Glaze in art refers to a translucent layer of paint applied over a dried layer to enhance depth and richness, often used in oil painting to create luminous effects. Varnish, on the other hand, is a transparent protective coating applied after the artwork is finished, designed to preserve colors and shield the surface from dust, moisture, and UV damage. While glaze modifies the appearance and texture during the painting process, varnish serves as a final sealant to maintain the artwork's longevity and visual integrity.
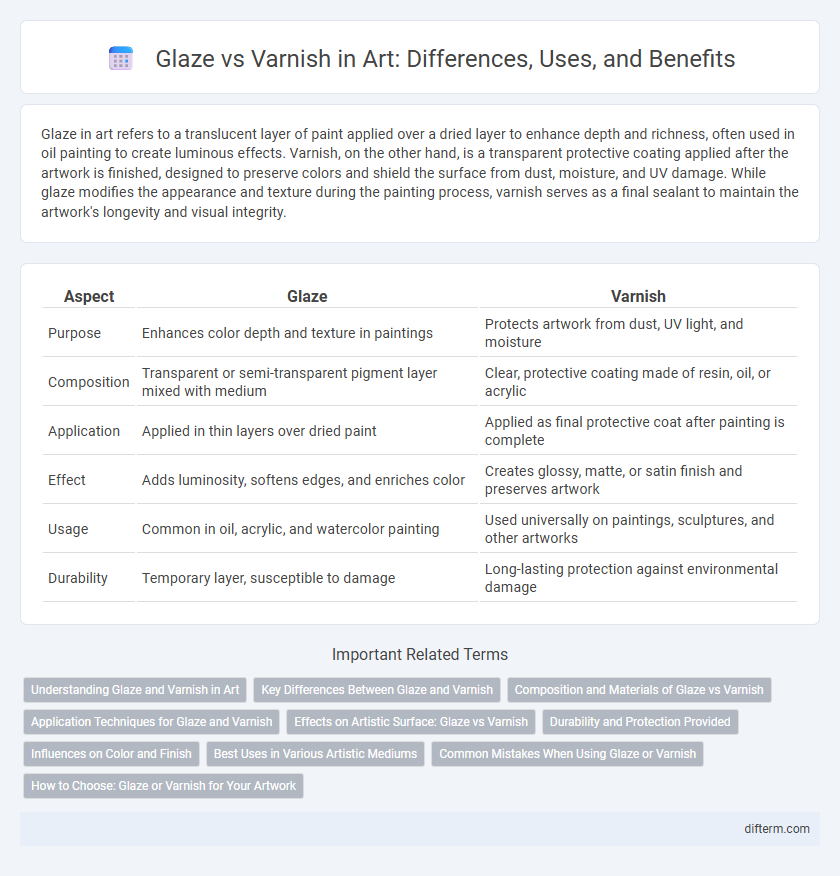
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Glaze | Varnish |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances color depth and texture in paintings | Protects artwork from dust, UV light, and moisture |
| Composition | Transparent or semi-transparent pigment layer mixed with medium | Clear, protective coating made of resin, oil, or acrylic |
| Application | Applied in thin layers over dried paint | Applied as final protective coat after painting is complete |
| Effect | Adds luminosity, softens edges, and enriches color | Creates glossy, matte, or satin finish and preserves artwork |
| Usage | Common in oil, acrylic, and watercolor painting | Used universally on paintings, sculptures, and other artworks |
| Durability | Temporary layer, susceptible to damage | Long-lasting protection against environmental damage |
Understanding Glaze and Varnish in Art
Glaze in art refers to a thin, transparent or semi-transparent layer of paint applied over a dried layer to create depth, enhance color richness, and produce luminosity, commonly used in oil and acrylic painting techniques. Varnish is a clear protective coating applied after a painting is complete, designed to shield the surface from dust, UV rays, and environmental damage while often enhancing the artwork's vibrancy and longevity. Understanding the distinct purposes of glaze for aesthetic effects and varnish for preservation is essential for artists aiming to perfect their finishing techniques.
Key Differences Between Glaze and Varnish
Glaze and varnish serve distinct purposes in art; glaze is a thin, transparent layer of paint applied to alter color depth and texture, while varnish is a protective finish that seals and preserves the artwork. Glaze enhances details and richness by manipulating light reflection, whereas varnish provides durability against environmental factors like moisture and UV rays. Artists use glaze for visual effects and varnish for longevity, making both essential but functionally different components in painting techniques.
Composition and Materials of Glaze vs Varnish
Glaze is typically composed of finely ground pigments suspended in a transparent medium such as oil or acrylic, designed to enhance color depth and luminosity in paintings. Varnish consists of natural or synthetic resins dissolved in solvents, forming a protective, clear coating that safeguards artwork from dust, moisture, and UV damage. The primary materials in glaze prioritize translucency and color modulation, whereas varnish materials emphasize durability and surface protection.
Application Techniques for Glaze and Varnish
Glaze application involves layering thin, translucent paint over a dried base to enhance depth and luminosity, often requiring multiple drying stages between coats for optimal effect. Varnish is typically applied in a single or few protective layers using a soft bristle brush or spray to seal and protect the artwork without altering underlying colors. Mastery in controlling brush strokes and drying times is essential in both techniques to achieve a smooth, even finish that preserves the integrity of the painting.
Effects on Artistic Surface: Glaze vs Varnish
Glaze enhances depth and luminosity by creating a translucent layer that interacts with light, allowing underlying colors to shine through and intensify. Varnish provides a protective coating that enhances color richness while offering a uniform sheen and safeguarding the artwork from dust, UV damage, and moisture. Artists choose glaze to achieve subtle tonal variations and a luminous finish, while varnish is applied to ensure long-term preservation and a balanced surface texture.
Durability and Protection Provided
Glaze enhances artwork durability by creating a resilient, glass-like coating that protects against scratches, moisture, and UV damage, extending the painting's lifespan. Varnish offers strong protection by sealing the surface, preventing dust accumulation and discoloration while maintaining color vibrancy over time. Both substances optimize artwork preservation, but glaze typically provides a thicker, more durable barrier suited for high-traffic or frequently handled pieces.
Influences on Color and Finish
Glaze enhances color depth and luminosity by adding translucent layers that interact with underlying pigments, creating rich, vibrant finishes. Varnish primarily serves as a protective coating with varying degrees of gloss, affecting overall sheen without significantly altering color intensity. The choice between glaze and varnish directly influences the final visual texture and perceived warmth or coolness of the artwork.
Best Uses in Various Artistic Mediums
Glaze is ideal for ceramics and pottery, providing a durable, glass-like coating that enhances color depth and surface texture. Varnish suits paintings on canvas and wood, offering a protective seal that preserves pigments and adds desired finishes like matte, gloss, or satin. Each medium benefits from the specific protective and aesthetic qualities that glaze and varnish impart, optimizing longevity and visual impact in their respective art forms.
Common Mistakes When Using Glaze or Varnish
Common mistakes when using glaze or varnish in art include applying too thick a layer, which can cause cracking or uneven drying. Artists often confuse the purpose of glaze, which enhances color depth and texture, with varnish, designed to protect the finished artwork. Skipping surface preparation or using incompatible products can lead to poor adhesion and long-term damage to paintings.
How to Choose: Glaze or Varnish for Your Artwork
Choosing between glaze and varnish for artwork depends on the desired visual effect and protection level; glaze enhances depth and luminosity by creating a translucent layer, while varnish primarily offers a protective coating against dust, moisture, and UV damage. Artists should consider glaze for adding richness and subtle color shifts in oil or acrylic paintings, whereas varnish is ideal for preserving finished work with a uniform gloss, matte, or satin finish. Evaluating the artwork medium, surface texture, and environmental exposure ensures selecting the optimal material that balances aesthetic enhancement with long-term durability.
glaze vs varnish Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com