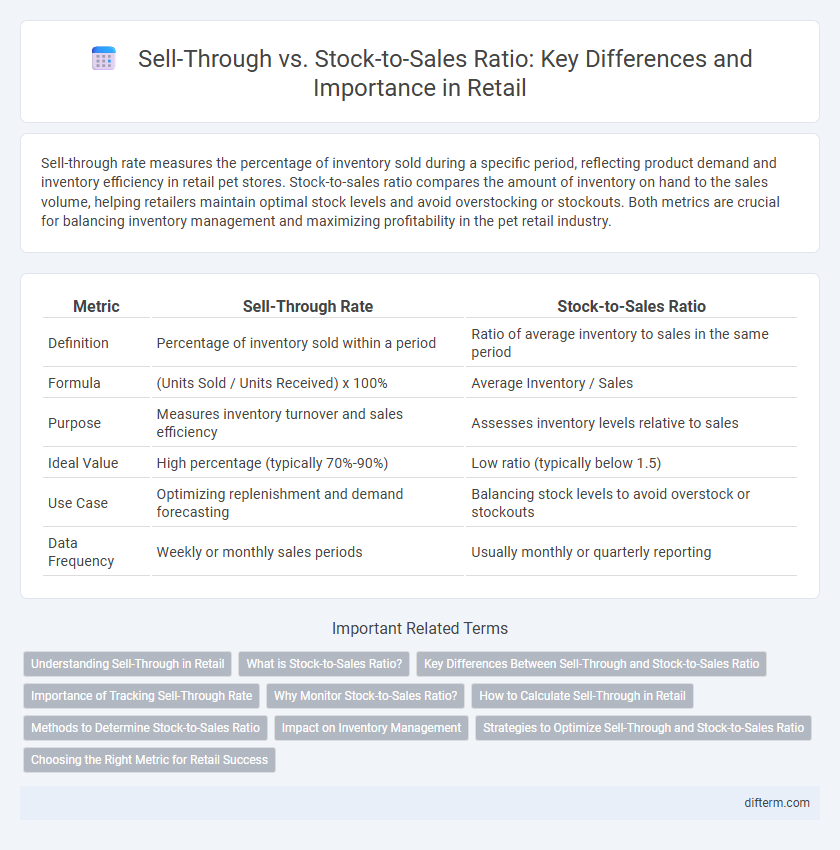
Sell-through rate measures the percentage of inventory sold during a specific period, reflecting product demand and inventory efficiency in retail pet stores. Stock-to-sales ratio compares the amount of inventory on hand to the sales volume, helping retailers maintain optimal stock levels and avoid overstocking or stockouts. Both metrics are crucial for balancing inventory management and maximizing profitability in the pet retail industry.
Table of Comparison
| Metric | Sell-Through Rate | Stock-to-Sales Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of inventory sold within a period | Ratio of average inventory to sales in the same period |
| Formula | (Units Sold / Units Received) x 100% | Average Inventory / Sales |
| Purpose | Measures inventory turnover and sales efficiency | Assesses inventory levels relative to sales |
| Ideal Value | High percentage (typically 70%-90%) | Low ratio (typically below 1.5) |
| Use Case | Optimizing replenishment and demand forecasting | Balancing stock levels to avoid overstock or stockouts |
| Data Frequency | Weekly or monthly sales periods | Usually monthly or quarterly reporting |
Understanding Sell-Through in Retail
Sell-through rate measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period, providing critical insight into product demand and sales effectiveness. It helps retailers optimize inventory levels by indicating how quickly stock moves off shelves, reducing overstock and understock risks. This metric is essential for aligning purchasing decisions with consumer demand, enhancing profitability and inventory turnover in retail operations.
What is Stock-to-Sales Ratio?
The Stock-to-Sales Ratio measures the amount of inventory available compared to the sales generated within a specific period, indicating how efficiently a retailer manages stock levels. A lower ratio signifies faster inventory turnover and effective stock management, whereas a higher ratio may indicate overstock or slow-moving products. Retailers use this metric to balance inventory investment against sales performance, optimizing cash flow and reducing holding costs.
Key Differences Between Sell-Through and Stock-to-Sales Ratio
Sell-through ratio measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period, indicating product demand and sales performance, while stock-to-sales ratio compares available inventory to sales volume, highlighting inventory levels relative to revenue generation. The sell-through ratio focuses on sales effectiveness and turnover speed, providing insights into how quickly stock moves, whereas the stock-to-sales ratio emphasizes inventory management efficiency and replenishment needs. Understanding these key differences helps retailers optimize inventory control, reduce overstock risks, and improve profitability by balancing sales velocity with stock availability.
Importance of Tracking Sell-Through Rate
Tracking the sell-through rate is crucial for retailers to monitor product performance and optimize inventory levels efficiently. A high sell-through rate indicates strong demand and effective pricing strategies, directly influencing cash flow and reducing excess stock costs. Accurate analysis of sell-through data helps retailers make informed purchasing decisions and improves overall supply chain responsiveness.
Why Monitor Stock-to-Sales Ratio?
Monitoring the stock-to-sales ratio is essential for retail businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels and avoid overstocking or stockouts. A balanced stock-to-sales ratio ensures efficient cash flow management by aligning inventory purchases with actual sales demand. Tracking this ratio helps retailers identify sales trends, improve turnover rates, and make data-driven decisions to maximize profitability.
How to Calculate Sell-Through in Retail
Sell-through in retail is calculated by dividing the units sold by the units received during a specific period, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. This metric helps retailers assess product performance and inventory effectiveness compared to the stock-to-sales ratio, which relates inventory levels to sales volume. Monitoring sell-through rates enables timely restocking and reduces overstock, optimizing overall inventory management.
Methods to Determine Stock-to-Sales Ratio
Methods to determine the stock-to-sales ratio in retail include calculating the average inventory value over a specific period divided by the total sales during that same period, providing insights into inventory efficiency. Retailers often analyze daily or weekly stock levels against corresponding sales figures to identify trends and optimize replenishment cycles. Advanced approaches may utilize point-of-sale data integrated with inventory management systems for real-time ratio monitoring, enhancing decision-making accuracy.
Impact on Inventory Management
Sell-through rate directly measures how quickly inventory sells relative to stock levels, providing real-time insights for optimizing product replenishment and avoiding overstock situations. The stock-to-sales ratio evaluates the amount of inventory held against sales volume, helping retailers balance supply and demand to reduce carrying costs and minimize markdowns. Effective management of both metrics enhances inventory turnover, improves cash flow, and supports data-driven decisions that align stock levels with consumer demand.
Strategies to Optimize Sell-Through and Stock-to-Sales Ratio
Optimizing sell-through and stock-to-sales ratios involves precise inventory management and demand forecasting, ensuring products align with customer preferences to reduce excess stock and increase turnover rates. Implementing dynamic pricing strategies and targeted promotions accelerates sales velocity, improving sell-through metrics while maintaining healthy stock levels. Leveraging real-time sales data and analytics enables retailers to adjust purchasing and merchandising decisions swiftly, balancing inventory investment against revenue generation.
Choosing the Right Metric for Retail Success
Sell-through rate measures the percentage of inventory sold over a specific period, directly indicating product demand and sales performance. Stock-to-sales ratio reflects the relationship between current inventory levels and sales volume, highlighting inventory management efficiency and potential overstock or stockout risks. Retailers choosing the right metric should align sell-through rate with demand forecasting and product lifecycle, while using stock-to-sales ratio to optimize inventory replenishment and reduce holding costs.
Sell-through vs Stock-to-sales Ratio Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com