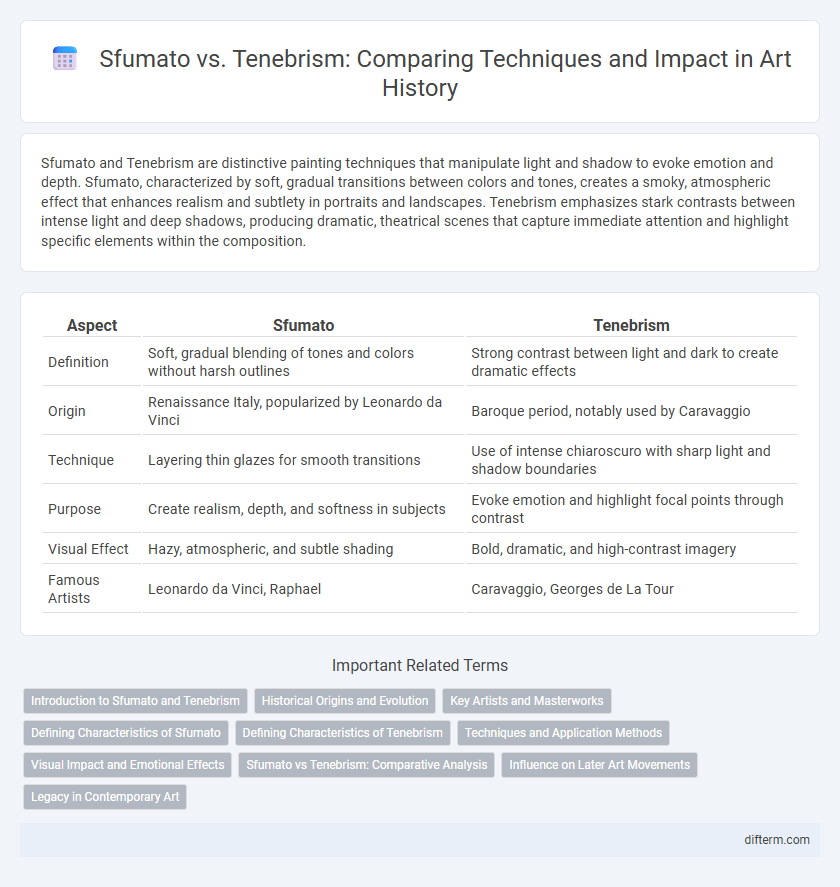
Sfumato and Tenebrism are distinctive painting techniques that manipulate light and shadow to evoke emotion and depth. Sfumato, characterized by soft, gradual transitions between colors and tones, creates a smoky, atmospheric effect that enhances realism and subtlety in portraits and landscapes. Tenebrism emphasizes stark contrasts between intense light and deep shadows, producing dramatic, theatrical scenes that capture immediate attention and highlight specific elements within the composition.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sfumato | Tenebrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Soft, gradual blending of tones and colors without harsh outlines | Strong contrast between light and dark to create dramatic effects |
| Origin | Renaissance Italy, popularized by Leonardo da Vinci | Baroque period, notably used by Caravaggio |
| Technique | Layering thin glazes for smooth transitions | Use of intense chiaroscuro with sharp light and shadow boundaries |
| Purpose | Create realism, depth, and softness in subjects | Evoke emotion and highlight focal points through contrast |
| Visual Effect | Hazy, atmospheric, and subtle shading | Bold, dramatic, and high-contrast imagery |
| Famous Artists | Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael | Caravaggio, Georges de La Tour |
Introduction to Sfumato and Tenebrism
Sfumato is a painting technique characterized by soft, gradual transitions between colors and tones, creating a smoky, hazy effect that enhances realism and depth. Tenebrism, in contrast, emphasizes dramatic contrasts of light and dark, using intense chiaroscuro to create a stark, theatrical atmosphere. Both techniques have roots in Renaissance and Baroque art, with Sfumato popularized by Leonardo da Vinci and Tenebrism associated with Caravaggio and his followers.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Sfumato, developed during the Italian Renaissance by artists like Leonardo da Vinci, originated as a technique to create soft transitions between colors and tones, enhancing realism and depth in paintings. Tenebrism emerged in the early 17th century with Baroque artists such as Caravaggio, characterized by stark contrasts between light and dark to heighten drama and emotional intensity. While sfumato evolved to achieve subtle gradations and atmospheric effects, tenebrism focused on dramatic illumination and shadow play, marking distinct stylistic shifts rooted in their historical periods.
Key Artists and Masterworks
Sfumato, pioneered by Leonardo da Vinci in masterpieces like the "Mona Lisa," employs delicate gradations of light and shadow to create soft, lifelike transitions without harsh lines. Tenebrism, exemplified by Caravaggio's "The Calling of Saint Matthew," emphasizes dramatic contrasts with intense chiaroscuro, where dark shadows dominate and highlight focal points in a theatrical manner. Key artists such as Leonardo for Sfumato and Caravaggio for Tenebrism defined these techniques, influencing Renaissance and Baroque art through their masterful use of light to evoke mood and depth.
Defining Characteristics of Sfumato
Sfumato is defined by its soft, gradual blending of colors and tones, creating a smoky, almost imperceptible transition between light and shadow that enhances realism and depth. This technique avoids harsh outlines, producing a delicate, atmospheric effect that mimics the way light diffuses through air. Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa exemplifies sfumato's characteristic subtle gradations, contrasting with the stark chiaroscuro and dramatic contrasts found in tenebrism.
Defining Characteristics of Tenebrism
Tenebrism is defined by its dramatic use of intense chiaroscuro, where bold contrasts between light and dark create a spotlight effect that emphasizes specific elements within the composition. Unlike sfumato's soft, gradual transitions and blurred edges, tenebrism relies on stark, abrupt shifts in illumination to evoke emotional intensity and depth. Masters like Caravaggio employed tenebrism to heighten realism and theatricality, making figures emerge powerfully from shadowed backgrounds.
Techniques and Application Methods
Sfumato is a painting technique characterized by the delicate blending of colors and tones to create soft transitions without harsh lines, often achieved through multiple thin glazes that mimic the natural gradation of light and shadow. Tenebrism, in contrast, employs dramatic contrasts between intense light and deep shadows to heighten emotional impact, using strong chiaroscuro effects with abrupt tonal shifts to emphasize volume and spatial depth. While sfumato produces a subtle, smoky atmosphere ideal for capturing realistic skin textures and gentle contours, tenebrism is applied to evoke theatricality and focus attention on specific elements within a composition.
Visual Impact and Emotional Effects
Sfumato creates a soft, gradual transition between colors and tones, producing a hazy, dreamlike visual effect that evokes subtle emotional depth and mystery. Tenebrism employs stark contrasts of light and dark, generating dramatic intensity and heightened emotional tension by spotlighting particular elements within the composition. These techniques distinctly influence viewer perception: sfumato fosters a contemplative, serene atmosphere, while tenebrism commands attention through theatrical boldness and emotional immediacy.
Sfumato vs Tenebrism: Comparative Analysis
Sfumato and Tenebrism are distinct painting techniques that manipulate light and shadow to achieve different visual effects. Sfumato, pioneered by Leonardo da Vinci, creates soft transitions between colors and tones, producing a hazy, atmospheric quality without harsh lines. In contrast, Tenebrism, popularized by Caravaggio, employs dramatic chiaroscuro with stark contrasts between intense light and dark areas, emphasizing emotional intensity and three-dimensionality.
Influence on Later Art Movements
Sfumato's subtle blending of tones influenced Impressionism and Modernism by encouraging softer transitions and atmospheric effects in painting. Tenebrism's dramatic contrast between light and shadow directly inspired Baroque artists and later impacted Expressionism and Chiaroscuro techniques in contemporary art. Both styles significantly shaped the evolution of emotional depth and realism in subsequent Western art movements.
Legacy in Contemporary Art
Sfumato and Tenebrism both continue to influence contemporary art through their distinct handling of light and shadow; sfumato's soft, gradual transitions create atmospheric depth, while tenebrism's stark contrasts emphasize dramatic intensity. Modern artists integrate sfumato's subtle tonal gradations to evoke emotional complexity, and tenebrism's bold chiaroscuro techniques to highlight narrative focus. The legacy of these Renaissance and Baroque methods persists in digital art, photography, and painting, shaping visual storytelling and mood.
Sfumato vs Tenebrism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com