high speed to erode the surface, resulting in a textured, frosted appearance ideal for bold, opaque patterns. Acid etching uses strong acids to chemically corrode the surface, allowing for more delicate, detailed, and translucent designs with smooth edges.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandblasting | Acid Etching |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Propelling abrasive particles to erode surface | Applying acid to chemically bite into surface |
| Surface Texture | Rough, matte finish | Smooth, subtle matte or frosted finish |
| Material Suitability | Stone, glass, metal | Glass, metal, stone (with varying acid strength) |
| Detail Precision | Good for bold designs | Excellent for fine, intricate details |
| Health & Safety | Requires dust control and protective gear | Requires acid handling precautions and ventilation |
| Environmental Impact | Produces dust; abrasive waste disposal needed | Uses chemicals; acid neutralization required |
| Cost | Moderate equipment cost | Lower equipment cost but chemical expenses |
| Common Uses in Art | Texturing, patterns on stone and metal sculptures | Delicate etchings on glassware and metal art |
Introduction to Surface Preparation in Art
Sandblasting and acid etching are essential surface preparation techniques in art used to create texture and enhance adhesion on various materials such as glass, metal, and stone. Sandblasting involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high velocity to physically abrade the surface, producing a uniform matte finish ideal for intricate designs and durability. Acid etching employs chemical solutions, typically hydrofluoric or nitric acid, to selectively corrode the surface, allowing for detailed patterns with subtle depth variations and a smoother tactile quality.
What is Sandblasting?
Sandblasting is a technique that uses high-pressure air to propel abrasive materials like sand or glass beads onto a surface, creating a textured or frosted effect ideal for glass and metal artworks. This method allows precise control over depth and pattern, enhancing surface details without compromising structural integrity. Sandblasting is favored for its versatility in producing intricate designs and sharp contrasts in art installations and decorative pieces.
What is Acid Etching?
Acid etching is a technique used in art to create intricate designs on metal or glass surfaces by applying acid to dissolve the material selectively. This process allows for precise control over depth and texture, producing detailed and permanent patterns. Unlike sandblasting, acid etching is chemical-based, making it ideal for fine line work and delicate artwork.
Materials Suitable for Sandblasting and Acid Etching
Sandblasting is ideal for durable materials such as glass, stone, metal, and ceramics, allowing precise surface texture creation without damaging the substrate. Acid etching works best on glass and certain metals like stainless steel and aluminum, where chemical reactions selectively corrode the surface to form intricate designs. Both techniques require material compatibility to achieve optimum artistic detail and longevity of the artwork.
Artistic Effects: Comparing Visual Outcomes
Sandblasting produces sharp, precise textures by using high-pressure abrasive materials, resulting in a matte finish with consistent depth and intricate detailing ideal for glass and stone art. Acid etching delivers softer, more nuanced gradients due to chemical reactions on surfaces, creating elegant translucent effects suited for delicate and subtle designs on metals and glass. Both techniques enhance artistic expression, but sandblasting excels in bold, defined patterns while acid etching favors smooth, ethereal aesthetics.
Technique Application: Step-by-Step Processes
Sandblasting involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high velocity onto a surface to create detailed textures or patterns, commonly applied using specialized equipment like a blast cabinet or handheld nozzle. Acid etching requires carefully applying acid-resistant resist materials to protect desired areas before submerging the object in acid baths, which selectively corrode exposed surfaces to create intricate designs. Both techniques demand precise preparation, safety measures, and controlled execution to achieve durable and visually striking artistic effects on glass, metal, or stone substrates.
Safety Considerations in Sandblasting and Acid Etching
Sandblasting requires rigorous safety measures including protective gear to prevent inhalation of silica dust, which can cause severe respiratory diseases like silicosis. Acid etching demands careful handling of corrosive chemicals such as hydrofluoric or nitric acid, necessitating the use of gloves, eye protection, and ventilation to avoid chemical burns and toxic fume exposure. Both techniques mandate strict adherence to safety protocols to minimize health risks during artistic glass or metal surface treatments.
Environmental Impact of Each Method
Sandblasting involves propelling abrasive materials, often silica or glass beads, which can generate significant airborne particulate matter, posing health risks and environmental pollution if not properly contained. Acid etching uses strong chemicals like hydrofluoric or nitric acid, which require careful handling and disposal to prevent soil and water contamination, thus necessitating strict regulatory compliance. Choosing between the two methods depends on available safety measures, waste management protocols, and the potential ecological footprint of each technique.
Cost and Accessibility for Artists
Sandblasting offers a more cost-effective option for artists due to the reuse of abrasive materials and the affordability of entry-level equipment compared to acid etching supplies. Acid etching involves purchasing hazardous chemicals and requires specialized safety gear, increasing both the initial investment and ongoing expenses. Artists often find sandblasting more accessible because it demands less stringent safety protocols and allows for faster setup and cleanup times.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Art Project
Selecting the appropriate technique between sandblasting and acid etching depends on the desired texture and detail in your artwork. Sandblasting offers a more controlled, textured finish ideal for creating depth on glass or stone, while acid etching produces fine, intricate designs with a smooth surface. Assessing the material compatibility, project scale, and safety considerations ensures you achieve the optimal aesthetic and durability for your art piece.
sandblasting vs acid etching Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com