Gouache offers a more opaque and vibrant finish compared to watercolor, making it ideal for artists seeking bold, solid colors and detailed textures. Watercolor, known for its translucency and fluidity, allows for delicate washes and subtle gradients that create a luminous, ethereal effect. Both mediums require different techniques and layering approaches, with gouache providing greater correction flexibility and watercolor emphasizing spontaneous, light-filled compositions.
Table of Comparison
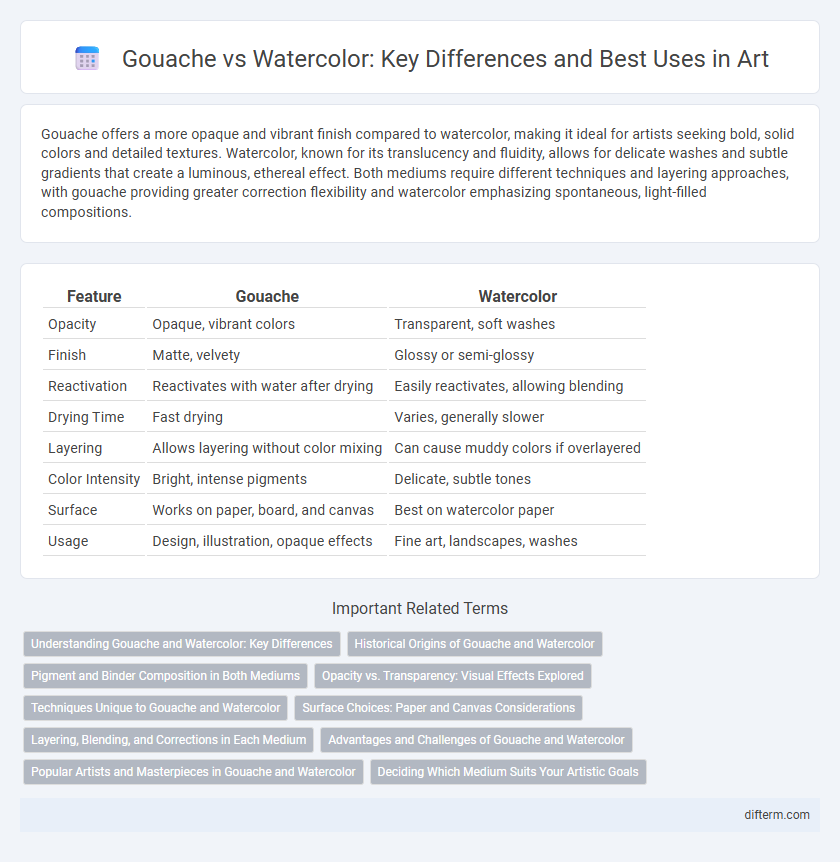
| Feature | Gouache | Watercolor |
|---|---|---|
| Opacity | Opaque, vibrant colors | Transparent, soft washes |
| Finish | Matte, velvety | Glossy or semi-glossy |
| Reactivation | Reactivates with water after drying | Easily reactivates, allowing blending |
| Drying Time | Fast drying | Varies, generally slower |
| Layering | Allows layering without color mixing | Can cause muddy colors if overlayered |
| Color Intensity | Bright, intense pigments | Delicate, subtle tones |
| Surface | Works on paper, board, and canvas | Best on watercolor paper |
| Usage | Design, illustration, opaque effects | Fine art, landscapes, washes |
Understanding Gouache and Watercolor: Key Differences
Gouache and watercolor are both water-based paints, but gouache contains higher pigment concentration and opaque qualities, allowing for vibrant, solid color coverage and easy layering. Watercolor offers translucent washes and subtle gradients, emphasizing light reflection on paper and delicate blending techniques. Artists choose gouache for bold, flat illustrations and watercolor for fluid, transparent effects in landscapes and portraits.
Historical Origins of Gouache and Watercolor
Gouache originated in the Middle Ages, evolving from opaque water-based paints used by manuscript illuminators and later adopted by European painters for its vibrant, matte finish. Watercolor traces back to ancient Egypt and China, where artists applied translucent pigments on papyrus and silk, emphasizing lightness and fluidity. Both mediums have distinct historical trajectories that shaped their unique techniques and artistic applications.
Pigment and Binder Composition in Both Mediums
Gouache contains higher pigment concentration and a chalk-based binder, resulting in a more opaque and matte finish compared to watercolor, which uses transparent pigments suspended in a gum arabic binder for translucency. The pigment particles in gouache are larger and more densely packed, enabling vibrant, solid color application, whereas watercolor pigments are finely ground and diluted for fluid, layered washes. This fundamental difference in pigment and binder composition affects drying times, texture, and color intensity in each medium.
Opacity vs. Transparency: Visual Effects Explored
Gouache offers superior opacity compared to watercolor, allowing artists to achieve bold, solid colors and easily correct mistakes with layers that fully cover underlying paint. In contrast, watercolor excels in transparency, creating luminous washes and subtle gradients that capture light through its translucent pigments. This fundamental difference influences the visual effects artists select, with gouache providing matte, vibrant finishes and watercolor producing delicate, glowing compositions.
Techniques Unique to Gouache and Watercolor
Gouache techniques leverage its opacity, enabling artists to layer vibrant colors and create solid shapes with quick drying times, which is ideal for detailed illustrations and graphic designs. Watercolor techniques emphasize transparency and fluidity, allowing for smooth color gradients, washes, and subtle blending effects that create luminous, delicate images. Mastery of gouache requires controlling its matte finish and layering without muddying, while watercolor demands precision in water control and timing to avoid overworking the pigment.
Surface Choices: Paper and Canvas Considerations
Gouache performs best on heavier, textured paper or primed canvas due to its opaque and matte finish, allowing vibrant colors to stand out with smooth coverage. Watercolor requires specific watercolor paper that is absorbent and often textured to handle its transparency and fluidity, preventing warping and enabling delicate washes. Canvas is less suitable for watercolor as it lacks absorbency, while gouache's thickness adheres well to various primed surfaces, expanding artists' creative options.
Layering, Blending, and Corrections in Each Medium
Gouache offers superior layering capabilities thanks to its opaque and vibrant pigments, allowing artists to paint lighter colors over darker ones without losing intensity. Watercolor excels in blending with its transparent qualities, facilitating smooth gradients but making corrections challenging due to the paint's reactivation with water. Corrections in gouache are more forgiving, as reworking areas is easier, while watercolor requires careful planning to avoid muddying colors during layering and blending.
Advantages and Challenges of Gouache and Watercolor
Gouache offers vibrant opacity and strong color layering, making it ideal for bold, expressive artwork, but it can be challenging to rework once dry due to its matte finish. Watercolor provides transparency and subtle blending effects that enhance light and texture, though it requires precision to control water flow and avoid unwanted blooms or streaks. Both mediums demand unique techniques that impact drying times, color intensity, and overall composition flexibility in artistic projects.
Popular Artists and Masterpieces in Gouache and Watercolor
Famous artists such as Henri Matisse and Paul Klee are renowned for their innovative use of gouache, showcasing vibrant, opaque layers in masterpieces like Matisse's "Jazz" series. In contrast, watercolor has been the medium of choice for artists like J.M.W. Turner and Winslow Homer, celebrated for their luminous, translucent washes exemplified in Turner's "The Blue Rigi" and Homer's "Breezing Up." Both mediums continue to inspire contemporary artists who exploit gouache's bold opacity and watercolor's fluid transparency to create distinctive artistic expressions.
Deciding Which Medium Suits Your Artistic Goals
Gouache offers vibrant opacity and quick drying times, making it ideal for artists seeking bold, solid colors and precise details. Watercolor provides translucent layers and fluid blending, perfect for those aiming to capture delicate washes and subtle gradients. Evaluating your desired texture, color intensity, and drying speed will guide the choice between gouache and watercolor to best align with your artistic goals.
gouache vs watercolor Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com