Tempera paint, known for its fast-drying properties and matte finish, uses pigment mixed with a water-soluble binder like egg yolk, offering artists precise detail and color longevity. Acrylic paint, versatile and quick-drying, is water-based with a synthetic polymer binder, allowing for vibrant colors and easy layering, suitable for various surfaces. Both mediums provide distinct textures and effects, with tempera favored in traditional works and acrylic valued for its adaptability and durability in contemporary art.
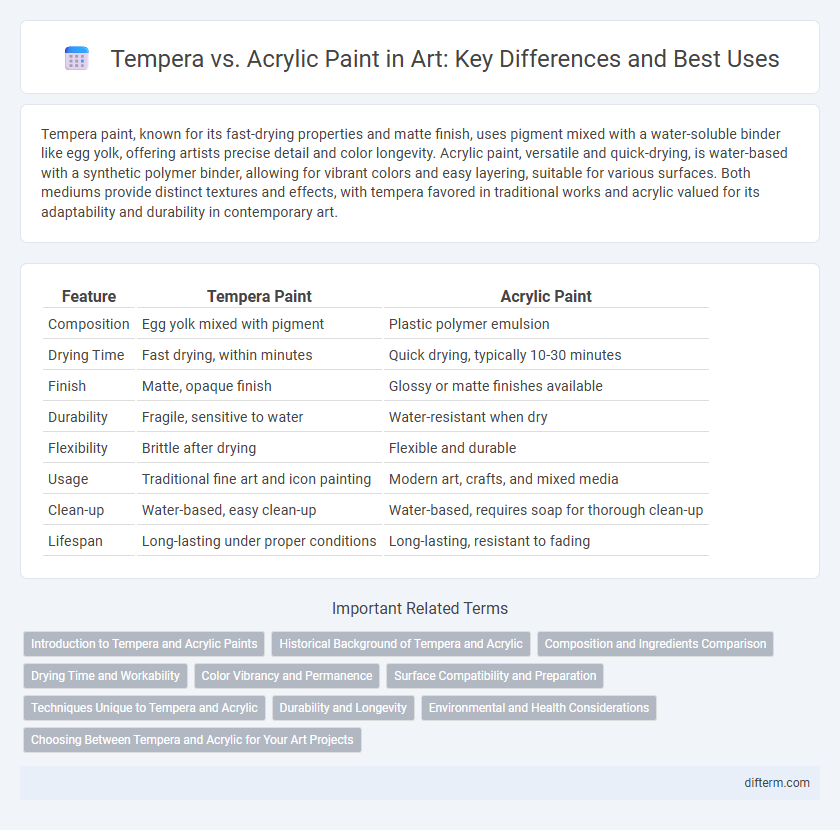
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempera Paint | Acrylic Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Egg yolk mixed with pigment | Plastic polymer emulsion |
| Drying Time | Fast drying, within minutes | Quick drying, typically 10-30 minutes |
| Finish | Matte, opaque finish | Glossy or matte finishes available |
| Durability | Fragile, sensitive to water | Water-resistant when dry |
| Flexibility | Brittle after drying | Flexible and durable |
| Usage | Traditional fine art and icon painting | Modern art, crafts, and mixed media |
| Clean-up | Water-based, easy clean-up | Water-based, requires soap for thorough clean-up |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting under proper conditions | Long-lasting, resistant to fading |
Introduction to Tempera and Acrylic Paints
Tempera paint, traditionally made by mixing pigment with a water-soluble binder like egg yolk, offers a matte finish and quick drying time, valued for its durability and precision in fine art. Acrylic paint consists of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, known for its vibrant colors, versatility, and fast drying properties that allow layering and textural effects. Both mediums serve distinct artistic techniques, with tempera favored in classical and detailed works, while acrylics dominate contemporary and mixed-media art.
Historical Background of Tempera and Acrylic
Tempera paint, dating back to ancient Egypt and widely used throughout the Middle Ages and Renaissance, consists of pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder such as egg yolk, providing a fast-drying and durable medium favored for its luminous, matte finish on wood panels. Acrylic paint, developed in the 20th century, emerged as a revolutionary synthetic medium composed of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, known for its versatility, quick drying time, and water resistance once dry. The historical evolution of tempera reflects traditional, labor-intensive techniques, whereas acrylic represents modern innovation in art materials, influencing diverse contemporary artistic practices.
Composition and Ingredients Comparison
Tempera paint consists primarily of pigment mixed with a water-soluble binder like egg yolk, creating a fast-drying and matte finish ideal for fine details. Acrylic paint, composed of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, offers flexible, water-resistant properties and a glossy finish when dry. The difference in binders fundamentally impacts drying time, durability, and texture, with tempera providing a delicate, layered effect and acrylic enabling vibrant, versatile applications.
Drying Time and Workability
Tempera paint dries rapidly, often within minutes, allowing for quick layering but limiting extended blending and reworking time. Acrylic paint offers a longer open time, ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, enabling smoother blending and more detailed manipulation before drying. Artists favor tempera for fast, precise work and acrylic for versatile techniques requiring flexibility in drying and texture control.
Color Vibrancy and Permanence
Tempera paint offers a matte, slightly muted finish with less vibrant colors compared to acrylic, which delivers intense, bright hues due to its synthetic polymer base. Acrylic paint is renowned for its durability and resistance to fading, maintaining color vibrancy over time even when exposed to light and environmental factors. Tempera, being water-based and prone to chalking, tends to lose color intensity and permanence more rapidly, making acrylic the preferred choice for lasting, vivid artworks.
Surface Compatibility and Preparation
Tempera paint excels on rigid surfaces like wood panels and heavy paper due to its fast-drying, water-soluble nature, requiring a smooth, absorbent ground such as gesso for optimal adhesion. Acrylic paint offers superior versatility, adhering well to a wide range of surfaces including canvas, paper, wood, and even plastic, with minimal preparation needed beyond cleaning and sometimes priming the surface. Proper surface preparation significantly enhances paint longevity, with acrylic accommodating flexible substrates better than tempera, which can crack on improperly prepared or flexible surfaces.
Techniques Unique to Tempera and Acrylic
Tempera painting employs a unique technique of mixing pigment with egg yolk, resulting in quick-drying, matte finishes that allow for delicate layering and fine detailing not achievable with acrylics. Acrylic paint, conversely, offers versatility with its water-based formula that can mimic oils or watercolors, drying rapidly to create durable, flexible surfaces ideal for impasto and glazing effects. The intrinsic properties of tempera enable precision and crisp lines, whereas acrylics accommodate textural experimentation and vibrant color intensity.
Durability and Longevity
Tempera paint, composed primarily of pigment mixed with egg yolk or another binder, is known for its matte finish and long-lasting vibrancy but is more brittle and susceptible to cracking over time. Acrylic paint, made from pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, offers superior durability and flexibility, resisting yellowing and deterioration under environmental stress. Artists seeking longevity and resilience often prefer acrylics for their moisture resistance and ability to maintain color integrity over decades.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Tempera paint, made from natural pigments and egg yolk, presents lower environmental toxicity and biodegrades more easily compared to acrylics, which are synthetic and derived from petroleum products. Acrylic paints emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that may contribute to air pollution and pose respiratory health risks during prolonged exposure. Proper ventilation and using non-toxic, water-based acrylic variants can reduce adverse health effects while allowing artists to balance durability with environmental concerns.
Choosing Between Tempera and Acrylic for Your Art Projects
Tempera paint, known for its quick-drying and matte finish, is ideal for detailed, layered work and traditional art techniques, while acrylic paint offers versatility with vibrant colors and water-resistant durability perfect for mixed media and outdoor projects. Artists choosing between tempera and acrylic should consider factors like surface compatibility, drying time, and desired texture to match their creative vision. For long-lasting artwork with richer pigmentation, acrylics provide superior archival quality compared to the more fragile and less flexible tempera medium.
Tempera vs acrylic Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com