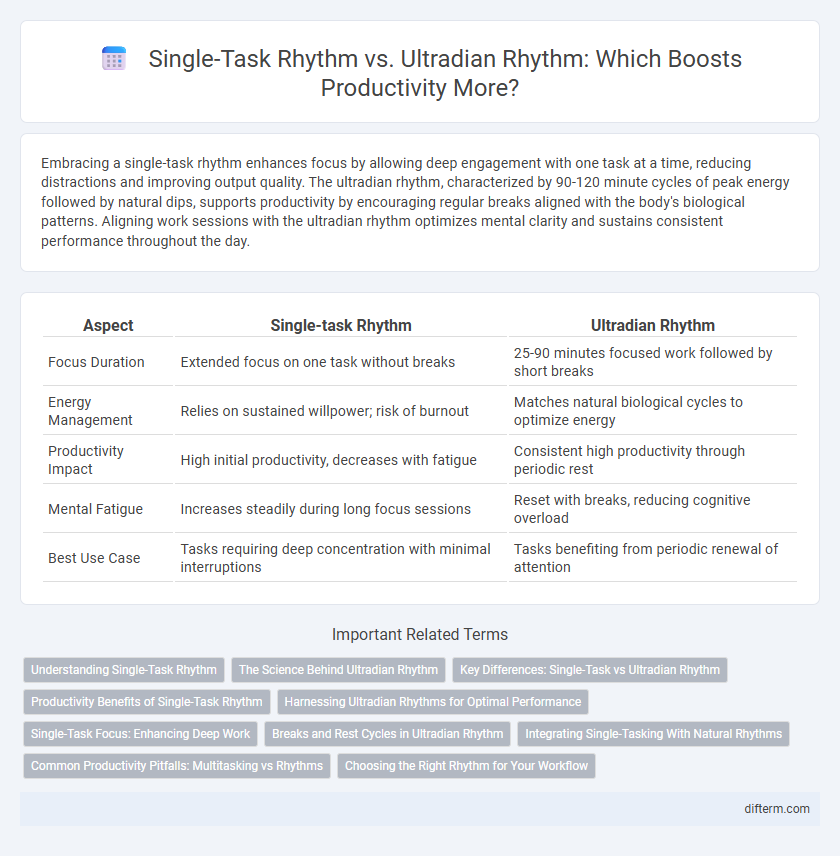
Embracing a single-task rhythm enhances focus by allowing deep engagement with one task at a time, reducing distractions and improving output quality. The ultradian rhythm, characterized by 90-120 minute cycles of peak energy followed by natural dips, supports productivity by encouraging regular breaks aligned with the body's biological patterns. Aligning work sessions with the ultradian rhythm optimizes mental clarity and sustains consistent performance throughout the day.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single-task Rhythm | Ultradian Rhythm |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Duration | Extended focus on one task without breaks | 25-90 minutes focused work followed by short breaks |
| Energy Management | Relies on sustained willpower; risk of burnout | Matches natural biological cycles to optimize energy |
| Productivity Impact | High initial productivity, decreases with fatigue | Consistent high productivity through periodic rest |
| Mental Fatigue | Increases steadily during long focus sessions | Reset with breaks, reducing cognitive overload |
| Best Use Case | Tasks requiring deep concentration with minimal interruptions | Tasks benefiting from periodic renewal of attention |
Understanding Single-Task Rhythm
Single-task rhythm maximizes productivity by concentrating on one task without interruption, enhancing focus and minimizing cognitive overload. This approach aligns with the brain's natural capacity to engage deeply, leading to higher quality work and reduced error rates. Consistently applying single-task rhythm helps build sustainable habits that support long-term efficiency and mental clarity.
The Science Behind Ultradian Rhythm
Ultradian rhythms are natural cycles in the human body lasting about 90 to 120 minutes, during which cognitive performance and energy levels fluctuate. Scientific studies show that aligning work sessions with these rhythms enhances productivity by optimizing focus and reducing mental fatigue. Embracing ultradian rhythm work patterns leverages brainwave activity and hormonal fluctuations, such as cortisol peaks, to maintain sustained attention and efficient task completion.
Key Differences: Single-Task vs Ultradian Rhythm
Single-task rhythm emphasizes sustained focus on one task for extended periods, enhancing deep work and reducing cognitive switching costs. Ultradian rhythm follows natural biological cycles of approximately 90-120 minutes, balancing focused work with frequent rest to optimize energy levels and mental clarity. Key differences lie in duration and break patterns: single-task rhythm favors long, uninterrupted sessions, while ultradian rhythm integrates regular breaks aligned with bodily energy fluctuations.
Productivity Benefits of Single-Task Rhythm
Single-task rhythm enhances productivity by allowing focused attention on one task at a time, reducing cognitive switching costs and minimizing mental fatigue. This structured approach aligns with the brain's natural capacity to sustain deep work over extended periods, which contrasts with the frequent breaks suggested by ultradian rhythms. Concentrating on a single task improves work quality, accelerates completion times, and supports sustained motivation throughout the workday.
Harnessing Ultradian Rhythms for Optimal Performance
Harnessing ultradian rhythms, which naturally cycle every 90 to 120 minutes, allows individuals to optimize productivity by aligning work and rest periods with the brain's peak focus phases. Unlike single-task rhythms that promote continuous work on one task, ultradian rhythm-based schedules incorporate regular breaks, preventing burnout and sustaining high cognitive performance. Embracing these biological cycles enhances energy management, improving concentration, creativity, and overall work efficiency throughout the day.
Single-Task Focus: Enhancing Deep Work
Single-task focus aligns with ultradian rhythms by promoting periods of intense concentration lasting 90-120 minutes, maximizing cognitive function and deep work efficiency. Leveraging single-tasking during these natural energy peaks reduces mental fatigue and enhances sustained attention. Prioritizing uninterrupted work blocks supports optimal productivity through enhanced information processing and creative problem-solving.
Breaks and Rest Cycles in Ultradian Rhythm
The Ultradian rhythm emphasizes work cycles of approximately 90-120 minutes followed by short breaks lasting 15-20 minutes, aligning with the brain's natural energy fluctuations to maximize focus and productivity. In contrast to single-task rhythm, which focuses on uninterrupted long periods of work, the Ultradian rhythm incorporates frequent rest cycles to prevent cognitive fatigue and maintain high performance throughout the day. Scientific studies on circadian biology highlight that these rest intervals enhance mental clarity, memory consolidation, and overall work efficiency.
Integrating Single-Tasking With Natural Rhythms
Aligning single-tasking with the body's natural ultradian rhythm enhances productivity by structuring work in 90- to 120-minute intervals followed by short breaks. This approach maximizes focus during high-energy phases and prevents burnout through strategic rest, optimizing cognitive performance. Integrating single-tasking within these biological cycles supports sustained attention and efficient task completion.
Common Productivity Pitfalls: Multitasking vs Rhythms
Multitasking often disrupts productivity by fragmenting attention and increasing cognitive load, whereas aligning work with the ultradian rhythm--approximately 90-minute cycles of high and low focus--enhances sustained concentration and efficiency. Single-task rhythm leverages deep focus on one task at a time, reducing errors and mental fatigue compared to frequent task-switching. Ignoring these natural rhythms increases the risk of burnout and lowers overall output quality.
Choosing the Right Rhythm for Your Workflow
Selecting the right work rhythm significantly impacts productivity, with single-task rhythm emphasizing prolonged focus on one task, while the ultradian rhythm advocates for 90-120 minute work intervals followed by short breaks to align with natural energy cycles. Research on ultradian rhythms highlights enhanced cognitive performance and reduced burnout by syncing tasks with the body's biological energy peaks. For professionals seeking sustained efficiency, integrating ultradian cycles into workflows can optimize concentration and task completion compared to extended single-task periods that risk mental fatigue.
Single-task rhythm vs Ultradian rhythm Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com