Algorithmic curation in social pet platforms leverages machine learning to personalize content based on user behavior, ensuring timely and relevant pet-related posts. Manual curation relies on expert moderators to select high-quality, engaging content, promoting authenticity and community trust. Combining both methods can enhance user experience by balancing efficiency with thoughtful content selection.
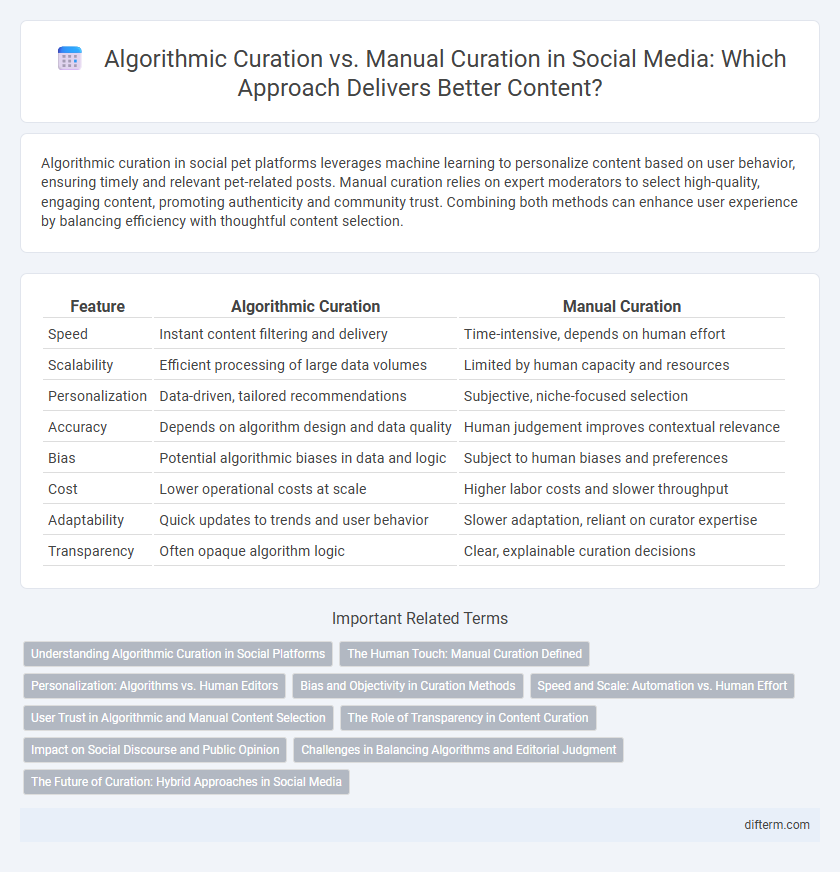
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Algorithmic Curation | Manual Curation |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Instant content filtering and delivery | Time-intensive, depends on human effort |
| Scalability | Efficient processing of large data volumes | Limited by human capacity and resources |
| Personalization | Data-driven, tailored recommendations | Subjective, niche-focused selection |
| Accuracy | Depends on algorithm design and data quality | Human judgement improves contextual relevance |
| Bias | Potential algorithmic biases in data and logic | Subject to human biases and preferences |
| Cost | Lower operational costs at scale | Higher labor costs and slower throughput |
| Adaptability | Quick updates to trends and user behavior | Slower adaptation, reliant on curator expertise |
| Transparency | Often opaque algorithm logic | Clear, explainable curation decisions |
Understanding Algorithmic Curation in Social Platforms
Algorithmic curation in social platforms employs machine learning models to personalize content feeds based on user behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns, optimizing user experiences and retention. Unlike manual curation, which relies on human editors to select and organize content, algorithmic curation processes vast amounts of data in real-time, enhancing scalability and relevance. Key algorithms such as collaborative filtering, natural language processing, and deep learning drive content recommendations, highlighting the importance of transparency and bias mitigation in algorithmic design.
The Human Touch: Manual Curation Defined
Manual curation involves human experts selecting and organizing content based on nuanced understanding, cultural context, and emotional resonance, which algorithms often overlook. This human touch allows for personalized, ethically-aware, and contextually rich content that algorithms struggle to replicate. Manual curation enhances social platforms by fostering authentic connections and trust among users through thoughtfully crafted content.
Personalization: Algorithms vs. Human Editors
Algorithmic curation leverages machine learning and user data to deliver hyper-personalized content at scale, adapting quickly to changing preferences and behaviors. Human editors provide nuanced understanding and context, offering curated experiences enriched by empathy and cultural awareness that algorithms may lack. Balancing these approaches enhances personalization by combining data-driven precision with human judgment.
Bias and Objectivity in Curation Methods
Algorithmic curation often introduces bias through data-driven patterns that reinforce existing prejudices, whereas manual curation relies on human judgment that can reflect subjective preferences. Bias in algorithmic methods stems from training data and model design, potentially limiting diversity and objectivity in content selection. Manual curation allows for nuanced evaluation but is susceptible to inconsistencies and personal bias, challenging the balance between fairness and comprehensive representation.
Speed and Scale: Automation vs. Human Effort
Algorithmic curation leverages machine learning models to analyze vast amounts of social data in real-time, enabling rapid content sorting and personalized recommendations at an unprecedented scale. Manual curation depends on human judgment and expertise but struggles with speed and scalability, often leading to slower updates and limited content coverage. Automated systems excel in processing millions of interactions per second, whereas manual efforts excel in nuanced understanding but face significant constraints in throughput.
User Trust in Algorithmic and Manual Content Selection
User trust in algorithmic curation hinges on transparency, accuracy, and perceived fairness, while manual curation depends more on human judgment and personalized expertise. Algorithmic systems can process vast amounts of data quickly, yet their opacity often raises concerns about bias and manipulation. Manual curation fosters deeper trust through human oversight but may lack scalability and consistency in content selection.
The Role of Transparency in Content Curation
Transparency plays a crucial role in content curation by building user trust and enabling informed engagement with curated social feeds. Algorithmic curation often lacks openness, making it difficult for users to understand why specific content appears, whereas manual curation provides clearer insight into selection criteria. Enhancing transparency through clear labeling and accessible explanations helps balance algorithmic efficiency with accountability in content delivery.
Impact on Social Discourse and Public Opinion
Algorithmic curation leverages data-driven models to tailor content delivery, significantly shaping social discourse by amplifying trending topics and personalized viewpoints, often leading to echo chambers and filter bubbles. Manual curation involves human judgment to select and contextualize information, promoting diverse perspectives and critical engagement, which can foster more balanced public opinion. The interplay between automated algorithms and human curators critically influences how information ecosystems evolve, affecting societal narratives and democratic decision-making processes.
Challenges in Balancing Algorithms and Editorial Judgment
Balancing algorithmic curation and manual editorial judgment presents challenges in maintaining content relevance and authenticity while avoiding bias and echo chambers. Algorithms optimize for engagement through data-driven recommendations, yet lack the nuanced understanding of context and ethical considerations that human editors provide. Ensuring transparency, accountability, and diversified content requires continuous refinement of hybrid models integrating AI efficiency with editorial insight.
The Future of Curation: Hybrid Approaches in Social Media
Hybrid approaches in social media curation combine algorithmic precision with human judgment to enhance content relevance and user engagement. Algorithms efficiently analyze large data sets, while manual curation offers nuanced understanding of cultural context and ethical considerations. This synergy drives personalized experiences and addresses biases, shaping the future landscape of social media content delivery.
algorithmic curation vs manual curation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com