A social pet thrives at the intersection of network society and information society, leveraging interconnected digital platforms to foster real-time, meaningful interactions among users. Network society emphasizes the dynamic web of social connections facilitated by technology, while information society centers on the vast availability and exchange of data. Integrating these concepts, a social pet harnesses both social networks and information flows to enhance community engagement and personalized experiences.
Table of Comparison
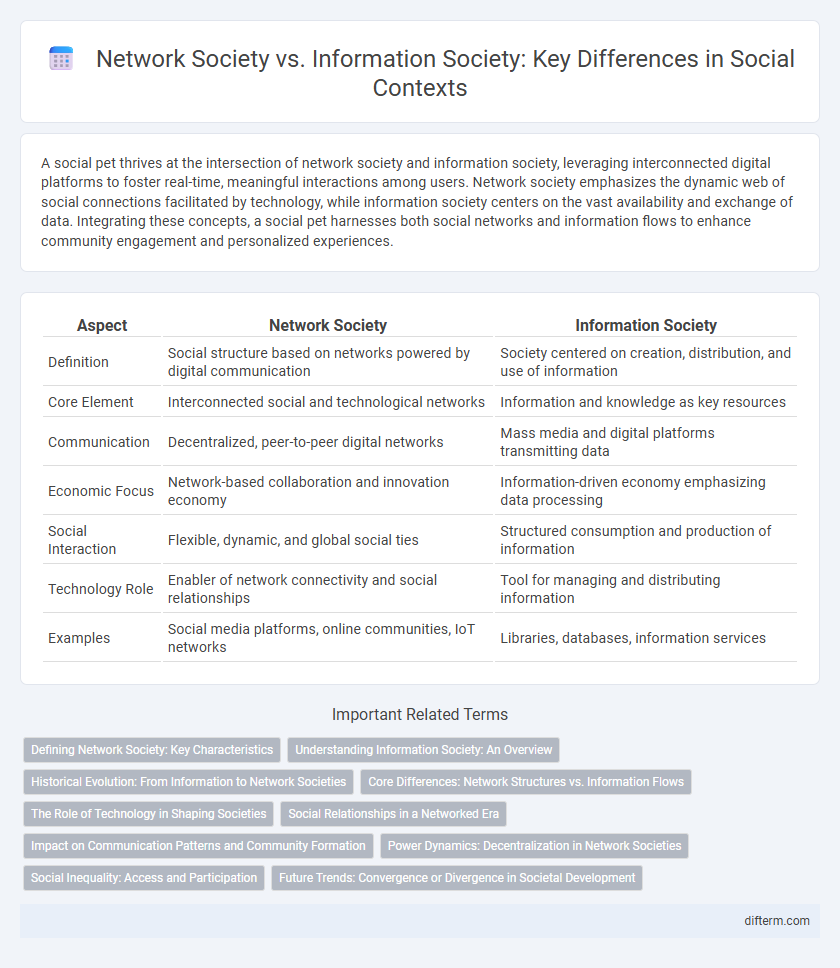
| Aspect | Network Society | Information Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social structure based on networks powered by digital communication | Society centered on creation, distribution, and use of information |
| Core Element | Interconnected social and technological networks | Information and knowledge as key resources |
| Communication | Decentralized, peer-to-peer digital networks | Mass media and digital platforms transmitting data |
| Economic Focus | Network-based collaboration and innovation economy | Information-driven economy emphasizing data processing |
| Social Interaction | Flexible, dynamic, and global social ties | Structured consumption and production of information |
| Technology Role | Enabler of network connectivity and social relationships | Tool for managing and distributing information |
| Examples | Social media platforms, online communities, IoT networks | Libraries, databases, information services |
Defining Network Society: Key Characteristics
Network society is defined by the prevalence of digital communication technologies that facilitate decentralized social interactions and real-time data exchange. Key characteristics include widespread connectivity, enabling individuals and organizations to form dynamic, flexible networks across geographic boundaries. This structure contrasts with the information society, which emphasizes the production and consumption of information rather than the relational networks enabled by technology.
Understanding Information Society: An Overview
The information society is characterized by the central role of information production, processing, and distribution in economic, social, and cultural activities, driven by advancements in digital technologies and communication networks. In contrast, the network society emphasizes the social structure shaped by global networks enabled through the internet, linking individuals, organizations, and nations in real-time interactions. Both concepts highlight the transformative impact of ICTs but differ in focus, with the information society prioritizing informational content and the network society foregrounding relational connectivity.
Historical Evolution: From Information to Network Societies
The historical evolution from information society to network society reflects the shift from centralized information control to decentralized, interconnected digital platforms enabling real-time communication and collaboration. Unlike the information society, characterized by the dominance of mass media and hierarchical knowledge dissemination, the network society thrives on peer-to-peer interactions facilitated by social media, cloud computing, and mobile networks. This transformation highlights the rise of flexible social structures where data flows horizontally, fostering global connectivity and reshaping social, economic, and political dynamics.
Core Differences: Network Structures vs. Information Flows
Network society emphasizes decentralized, interconnected social structures where relationships and interactions form complex, dynamic networks. Information society centers on the production, distribution, and consumption of data, highlighting the flow of information as a key resource shaping social and economic activities. Core differences lie in network society's focus on social connectivity patterns, while information society prioritizes the management and accessibility of information flows.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Societies
Technology drives the transformation from information society to network society by enabling real-time communication, digital collaboration, and decentralized data sharing. Social media platforms, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things facilitate interconnectedness beyond traditional information exchange, fostering collective intelligence and social interaction. These technological advancements reshape social structures, influence cultural norms, and expand the scope of community participation in the digital age.
Social Relationships in a Networked Era
Network society emphasizes dynamic social relationships shaped by digital connections and online communities, enabling rapid information exchange and collaborative interactions. Unlike traditional information societies centered on data dissemination, network societies foster interactive communication patterns that restructure social bonds across geographic and cultural boundaries. These digitally mediated networks transform social capital, enhancing opportunities for participation, identity formation, and collective action in a globally interconnected environment.
Impact on Communication Patterns and Community Formation
Network society transforms communication patterns by enabling decentralized, real-time interactions across global digital platforms, fostering diverse, flexible communities based on shared interests rather than geographic proximity. Information society centers on the widespread accessibility and dissemination of data, enhancing knowledge exchange but often preserving traditional communication hierarchies and localized community structures. The shift towards network society emphasizes dynamic, multimodal communication that reshapes community formation into fluid, virtual networks transcending conventional social boundaries.
Power Dynamics: Decentralization in Network Societies
Network societies exhibit a shift in power dynamics through decentralization, enabling individuals and decentralized groups to exercise influence outside traditional hierarchical structures. This contrasts with information societies, where centralized control often governs data flows and information dissemination. Decentralization in network societies promotes greater democratization of communication and power distribution by leveraging interconnected digital platforms.
Social Inequality: Access and Participation
Network society intensifies social inequality due to uneven access to digital infrastructures and platforms, limiting participation for marginalized groups. Information society emphasizes equitable information flow, yet disparities in digital literacy and resource distribution persist, hindering full inclusion. Bridging the digital divide requires targeted policies to enhance connectivity, education, and affordable technology to foster equal social participation.
Future Trends: Convergence or Divergence in Societal Development
Future trends in societal development reveal a complex interplay between network society and information society paradigms, with increasing integration of digital communication infrastructures fostering convergence through enhanced connectivity and data exchange. However, divergent trajectories emerge due to disparities in access, governance, and cultural adaptation, leading to heterogeneous patterns of digital inclusion and social interaction. Advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and ubiquitous computing are poised to either bridge or widen these divides, shaping the evolution of social structures and power dynamics in the coming decades.
network society vs information society Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com