Portraiture captures the true essence and personality of a subject through detailed and realistic representation, highlighting individuality and emotional depth. Caricature exaggerates distinctive features to create a humorous or satirical effect, often emphasizing societal or personal traits with bold distortion. Both forms challenge viewers to interpret identity, offering contrasting perspectives on human character and expression.
Table of Comparison
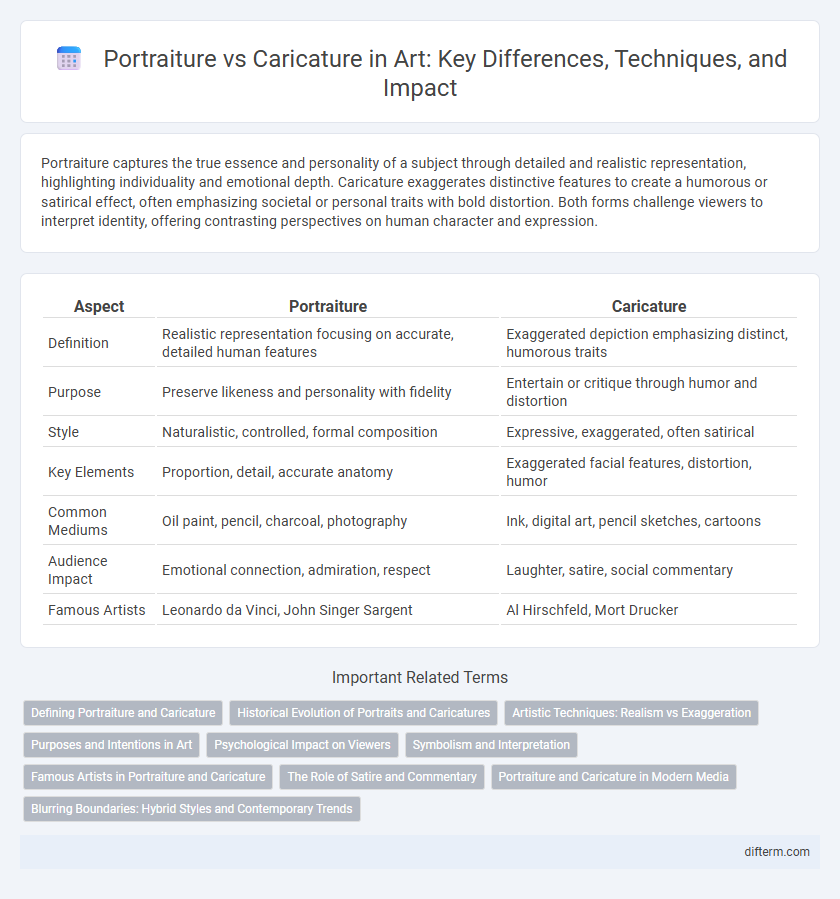
| Aspect | Portraiture | Caricature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Realistic representation focusing on accurate, detailed human features | Exaggerated depiction emphasizing distinct, humorous traits |
| Purpose | Preserve likeness and personality with fidelity | Entertain or critique through humor and distortion |
| Style | Naturalistic, controlled, formal composition | Expressive, exaggerated, often satirical |
| Key Elements | Proportion, detail, accurate anatomy | Exaggerated facial features, distortion, humor |
| Common Mediums | Oil paint, pencil, charcoal, photography | Ink, digital art, pencil sketches, cartoons |
| Audience Impact | Emotional connection, admiration, respect | Laughter, satire, social commentary |
| Famous Artists | Leonardo da Vinci, John Singer Sargent | Al Hirschfeld, Mort Drucker |
Defining Portraiture and Caricature
Portraiture captures a realistic and detailed representation of a subject's appearance, emphasizing accurate facial features and personality expression. Caricature exaggerates distinctive traits to create a humorous or satirical effect, often distorting proportions for visual impact. Both forms highlight individual identity but differ in intent and stylistic approach, with portraiture aiming for fidelity and caricature for commentary.
Historical Evolution of Portraits and Caricatures
Portraiture originated as a means to immortalize influential figures with realism and dignity, evolving through styles from Renaissance naturalism to modern expressionism. Caricature emerged in the 16th century as a satirical art form, exaggerating features for social commentary and political critique. Both genres reflect shifting cultural values, with portraits emphasizing identity preservation and caricatures highlighting public opinions and humor.
Artistic Techniques: Realism vs Exaggeration
Portraiture employs meticulous brushwork and precise shading to capture realistic facial features and subtle expressions, emphasizing proportional accuracy and depth to convey an authentic likeness. Caricature relies on deliberate exaggeration of distinctive traits, using bold lines and stylized distortions to amplify personality and evoke humor or satire. The contrast between realism in portraiture and exaggeration in caricature highlights different artistic objectives, balancing fidelity with interpretive freedom.
Purposes and Intentions in Art
Portraiture aims to capture the true likeness, personality, and status of the subject, often serving as a means of commemoration or historical record. Caricature exaggerates distinctive features and traits to evoke humor, satire, or social commentary, emphasizing interpretation over realism. Both forms engage viewers differently, with portraiture fostering recognition and respect, while caricature provokes reflection and critique through distortion.
Psychological Impact on Viewers
Portraiture captures the nuanced emotions and personality traits of subjects, fostering empathy and deeper psychological connection in viewers. Caricature exaggerates distinctive features, often eliciting humor or critique, which can provoke reflection or challenge social perceptions. Both forms manipulate visual cues to influence viewers' emotional and cognitive responses uniquely within the realm of psychological impact.
Symbolism and Interpretation
Portraiture captures the essence and personality of the subject through realistic representation, emphasizing symbolic elements that convey status, character, or emotional depth. Caricature exaggerates distinctive features to create a visual metaphor, often symbolizing societal critiques or highlighting idiosyncrasies humorously. The interpretation of portraiture invites introspection and admiration, while caricature prompts critical reflection and satire.
Famous Artists in Portraiture and Caricature
Famous artists in portraiture such as Leonardo da Vinci and Rembrandt van Rijn excelled in capturing intricate human emotions and realistic details, establishing timeless works that highlight skillful anatomical precision. Conversely, caricature artists like Honore Daumier and Al Hirschfeld use exaggerated features and satirical elements to convey personality and social commentary, blending humor with sharp observation. Both art forms uniquely emphasize expressive human identity, yet portraiture emphasizes fidelity and depth, while caricature prioritizes distortion and critique.
The Role of Satire and Commentary
Portraiture captures the essence and personality of the subject, often aiming for realism and respect, while caricature employs exaggeration and distortion to highlight flaws or societal critiques. Satire in caricature serves as a powerful tool for social commentary, using humor and visual irony to challenge political figures, norms, and cultural issues. This dynamic interaction between art forms reflects the evolving role of visual media in shaping public opinion and discourse.
Portraiture and Caricature in Modern Media
Portraiture in modern media emphasizes realism and emotional depth, capturing the true essence of subjects through high-resolution photography and digital painting. Caricature uses exaggerated features and stylized distortion to convey humor, critique, or social commentary, often seen in editorial cartoons and animated content. Both forms serve distinct cultural functions, with portraiture preserving identity and caricature challenging perceptions in contemporary visual storytelling.
Blurring Boundaries: Hybrid Styles and Contemporary Trends
Hybrid styles in portraiture and caricature blur traditional boundaries by merging realistic detail with exaggerated features, creating dynamic visual narratives that challenge conventional representation. Contemporary trends emphasize experimental techniques, incorporating digital manipulation and mixed media to explore identity and social commentary in multidimensional ways. This fusion fosters innovative expressions that engage viewers through a spectrum of emotional and interpretive responses, redefining portraiture's role in modern art.
portraiture vs caricature Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com