Social exclusion refers to the experience of being deliberately left out or marginalized within social groups, leading to feelings of rejection and low self-esteem. Social isolation, on the other hand, is the objective state of having minimal contact with others, which can result from or contribute to loneliness and mental health challenges. Understanding the difference between these concepts is essential for addressing the emotional and psychological well-being of pets in social environments.
Table of Comparison
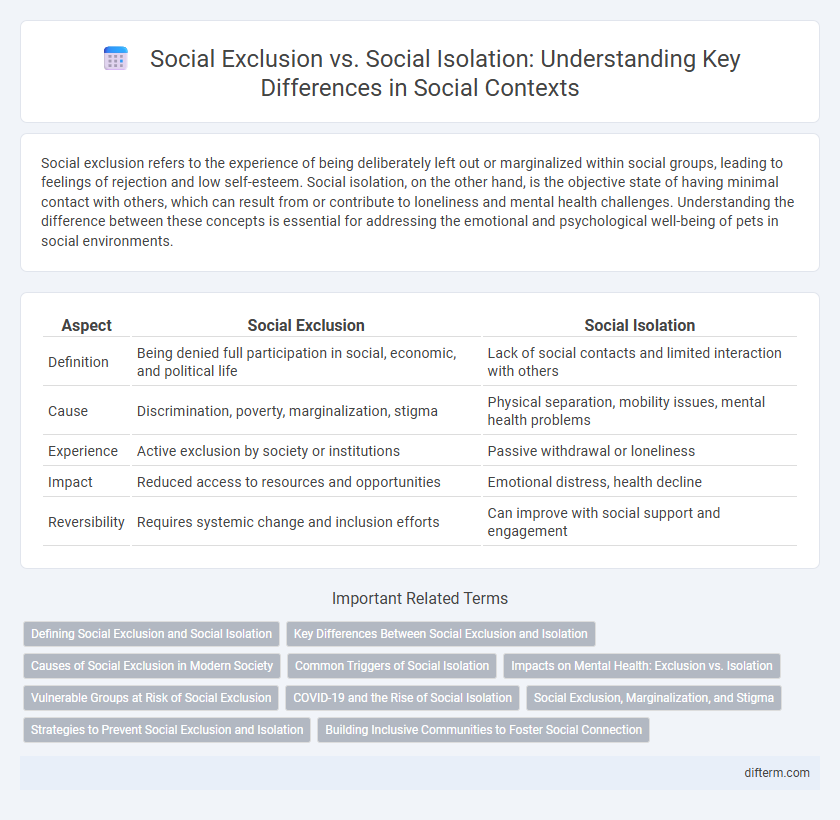
| Aspect | Social Exclusion | Social Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Being denied full participation in social, economic, and political life | Lack of social contacts and limited interaction with others |
| Cause | Discrimination, poverty, marginalization, stigma | Physical separation, mobility issues, mental health problems |
| Experience | Active exclusion by society or institutions | Passive withdrawal or loneliness |
| Impact | Reduced access to resources and opportunities | Emotional distress, health decline |
| Reversibility | Requires systemic change and inclusion efforts | Can improve with social support and engagement |
Defining Social Exclusion and Social Isolation
Social exclusion refers to the process through which individuals or groups are systematically blocked from various rights, opportunities, and resources, such as housing, employment, healthcare, and social networks. Social isolation is the state of having minimal contact or interaction with others, often resulting in feelings of loneliness and detachment from the community. While social exclusion emphasizes structural barriers and inequality, social isolation highlights the individual experience of reduced social relationships.
Key Differences Between Social Exclusion and Isolation
Social exclusion refers to the systemic barriers and discrimination that prevent individuals or groups from fully participating in society, impacting access to resources, rights, and social networks. Social isolation, on the other hand, describes an individual's physical separation or lack of social interactions resulting in loneliness or minimal social contact. The key differences lie in social exclusion being a structural, societal issue affecting opportunities and belonging, while social isolation is a personal experience of disconnection that can result from exclusion but also from other factors like health or mobility.
Causes of Social Exclusion in Modern Society
Economic inequality, discrimination based on race, gender, or disability, and limited access to education and employment opportunities are primary causes of social exclusion in modern society. Urbanization and technological advancements can inadvertently marginalize individuals lacking digital literacy or resources, intensifying social divides. Social policies that fail to address these systemic barriers often perpetuate exclusion, hindering community integration and equal participation.
Common Triggers of Social Isolation
Common triggers of social isolation include significant life changes such as retirement, relocation, or the loss of a loved one, which disrupt established social networks. Chronic health conditions and mobility limitations often reduce opportunities for social interaction, increasing the risk of isolation. Additionally, experiences of social exclusion, such as discrimination or bullying, can lead individuals to withdraw from social activities, deepening their isolation.
Impacts on Mental Health: Exclusion vs. Isolation
Social exclusion often leads to feelings of rejection and low self-esteem, significantly increasing the risk of depression and anxiety disorders. In contrast, social isolation results in a lack of social interaction that exacerbates loneliness, contributing to cognitive decline and increased stress levels. Both conditions negatively impact mental health but through distinct psychological and emotional pathways.
Vulnerable Groups at Risk of Social Exclusion
Vulnerable groups at risk of social exclusion include the elderly, individuals with disabilities, ethnic minorities, and low-income families, who often face systemic barriers to full participation in social, economic, and cultural life. Social exclusion manifests through restricted access to education, employment, healthcare, and social networks, leading to marginalization and reduced quality of life. Addressing these issues requires targeted interventions to enhance social inclusion, promote equal opportunities, and strengthen community support systems.
COVID-19 and the Rise of Social Isolation
Social isolation surged dramatically during the COVID-19 pandemic, intensifying feelings of loneliness and mental health challenges worldwide. Unlike social exclusion, which involves systemic barriers preventing participation in societal activities, social isolation refers to the physical separation and lack of social contacts experienced by individuals. The rise of remote work, lockdowns, and social distancing measures exacerbated social isolation, highlighting its profound impact on vulnerable populations and the urgent need for targeted interventions.
Social Exclusion, Marginalization, and Stigma
Social exclusion involves the systematic marginalization of individuals or groups, preventing their full participation in economic, social, and political life. This exclusion fosters stigma, which reinforces negative stereotypes and perpetuates barriers to inclusion and equal opportunity. Understanding the dynamics of social exclusion is crucial for developing policies that promote social justice and community cohesion.
Strategies to Prevent Social Exclusion and Isolation
Community engagement programs enhance social inclusion by fostering meaningful connections among diverse groups, reducing feelings of isolation. Implementing accessible social services, such as mental health support and transportation, addresses barriers that contribute to exclusion and isolation. Promoting inclusive policies in education and employment ensures equal opportunities, strengthening individuals' social networks and sense of belonging.
Building Inclusive Communities to Foster Social Connection
Social exclusion denies individuals access to resources, rights, and opportunities, leading to marginalization, while social isolation refers to the physical or emotional separation from others. Building inclusive communities involves creating environments that promote participation, respect diversity, and provide supportive networks to reduce feelings of loneliness and exclusion. Effective strategies include community engagement programs, accessible social services, and culturally sensitive outreach to foster meaningful social connections and enhance collective well-being.
social exclusion vs social isolation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com