When traveling with pets, understanding the difference between a tourist visa and a transit visa is crucial to ensure smooth entry and compliance with pet import regulations. A tourist visa allows extended stay and access to country-specific pet import requirements, including necessary vaccinations and quarantine procedures, whereas a transit visa is typically short-term and may restrict pet movement and accommodation options during layovers. Proper documentation and adherence to each visa type's regulations prevent delays and guarantee the well-being of pets throughout international travel.
Table of Comparison
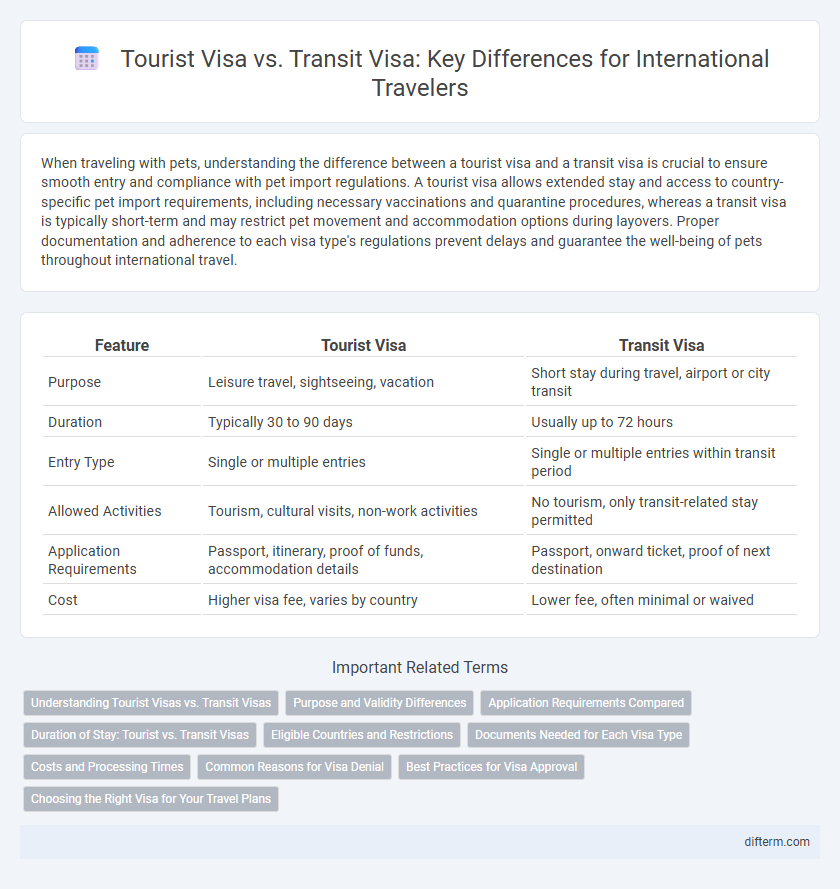
| Feature | Tourist Visa | Transit Visa |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Leisure travel, sightseeing, vacation | Short stay during travel, airport or city transit |
| Duration | Typically 30 to 90 days | Usually up to 72 hours |
| Entry Type | Single or multiple entries | Single or multiple entries within transit period |
| Allowed Activities | Tourism, cultural visits, non-work activities | No tourism, only transit-related stay permitted |
| Application Requirements | Passport, itinerary, proof of funds, accommodation details | Passport, onward ticket, proof of next destination |
| Cost | Higher visa fee, varies by country | Lower fee, often minimal or waived |
Understanding Tourist Visas vs. Transit Visas
Tourist visas grant travelers permission to enter a country for leisure, sightseeing, and short-term stays, typically lasting from 30 to 90 days depending on the destination. Transit visas allow passengers to pass through a country en route to another destination, usually limiting the stay to a few hours or days without granting full entry privileges. Understanding the specific requirements, duration, and restrictions of each visa type is crucial for seamless international travel planning.
Purpose and Validity Differences
A tourist visa is issued for travelers intending to visit a country for leisure, sightseeing, or holiday purposes, typically valid for 30 to 90 days, allowing multiple entries in some cases. A transit visa permits a traveler to pass through a country en route to a third destination, generally valid for a short duration ranging from a few hours up to 72 hours, and does not authorize full entry or extended stays. The primary distinction lies in the purpose, where a tourist visa supports tourism activities, whereas a transit visa strictly facilitates temporary passage.
Application Requirements Compared
Tourist visa applications typically require proof of accommodation, financial solvency, and a detailed travel itinerary, emphasizing the intent to explore the destination. Transit visa applications demand documentation of onward travel, visa for the final destination if applicable, and limited duration of stay evidence. Understanding these distinct requirements ensures compliance and smooth processing for international travelers.
Duration of Stay: Tourist vs. Transit Visas
Tourist visas typically allow travelers to stay in a country for an extended period, ranging from 30 to 180 days depending on the destination's immigration policies. Transit visas, by contrast, are designed for short stays, often limited to 24 to 72 hours, facilitating layovers or quick transfers between flights without entering the country fully. The duration of stay for a transit visa is strictly shorter to ensure travelers do not engage in tourism or long-term activities during their brief passage.
Eligible Countries and Restrictions
Tourist visas are typically issued to travelers from a broad range of eligible countries allowing extended stays for leisure, with restrictions often including the prohibition of employment and requirements for proof of accommodation and financial sufficiency. Transit visas are usually granted to passengers from specific countries with strict eligibility, permitting only short-term stay within the airport or limited transit areas, often restricting entry beyond designated transit zones. Both visa types impose varying entry restrictions based on bilateral agreements, and travelers should verify country-specific eligibility and duration limits before planning their trip.
Documents Needed for Each Visa Type
Tourist visa applications typically require a valid passport, completed visa application form, recent passport-sized photographs, proof of accommodation, travel itinerary, and financial evidence to support the stay. Transit visa documentation generally includes a valid passport, confirmed onward travel ticket within a specific short period, visa for the next destination country if required, and sometimes proof of sufficient funds for the transit duration. Both visas may necessitate travel insurance and a clear background check depending on the destination country's policies.
Costs and Processing Times
Tourist visas generally cost more than transit visas due to their longer duration and broader travel privileges, with prices varying by country but often ranging from $30 to $150. Processing times for tourist visas can take anywhere from several days to a few weeks, influenced by factors such as consulate workload and applicant nationality. Transit visas typically have lower fees, often under $50, and faster processing times, sometimes within 24 to 72 hours, since they are intended for short stays during travel.
Common Reasons for Visa Denial
Common reasons for tourist and transit visa denial include insufficient financial proof, incomplete or inconsistent documentation, and failure to demonstrate a clear travel itinerary or purpose. Authorities often reject applications when applicants cannot prove strong ties to their home country, raising concerns about potential visa overstays. Security concerns, prior visa violations, and unclear travel intentions frequently contribute to visa refusals in both categories.
Best Practices for Visa Approval
Tourist visas require submitting detailed travel itineraries, proof of accommodations, and financial stability to demonstrate intent to explore the destination. Transit visas often demand confirmed onward tickets, valid visas for final destinations, and minimal paperwork to ensure brief airport or port stays. Consistently verifying specific embassy requirements, providing accurate documentation, and applying well in advance maximize chances of visa approval.
Choosing the Right Visa for Your Travel Plans
A tourist visa allows travelers to stay in a country for leisure, sightseeing, or visiting family, typically granting entry for 30 to 90 days depending on the destination's immigration policies. In contrast, a transit visa is designed for short stops, usually under 72 hours, enabling passengers to pass through a country en route to another destination without engaging in tourism activities. Selecting the correct visa depends on your itinerary, length of stay, and the specific entry requirements of the nation you plan to visit or transit through.
tourist visa vs transit visa Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com