Barcode technology offers a cost-effective and simple solution for retail pet inventory management, enabling quick scanning and tracking of products like pet food and accessories. RFID provides enhanced accuracy and efficiency by allowing contactless, real-time inventory monitoring and reducing human error in stock management. While barcodes require line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read remotely, improving the overall operational workflow in busy retail pet environments.
Table of Comparison
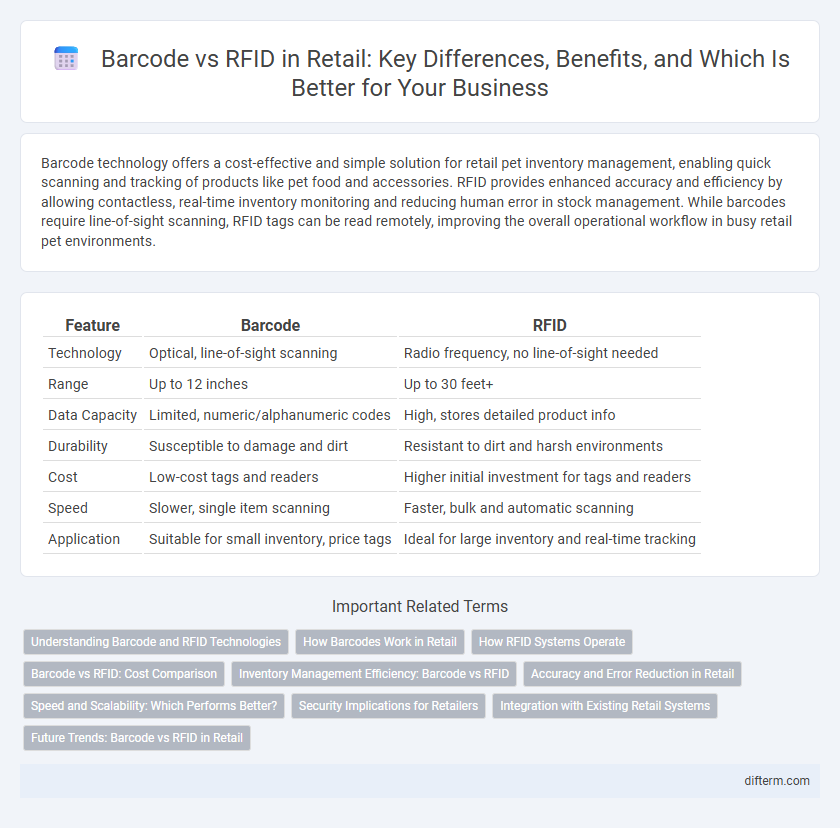
| Feature | Barcode | RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Optical, line-of-sight scanning | Radio frequency, no line-of-sight needed |
| Range | Up to 12 inches | Up to 30 feet+ |
| Data Capacity | Limited, numeric/alphanumeric codes | High, stores detailed product info |
| Durability | Susceptible to damage and dirt | Resistant to dirt and harsh environments |
| Cost | Low-cost tags and readers | Higher initial investment for tags and readers |
| Speed | Slower, single item scanning | Faster, bulk and automatic scanning |
| Application | Suitable for small inventory, price tags | Ideal for large inventory and real-time tracking |
Understanding Barcode and RFID Technologies
Barcode technology uses printed patterns of parallel lines to encode product information, which is scanned by optical readers for quick identification and inventory management. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) employs wireless radio waves to communicate data stored on microchips embedded in tags, allowing for non-line-of-sight scanning and simultaneous reading of multiple items. Understanding the distinctions between barcode's visual scanning and RFID's wireless data transmission is crucial for retailers aiming to enhance tracking accuracy and operational efficiency.
How Barcodes Work in Retail
Barcodes in retail utilize optical scanning technology to quickly capture product information encoded in black-and-white lines. These codes store essential data such as product ID, price, and inventory levels, facilitating efficient point-of-sale transactions and real-time stock management. Barcode scanning reduces human error, accelerates checkout processes, and streamlines supply chain operations across retail environments.
How RFID Systems Operate
RFID systems operate by using radio frequency waves to wirelessly transmit data between RFID tags and readers, enabling rapid and accurate identification of products without direct line of sight. Each RFID tag contains a microchip and antenna that communicate unique product information to the reader, which then processes the data for inventory management or checkout. This technology significantly enhances retail operations by improving stock accuracy, reducing theft, and accelerating the supply chain compared to traditional barcode scanning.
Barcode vs RFID: Cost Comparison
Barcode systems typically have lower initial setup costs, with printed labels costing only a few cents each, making them ideal for small-scale retail operations. RFID technology involves higher upfront expenses due to the need for specialized tags and readers, but it offers long-term savings through improved inventory accuracy and reduced labor costs. For large retail chains, the total cost of ownership may favor RFID despite the initial investment, as enhanced data capture and automation lead to operational efficiencies.
Inventory Management Efficiency: Barcode vs RFID
RFID technology enhances inventory management efficiency by enabling real-time, automated tracking of products without line-of-sight scanning, significantly reducing human error and labor costs compared to traditional barcode systems. Barcodes require manual scanning, often causing slower inventory counts and increased risk of misreads or missed items, limiting operational speed and accuracy. Implementing RFID improves stock visibility and turnover rates, optimizing replenishment processes and minimizing stockouts in retail environments.
Accuracy and Error Reduction in Retail
RFID technology significantly improves accuracy in retail inventory management compared to traditional barcode systems by enabling real-time, contactless scanning that reduces human error. Barcodes require line-of-sight scanning, which often leads to missed or incorrect reads, while RFID tags can be read simultaneously and at a distance, minimizing data capture errors. This enhanced precision in RFID tracking improves stock visibility, reduces shrinkage, and optimizes supply chain efficiency.
Speed and Scalability: Which Performs Better?
RFID technology significantly outperforms barcodes in speed as it allows simultaneous scanning of multiple items without line-of-sight, enabling faster inventory management and checkout processes. Scalability is also superior with RFID due to its capability to handle large volumes of tagged products efficiently in expansive retail environments. Barcodes, while cost-effective, require manual scanning and are less suited for high-speed, large-scale operations.
Security Implications for Retailers
Barcode systems offer basic security but are prone to duplication and tampering, making them less reliable for high-value retail inventory. RFID technology enhances security through encrypted data transmission and unique tag identifiers, significantly reducing theft and counterfeiting risks. Retailers leveraging RFID benefit from real-time inventory tracking and improved loss prevention capabilities, crucial for maintaining supply chain integrity and customer trust.
Integration with Existing Retail Systems
Barcode systems integrate seamlessly with most existing retail point-of-sale (POS) and inventory management software, relying on widely adopted scanners and straightforward data structures. RFID technology requires more specialized hardware and sophisticated software integration but offers real-time inventory tracking and automated data capture. Retailers must assess the compatibility and upgrade costs of their current systems to optimize the benefits of RFID over traditional barcode scanning.
Future Trends: Barcode vs RFID in Retail
Future trends in retail indicate a significant shift toward RFID technology due to its superior inventory tracking accuracy and real-time data capabilities. While barcodes remain cost-effective for small-scale operations, RFID's ability to enhance supply chain visibility and reduce shrinkage is driving widespread adoption among large retailers. Integration of RFID with Internet of Things (IoT) and AI analytics is expected to further optimize inventory management and customer experience in the retail sector.
Barcode vs RFID Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com