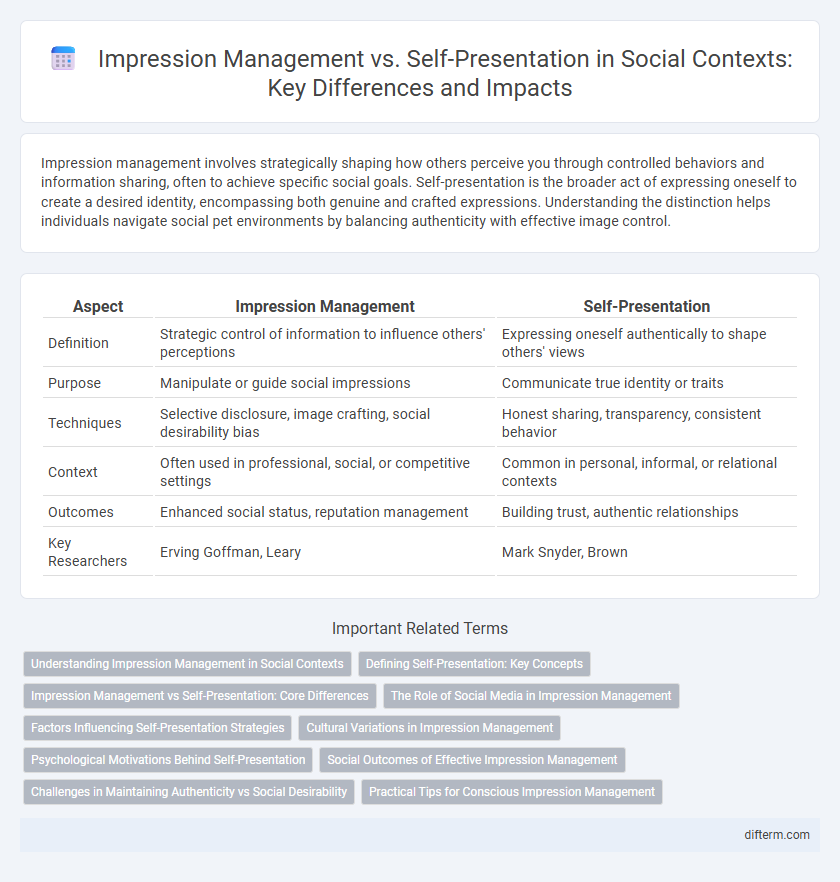
Impression management involves strategically shaping how others perceive you through controlled behaviors and information sharing, often to achieve specific social goals. Self-presentation is the broader act of expressing oneself to create a desired identity, encompassing both genuine and crafted expressions. Understanding the distinction helps individuals navigate social pet environments by balancing authenticity with effective image control.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Impression Management | Self-Presentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic control of information to influence others' perceptions | Expressing oneself authentically to shape others' views |
| Purpose | Manipulate or guide social impressions | Communicate true identity or traits |
| Techniques | Selective disclosure, image crafting, social desirability bias | Honest sharing, transparency, consistent behavior |
| Context | Often used in professional, social, or competitive settings | Common in personal, informal, or relational contexts |
| Outcomes | Enhanced social status, reputation management | Building trust, authentic relationships |
| Key Researchers | Erving Goffman, Leary | Mark Snyder, Brown |
Understanding Impression Management in Social Contexts
Impression management involves strategically controlling the image one projects in social interactions to influence others' perceptions, whereas self-presentation is the broader act of expressing oneself in various contexts. Effective impression management requires awareness of social norms, audience expectations, and situational cues to tailor behavior appropriately. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating social environments and building desired relationships.
Defining Self-Presentation: Key Concepts
Self-presentation involves deliberate behaviors and communication strategies individuals use to shape others' perceptions, often tailored to social contexts to achieve specific goals. Impression management, a broader psychological process, encompasses self-presentation but also includes subconscious efforts to influence others' impressions. Key concepts in self-presentation include authenticity, impression construction, and audience awareness, emphasizing how individuals balance genuine expression with strategic image crafting.
Impression Management vs Self-Presentation: Core Differences
Impression management involves strategic efforts to control the image perceived by others in various social contexts, often aimed at long-term relationship goals. Self-presentation, a subset of impression management, emphasizes moment-to-moment behaviors tailored to specific social interactions or situations. While impression management encompasses broader, consistent identity construction, self-presentation focuses on immediate social cues and role performance.
The Role of Social Media in Impression Management
Social media platforms have transformed impression management by enabling users to carefully curate and control the information shared about themselves, influencing how they are perceived by others. Algorithms and user-generated content amplify the visibility of curated identities, making impression management a continuous and dynamic process in virtual social environments. The interactive nature of social media fosters immediate feedback, reinforcing or prompting adjustments to self-presentation strategies to maintain desired impressions.
Factors Influencing Self-Presentation Strategies
Self-presentation strategies are shaped by factors such as audience characteristics, social context, and individual personality traits, which determine how people tailor their behavior to influence others' perceptions. Cultural norms and situational goals further guide the selection of specific self-presentation tactics, balancing authenticity with desired impressions. Technological platforms also play a crucial role by providing varying degrees of control over personal information and interaction styles.
Cultural Variations in Impression Management
Cultural variations in impression management significantly influence how individuals tailor their self-presentation to align with societal norms and values. In collectivist cultures, people prioritize group harmony and often engage in modest self-presentation to avoid disrupting social cohesion, while individualist cultures encourage assertive impression management to highlight personal achievements. Understanding these cultural differences is essential for interpreting social interactions and enhancing cross-cultural communication effectiveness.
Psychological Motivations Behind Self-Presentation
Self-presentation involves deliberate strategies individuals use to influence how others perceive them, driven by psychological motivations such as the need for social approval, self-esteem enhancement, and identity construction. Impression management encompasses these behaviors but extends to controlling public images in various social contexts to gain social rewards or avoid negative evaluations. Understanding these motivations reveals how individuals navigate social interactions to fulfill intrinsic desires for acceptance and belonging.
Social Outcomes of Effective Impression Management
Effective impression management enhances social outcomes by fostering trust, increasing likability, and facilitating stronger interpersonal connections. By strategically controlling the information others perceive, individuals can influence social judgments and create favorable impressions in various social contexts. This leads to improved social acceptance, greater opportunities for collaboration, and heightened social influence.
Challenges in Maintaining Authenticity vs Social Desirability
Impression management and self-presentation often create challenges in balancing authenticity with social desirability, as individuals must navigate the tension between staying true to their values and adapting to social norms. This dynamic can lead to cognitive dissonance, where the desire to be liked conflicts with personal integrity, impacting mental well-being and social relationships. Strategies to maintain authenticity while managing impressions include selective self-disclosure and situational adaptability, emphasizing genuine interactions within socially acceptable boundaries.
Practical Tips for Conscious Impression Management
Conscious impression management involves strategically crafting behaviors and appearances to influence others' perceptions while maintaining authenticity in self-presentation. Practical tips include aligning verbal and nonverbal cues with core values, practicing active listening to adapt responses effectively, and managing online profiles with consistent, genuine content. Regular self-reflection and feedback from trusted sources enhance awareness and help balance impression control without compromising true identity.
impression management vs self-presentation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com