Social contagion refers to the spread of behaviors, attitudes, and ideas through social networks, influencing individuals to adopt similar actions or thoughts. Emotional contagion, on the other hand, involves the automatic transfer of emotions between individuals, often through facial expressions, tone of voice, or body language. In social pets, emotional contagion plays a crucial role in fostering bonds and synchronizing moods, while social contagion drives shared behaviors and group dynamics.
Table of Comparison
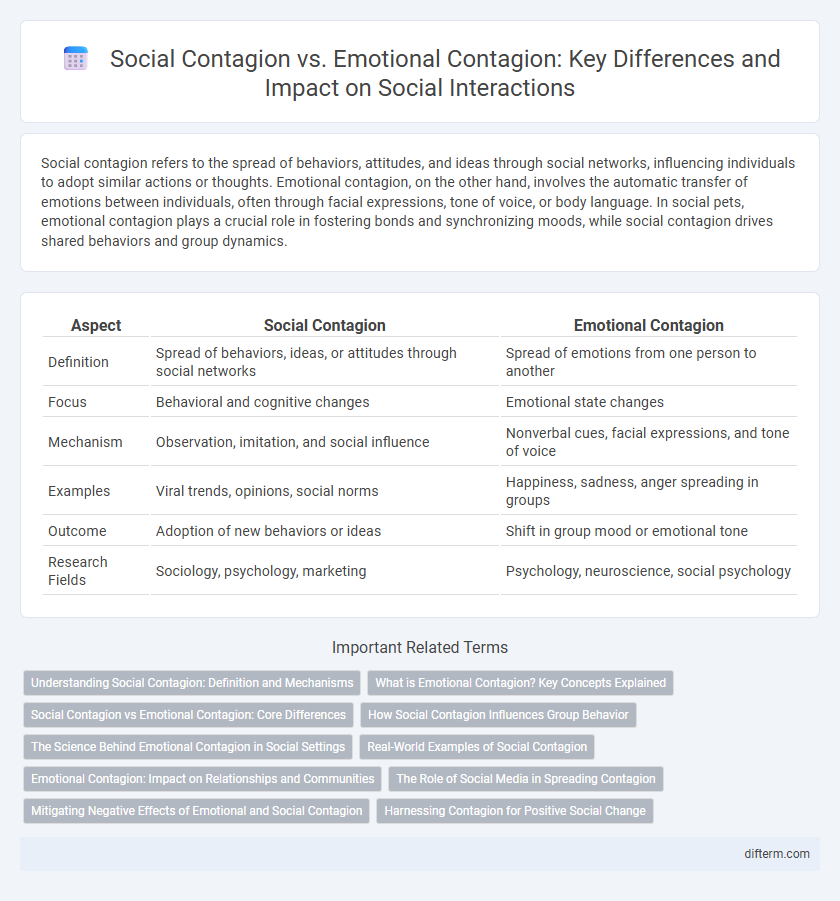
| Aspect | Social Contagion | Emotional Contagion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spread of behaviors, ideas, or attitudes through social networks | Spread of emotions from one person to another |
| Focus | Behavioral and cognitive changes | Emotional state changes |
| Mechanism | Observation, imitation, and social influence | Nonverbal cues, facial expressions, and tone of voice |
| Examples | Viral trends, opinions, social norms | Happiness, sadness, anger spreading in groups |
| Outcome | Adoption of new behaviors or ideas | Shift in group mood or emotional tone |
| Research Fields | Sociology, psychology, marketing | Psychology, neuroscience, social psychology |
Understanding Social Contagion: Definition and Mechanisms
Social contagion refers to the spread of behaviors, attitudes, and emotions through social networks via mechanisms such as imitation, social reinforcement, and shared environmental cues. It operates through both conscious and unconscious processes, influencing individuals' actions and emotional states within groups. Key factors include peer influence, social norms, and the structure of social connections that facilitate the rapid diffusion of information and behaviors.
What is Emotional Contagion? Key Concepts Explained
Emotional contagion refers to the automatic and unconscious transmission of emotions from one person to another, often through facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. Key concepts include empathy, mimicry, and neural coupling, which facilitate shared emotional experiences within social groups. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in social bonding, group dynamics, and collective emotional regulation.
Social Contagion vs Emotional Contagion: Core Differences
Social contagion refers to the spread of behaviors, attitudes, and ideas through social networks, while emotional contagion involves the automatic transfer of emotions from one individual to another. Social contagion is driven by conscious imitation and social influence, whereas emotional contagion occurs more subconsciously through nonverbal cues like facial expressions and tone of voice. Understanding these core differences highlights the distinct mechanisms by which group dynamics and individual emotions impact social interactions.
How Social Contagion Influences Group Behavior
Social contagion significantly shapes group behavior by facilitating the rapid spread of attitudes, emotions, and actions through interpersonal connections, often leading to synchronized group responses. This phenomenon relies on imitation, norm adherence, and emotional resonance within social networks, reinforcing collective decision-making and social cohesion. Understanding these dynamics allows for more effective influence strategies in organizational, community, and digital environments.
The Science Behind Emotional Contagion in Social Settings
Emotional contagion involves the automatic transfer of emotions between individuals within social settings through nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language, engaging mirror neurons in the brain. Studies in neuroscience reveal that this process activates the brain's limbic system, particularly the amygdala, which plays a critical role in emotional processing and empathy. Understanding the mechanisms of emotional contagion highlights its impact on group dynamics, decision-making, and social bonding in diverse environments.
Real-World Examples of Social Contagion
Social contagion manifests in phenomena such as viral social media challenges, where behaviors rapidly spread across networks through mimicry and peer influence. The spread of panic buying during crises, like the toilet paper shortages in early 2020, exemplifies how collective behavior can propagate through social cues. These real-world examples highlight how social contagion drives the diffusion of actions and attitudes within communities, influencing group dynamics and decision-making.
Emotional Contagion: Impact on Relationships and Communities
Emotional contagion significantly shapes relationships and communities by enabling individuals to unconsciously mimic and absorb the feelings of those around them, fostering empathy and social bonding. This process enhances group cohesion and collective emotional climates, influencing moods on both micro and macro social levels. Persistent exposure to positive or negative emotions through emotional contagion can alter relationship dynamics and community well-being over time.
The Role of Social Media in Spreading Contagion
Social media platforms accelerate the spread of both social contagion and emotional contagion by enabling rapid sharing of behaviors, ideas, and emotions across diverse networks. Viral content, trending challenges, and emotional posts amplify social influence, triggering collective behavior shifts and emotional resonance in online communities. Algorithms prioritize engaging and emotionally charged content, intensifying the contagion effect and shaping public opinion on a large scale.
Mitigating Negative Effects of Emotional and Social Contagion
Mitigating the negative effects of emotional and social contagion involves fostering awareness of how emotions and behaviors spread within groups, particularly through social media and interpersonal interactions. Implementing strategies such as promoting emotional intelligence, encouraging positive communication, and establishing supportive environments can reduce the amplification of stress, anxiety, and harmful behaviors. Organizations and communities benefit from training programs that help individuals recognize contagion patterns and develop resilience against negative emotional influence.
Harnessing Contagion for Positive Social Change
Social contagion and emotional contagion both play crucial roles in shaping group behaviors and societal norms, with social contagion focusing on the spread of ideas and behaviors, while emotional contagion pertains to the transmission of feelings and moods. Harnessing these phenomena for positive social change involves strategically promoting prosocial behaviors, empathy, and cooperative attitudes within communities through targeted communication and media channels. By leveraging influential social networks and fostering emotional resonance, leaders and organizations can amplify messages that encourage inclusivity, resilience, and collective well-being.
Social Contagion vs Emotional Contagion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com