Store clusters group retail pet stores based on shared characteristics such as location, size, and customer demographics, enabling targeted marketing and inventory strategies. Store prototypes serve as standardized models representing ideal store layouts and product assortments, streamlining operations and enhancing customer experience across the cluster. Comparing store clusters to prototypes helps retailers identify performance gaps and tailor strategies to optimize sales and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
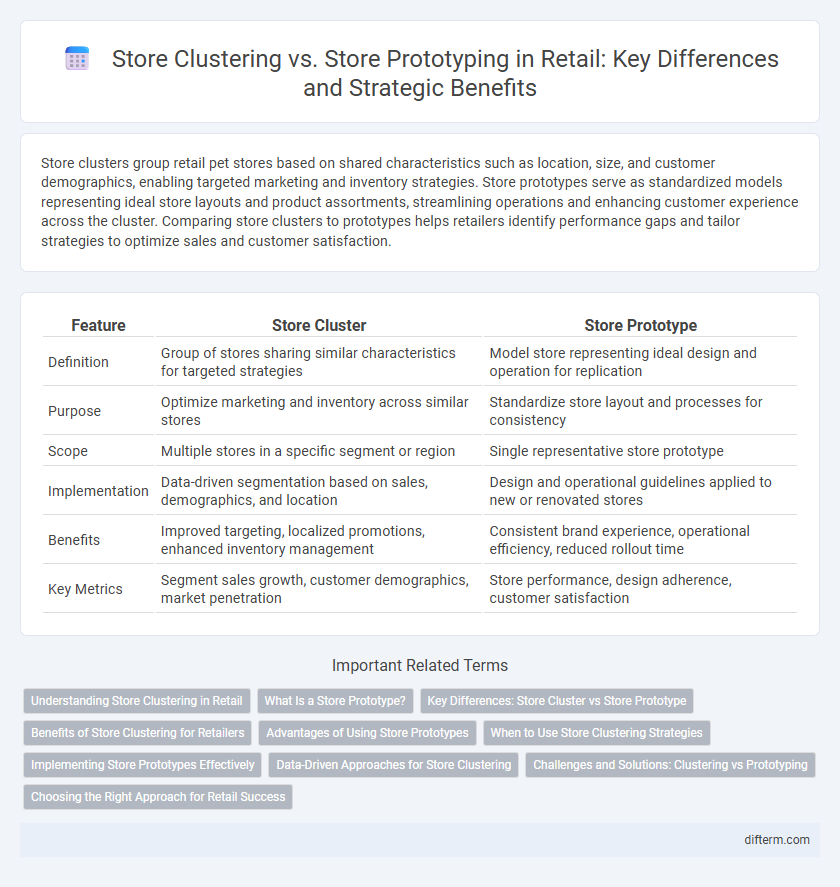
| Feature | Store Cluster | Store Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of stores sharing similar characteristics for targeted strategies | Model store representing ideal design and operation for replication |
| Purpose | Optimize marketing and inventory across similar stores | Standardize store layout and processes for consistency |
| Scope | Multiple stores in a specific segment or region | Single representative store prototype |
| Implementation | Data-driven segmentation based on sales, demographics, and location | Design and operational guidelines applied to new or renovated stores |
| Benefits | Improved targeting, localized promotions, enhanced inventory management | Consistent brand experience, operational efficiency, reduced rollout time |
| Key Metrics | Segment sales growth, customer demographics, market penetration | Store performance, design adherence, customer satisfaction |
Understanding Store Clustering in Retail
Store clustering in retail groups stores based on similar characteristics such as sales performance, customer demographics, and location to identify patterns and optimize marketing strategies. Store prototypes represent typical store models within each cluster, serving as benchmarks for performance evaluation and tailored operational approaches. Understanding these clusters enables retailers to customize product assortments, staffing, and promotions to meet specific local customer needs effectively.
What Is a Store Prototype?
A store prototype is a standardized retail design or layout that serves as a model for multiple store locations, ensuring consistent customer experience and operational efficiency. It incorporates key elements such as product placement, signage, and store flow tailored to a specific retail format, allowing for scalability and streamlined rollout across regions or clusters. Using a store prototype enables retailers to maintain brand identity and optimize store performance while adapting to local market needs.
Key Differences: Store Cluster vs Store Prototype
Store clusters group retail locations based on similar performance metrics and consumer demographics to enable targeted strategy development. Store prototypes represent idealized or average store models that serve as benchmarks for layout, assortment, and operations across a retail chain. Key differences lie in store clusters emphasizing real-world data variability while prototypes focus on standardized, optimized store characteristics.
Benefits of Store Clustering for Retailers
Store clustering enables retailers to group stores by similar characteristics such as location, sales volume, and customer demographics, optimizing inventory management and marketing strategies. This approach improves decision-making by allowing targeted promotions and tailored product assortments based on cluster-specific data. Enhanced operational efficiency and resource allocation result from identifying high-performing clusters and replicating their successful store prototypes across the retail network.
Advantages of Using Store Prototypes
Store prototypes streamline retail operations by providing a standardized blueprint that enhances brand consistency and reduces design and construction costs. These models enable quicker market entry and easier scalability across multiple locations, improving operational efficiency. Store prototypes also facilitate better inventory management and customer experience by implementing proven layouts tailored to target demographics.
When to Use Store Clustering Strategies
Store clustering strategies are most effective when managing large retail portfolios with diverse store formats and varied customer demographics to identify patterns and optimize resource allocation. Leveraging data on sales performance, location attributes, and consumer behavior enhances decision-making for merchandising, marketing, and operational improvements. Store clustering enables retailers to tailor strategies for groups of stores with similar characteristics, maximizing efficiency and market relevance compared to using generic store prototypes.
Implementing Store Prototypes Effectively
Implementing store prototypes effectively requires analyzing store clusters to identify shared characteristics such as demographics, purchasing behavior, and location metrics, enabling tailored prototype designs that resonate with target customer groups. Data-driven segmentation within store clusters enhances prototype customization, improving operational efficiency and customer experience consistency across retail locations. Leveraging advanced analytics and real-time feedback mechanisms ensures continuous refinement of store prototypes aligned with evolving market trends and consumer preferences.
Data-Driven Approaches for Store Clustering
Data-driven approaches for store clustering leverage customer demographics, purchasing behavior, and location analytics to group stores with similar profiles, enabling targeted marketing and inventory optimization. Store clusters group multiple stores sharing comparable characteristics and performance metrics, while store prototypes represent an idealized model or template derived from cluster insights for benchmarking and replication. Advanced machine learning algorithms analyze sales data, foot traffic, and regional trends to refine store prototypes, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency across retail networks.
Challenges and Solutions: Clustering vs Prototyping
Store clustering faces challenges in capturing nuanced consumer behaviors across diverse locations, often leading to oversimplified segments that hinder targeted marketing efforts. Store prototyping confronts difficulties in accurately modeling store layouts and operational dynamics, which can limit its effectiveness in predicting real-world performance. Combining advanced data analytics with machine learning algorithms enhances both clustering precision and prototype accuracy, enabling retailers to tailor strategies and optimize store formats effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Retail Success
Selecting the right approach between store cluster and store prototype hinges on maximizing retail performance through targeted strategies. Store clusters group locations by similar characteristics such as demographics and buying behaviors to tailor marketing and inventory decisions, while store prototypes establish standardized layouts and processes to ensure brand consistency and operational efficiency. Choosing an approach depends on balancing localization needs with scalability to drive customer engagement and optimize sales across diverse markets.
Store Cluster vs Store Prototype Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com