A planogram provides a detailed visual representation of product placement on retail shelves, optimizing space and enhancing customer experience through strategic arrangement. Schematics offer a broader layout blueprint of the entire retail store, outlining fixture locations and traffic flow for effective store design. Understanding the distinction ensures precise execution of merchandising strategies and maximizes sales potential in pet retail environments.
Table of Comparison
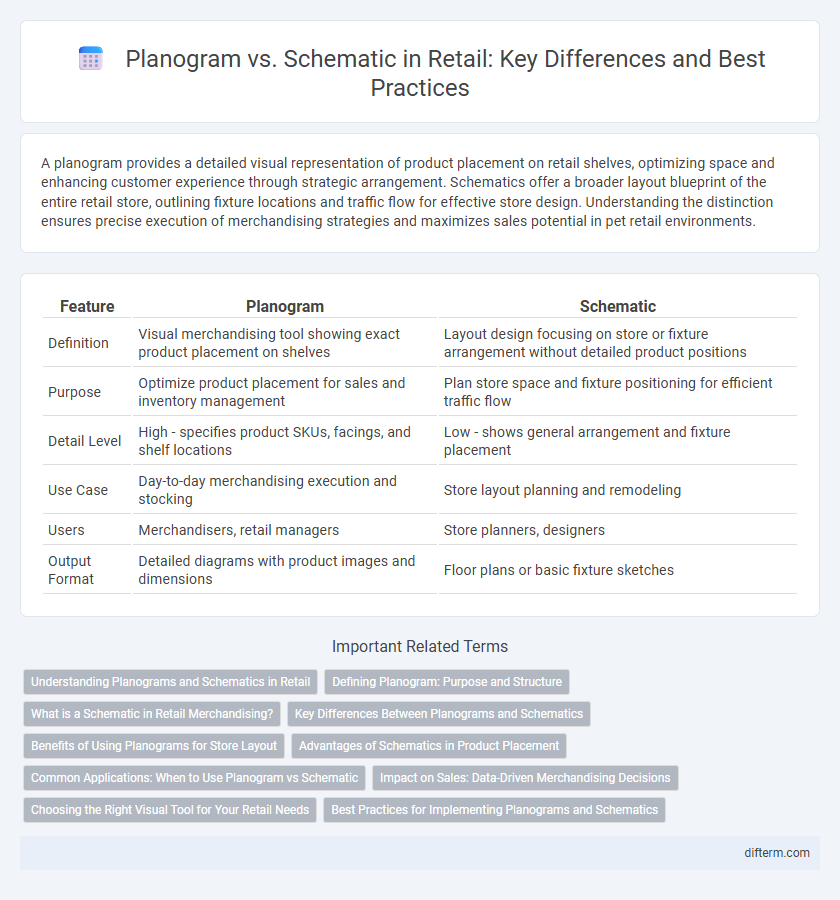
| Feature | Planogram | Schematic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual merchandising tool showing exact product placement on shelves | Layout design focusing on store or fixture arrangement without detailed product positions |
| Purpose | Optimize product placement for sales and inventory management | Plan store space and fixture positioning for efficient traffic flow |
| Detail Level | High - specifies product SKUs, facings, and shelf locations | Low - shows general arrangement and fixture placement |
| Use Case | Day-to-day merchandising execution and stocking | Store layout planning and remodeling |
| Users | Merchandisers, retail managers | Store planners, designers |
| Output Format | Detailed diagrams with product images and dimensions | Floor plans or basic fixture sketches |
Understanding Planograms and Schematics in Retail
Planograms are detailed visual diagrams that specify the exact placement of products on retail shelves to maximize sales and enhance customer experience. Schematics in retail represent broader layouts of store fixtures and overall floor plans, ensuring optimal traffic flow and space utilization. Understanding the distinction between planograms, which focus on product-level arrangement, and schematics, which emphasize store-wide design, is essential for efficient retail merchandising and store planning.
Defining Planogram: Purpose and Structure
A planogram is a detailed visual plan used in retail to optimize product placement on shelves, enhancing customer experience and maximizing sales by strategically organizing merchandise. It defines the exact arrangement, including product types, quantities, and positioning, based on sales data and consumer behavior analysis. The structure of a planogram typically includes shelf layout, product facings, and space allocation, ensuring consistency and efficiency across multiple store locations.
What is a Schematic in Retail Merchandising?
A schematic in retail merchandising is a detailed plan showing the layout and placement of products within a store, designed to optimize space and enhance customer experience. Unlike a planogram, which is a visual diagram specifying exact product positioning on shelves, a schematic provides an overall zoning concept and flow for the store's departments and fixtures. Effective schematics help retailers maximize sales by guiding strategic product grouping, aisle arrangement, and traffic patterns.
Key Differences Between Planograms and Schematics
Planograms are detailed visual representations of product placement on retail shelves, specifying exact product locations to maximize sales and inventory efficiency, while schematics provide broader layouts of store fixtures and overall store design without detailing individual product arrangements. Planograms focus on merchandising strategies and consumer behavior insights, using precise measurements to enhance product visibility and accessibility. Schematics serve as architectural or structural guides that support store setup and space planning rather than direct product placement decisions.
Benefits of Using Planograms for Store Layout
Planograms optimize retail store layouts by strategically placing products to enhance visibility and increase sales, utilizing data on customer behavior and product performance. This precise product positioning reduces stockouts and overstock situations, improving inventory management and operational efficiency. Compared to schematics, planograms provide actionable, detail-rich blueprints that support consistent brand presentation and maximize shelf space utilization across multiple store locations.
Advantages of Schematics in Product Placement
Schematics provide a flexible and visually intuitive layout for product placement, enabling retailers to optimize shelf space with scalable design elements that easily adapt to store variations. This approach enhances inventory management by clearly outlining product locations and facilitating quick plan adjustments based on sales data or seasonal promotions. Implementing schematics improves shopper navigation and increases product visibility, directly impacting sales efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Common Applications: When to Use Planogram vs Schematic
Planograms are essential for retail merchandising, guiding shelf layouts to maximize product visibility and sales by specifying exact product placements and quantities. Schematics serve broader purposes such as store design and fixture arrangement, providing architectural or spatial layouts without detailed product-level instructions. Retailers commonly use planograms for daily shelf stocking and merchandising optimization, while schematics support store construction and fixture planning phases.
Impact on Sales: Data-Driven Merchandising Decisions
Planogram and schematic both serve as visual merchandising tools, but planograms offer data-driven layouts based on consumer behavior and sales analytics, directly impacting product placement to maximize revenue. Schematics provide basic spatial arrangements without integrating sales data, limiting their ability to optimize shelf space effectively. Retailers leveraging planogram insights can enhance inventory turnover and increase sales by aligning product displays with shopper preferences and purchasing patterns.
Choosing the Right Visual Tool for Your Retail Needs
A planogram offers a detailed, product-level layout ideal for maximizing shelf space and improving product placement based on sales data and consumer behavior. Schematics provide a broader store layout perspective, emphasizing traffic flow and overall store organization rather than individual product positioning. Selecting the right visual tool depends on whether your goal is optimizing product arrangement or enhancing store navigation and layout strategy.
Best Practices for Implementing Planograms and Schematics
Effective implementation of planograms and schematics in retail hinges on precise product placement and accurate shelf measurements to maximize visual appeal and sales. Leveraging data analytics to tailor planograms based on customer behavior and inventory levels drives optimal stock rotation and reduces out-of-stock scenarios. Regular audits and employee training ensure adherence to layout standards, enhancing shopper experience and operational efficiency.
Planogram vs Schematic Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com