Encaustic painting involves using heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments, creating a luminous, textured surface that can be reshaped and layered for depth. Impasto technique applies thick layers of paint, often oil or acrylic, allowing brushstrokes and palette knife marks to stand out, enhancing the painting's dimensionality. Both methods emphasize texture but differ in materials and visual effects, with encaustic offering a smooth, waxy finish and impasto delivering bold, tactile expression.
Table of Comparison
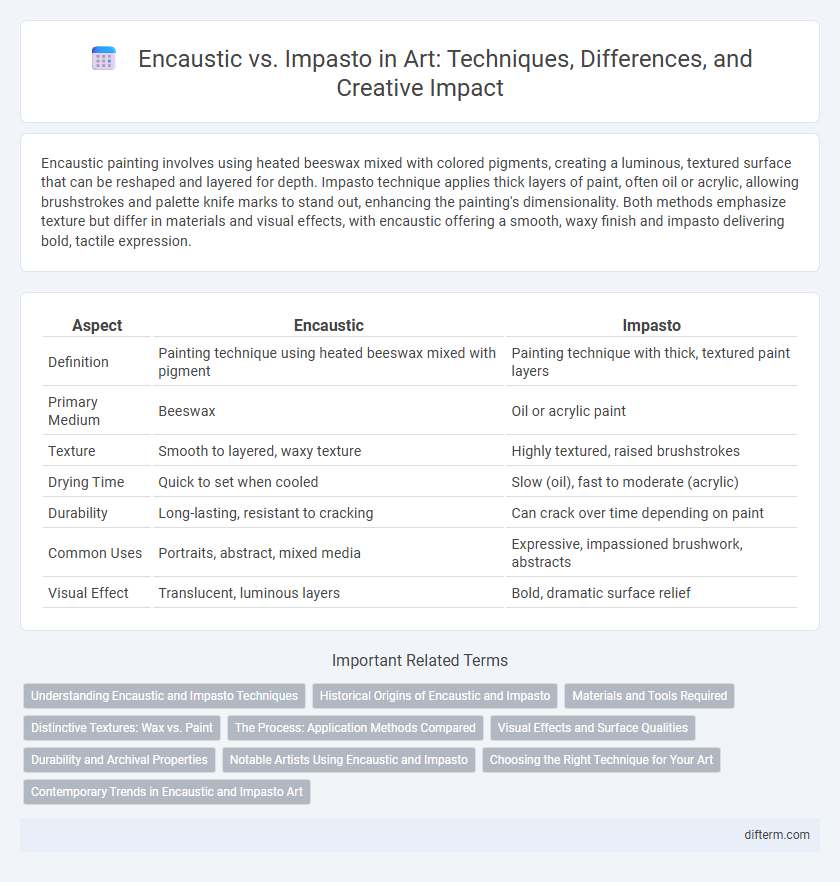
| Aspect | Encaustic | Impasto |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Painting technique using heated beeswax mixed with pigment | Painting technique with thick, textured paint layers |
| Primary Medium | Beeswax | Oil or acrylic paint |
| Texture | Smooth to layered, waxy texture | Highly textured, raised brushstrokes |
| Drying Time | Quick to set when cooled | Slow (oil), fast to moderate (acrylic) |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to cracking | Can crack over time depending on paint |
| Common Uses | Portraits, abstract, mixed media | Expressive, impassioned brushwork, abstracts |
| Visual Effect | Translucent, luminous layers | Bold, dramatic surface relief |
Understanding Encaustic and Impasto Techniques
Encaustic painting involves applying heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments to a surface, creating a rich, textured finish that can be layered and fused for depth and durability. Impasto technique uses thick, viscous paint--often oil or acrylic--applied with brushes or palette knives to build pronounced textures and expressive strokes on the canvas. Both methods emphasize texture but encaustic's wax medium allows for translucent layers and permanence, while impasto enhances surface relief and dynamic brushwork.
Historical Origins of Encaustic and Impasto
Encaustic painting, originating in ancient Greece around the 5th century BCE, utilizes heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments to create durable, luminous artworks, famously employed by the Fayum mummy portraits of Egypt. Impasto, emerging prominently during the Baroque period and perfected by artists like Rembrandt and later Impressionists such as Van Gogh, involves thick applications of oil paint to add texture and expressive dimensionality. The historical development of encaustic highlights its preservation qualities, while impasto reflects evolving techniques to enhance emotional impact through tactile paint surfaces.
Materials and Tools Required
Encaustic painting relies on heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments and requires specialized tools like heating panels, metal spatulas, and heat guns to manipulate and fuse layers of wax. Impasto technique uses thick oils or acrylic paints applied with brushes or palette knives to create textured surfaces, demanding high-quality, heavy-bodied paints and sturdy application tools. Both methods necessitate unique materials and equipment tailored to their distinct textural effects and durability.
Distinctive Textures: Wax vs. Paint
Encaustic art utilizes heated beeswax mixed with pigments, creating a luminous, layered texture that can be manipulated while warm for smooth or sculptural effects. Impasto employs thick oil or acrylic paint applied with brushes or palette knives, producing raised, textured surfaces with visible brushstrokes and dynamic depth. The wax in encaustic offers translucency and a tactile waxy finish, whereas impasto paint results in opaque, tactile ridges emphasizing movement and intensity.
The Process: Application Methods Compared
Encaustic painting involves applying heated beeswax mixed with pigment directly onto a surface, allowing for smooth blending and layering through reheating. Impasto uses thick applications of oil or acrylic paint, applied with brushes or palette knives to create textured, three-dimensional effects. Both techniques emphasize physical manipulation of materials but differ in temperature use and tactile results, with encaustic's wax offering translucency and impasto's paint delivering bold surface relief.
Visual Effects and Surface Qualities
Encaustic painting creates a luminous, translucent effect by layering molten beeswax mixed with pigment, resulting in a smooth, glossy surface that captures light subtly. In contrast, impasto technique builds up thick, textured layers of paint, often oil or acrylic, producing pronounced ridges and a tactile, three-dimensional quality that emphasizes brushstrokes and movement. The visual impact of encaustic is ethereal and polished, while impasto offers dynamic surface depth and expressive intensity.
Durability and Archival Properties
Encaustic painting, utilizing heated beeswax mixed with pigments, offers exceptional durability due to its resistance to moisture, UV light, and environmental pollutants, ensuring long-term preservation without significant color fading or cracking. Impasto, characterized by thickly applied oil or acrylic paints, tends to be more vulnerable to cracking and yellowing over time, especially if not properly varnished or maintained, impacting its archival stability. The archival properties of encaustic make it a preferred choice for artists seeking longevity, while impasto's texture and visual depth require careful handling to preserve the artwork's integrity.
Notable Artists Using Encaustic and Impasto
Jasper Johns is a notable artist known for his innovative use of encaustic, creating textured, multi-layered surfaces that enhance the depth and vibrancy of his iconic works. Vincent van Gogh exemplifies impasto technique with thick, expressive brushstrokes that add emotional intensity and physicality to his paintings. Both methods emphasize surface texture but differ in medium and application, with encaustic incorporating heated beeswax and impasto relying on heavy oil paint layering.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Art
Encaustic painting, using heated beeswax mixed with pigments, offers a luminous, textured surface that is ideal for artists seeking to create depth with layered translucency. Impasto, characterized by thick applications of oil or acrylic paint, emphasizes bold texture and dynamic brushstrokes, making it perfect for expressive, tactile works. Selecting between encaustic and impasto depends on whether your artistic vision prioritizes subtle light effects or pronounced surface texture.
Contemporary Trends in Encaustic and Impasto Art
Contemporary trends in encaustic and impasto art emphasize texture and depth, with encaustic artists leveraging beeswax's unique translucency to create layered, luminous effects, while impasto painters apply thick, expressive strokes to achieve bold three-dimensional surfaces. Innovations in encaustic techniques incorporate mixed media and digital elements, expanding its versatility beyond traditional boundaries. Impasto's resurgence in modern abstract and figurative works underscores artists' desire to evoke tactile engagement and emotional intensity through commanding paint applications.
encaustic vs impasto Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com