Procrastination delays task completion, often increasing stress and reducing overall productivity by pushing work beyond deadlines. Precrastination prompts individuals to start tasks immediately, potentially leading to rushed decisions and reduced focus on quality. Balancing these behaviors is essential for optimizing efficiency and maintaining consistent performance.
Table of Comparison
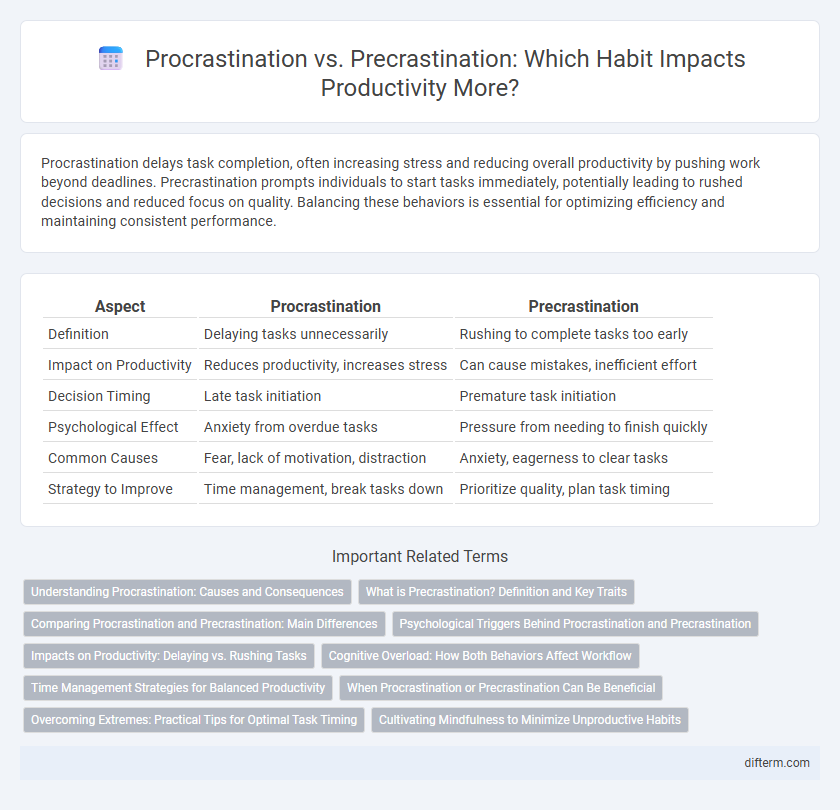
| Aspect | Procrastination | Precrastination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delaying tasks unnecessarily | Rushing to complete tasks too early |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduces productivity, increases stress | Can cause mistakes, inefficient effort |
| Decision Timing | Late task initiation | Premature task initiation |
| Psychological Effect | Anxiety from overdue tasks | Pressure from needing to finish quickly |
| Common Causes | Fear, lack of motivation, distraction | Anxiety, eagerness to clear tasks |
| Strategy to Improve | Time management, break tasks down | Prioritize quality, plan task timing |
Understanding Procrastination: Causes and Consequences
Procrastination stems from factors such as fear of failure, perfectionism, and lack of motivation, leading to stress and decreased productivity. It disrupts time management and hampers goal achievement by causing delays in task initiation and completion. Recognizing these causes enables better strategies to mitigate procrastination's negative impact on personal and professional productivity.
What is Precrastination? Definition and Key Traits
Precrastination is the tendency to complete tasks immediately, often before necessary preparation or optimal timing, driven by the desire to reduce cognitive load. Key traits include impulsive task initiation, prioritizing speed over accuracy, and a preference for early task completion, which can sometimes lead to inefficient outcomes. Understanding precrastination helps balance productivity by recognizing when starting too early may hinder overall performance.
Comparing Procrastination and Precrastination: Main Differences
Procrastination involves delaying tasks, often leading to increased stress and reduced productivity, while precrastination is characterized by rushing to complete tasks prematurely, sometimes resulting in lower quality outcomes. Procrastinators typically struggle with task initiation and time management, whereas precrastinators tend to prioritize speed over accuracy, potentially causing errors or inefficiencies. Understanding these behaviors highlights the importance of balanced time management strategies to enhance overall productivity and task performance.
Psychological Triggers Behind Procrastination and Precrastination
Psychological triggers behind procrastination include fear of failure, perfectionism, and anxiety, which lead individuals to delay tasks to avoid negative emotions. Precrastination stems from the desire for immediate task completion driven by cognitive load reduction and urgency perception, often causing rushed, suboptimal work. Understanding these opposing triggers helps optimize time management by addressing underlying emotional and cognitive factors influencing task initiation.
Impacts on Productivity: Delaying vs. Rushing Tasks
Procrastination often leads to missed deadlines and increased stress, significantly lowering productivity by delaying task completion. In contrast, precrastination can cause rushed work and errors due to hastily starting tasks without adequate planning. Balancing timely initiation with thoughtful preparation is crucial for maintaining high productivity and quality outcomes.
Cognitive Overload: How Both Behaviors Affect Workflow
Cognitive overload disrupts workflow by amplifying the negative impacts of both procrastination and precrastination. Procrastination delays task initiation, increasing mental clutter and stress as deadlines approach, while precrastination leads to hasty task completion, often resulting in errors and inefficient use of cognitive resources. Balancing task timing is crucial to managing cognitive load and optimizing productivity.
Time Management Strategies for Balanced Productivity
Procrastination delays important tasks, often leading to increased stress and reduced efficiency, while precrastination involves rushing to complete tasks prematurely, potentially compromising quality. Effective time management strategies balance these tendencies by prioritizing tasks using techniques such as the Eisenhower Matrix or Pomodoro Technique, ensuring focused effort without burnout. Implementing scheduled breaks and clear deadlines enhances productivity by maintaining consistent progress and preventing task overwhelm.
When Procrastination or Precrastination Can Be Beneficial
Procrastination can boost creativity by allowing ideas to incubate, leading to more innovative solutions when deadlines approach. Precrastination helps reduce cognitive load by completing tasks early, freeing mental space for other priorities. Both behaviors, when balanced, enhance overall productivity by aligning task urgency with individual work styles.
Overcoming Extremes: Practical Tips for Optimal Task Timing
Balancing procrastination and precrastination is key to maximizing productivity by avoiding delays and premature task completion. Prioritize tasks based on urgency and complexity, using techniques like time-blocking and the Eisenhower Matrix to allocate optimal effort. Incorporating mindfulness and realistic goal-setting helps maintain focus and prevent burnout, ensuring effective task timing and sustained efficiency.
Cultivating Mindfulness to Minimize Unproductive Habits
Procrastination involves delaying tasks despite knowing potential negative outcomes, while precrastination is the urge to complete tasks immediately, sometimes at the expense of efficiency. Cultivating mindfulness helps individuals recognize these counterproductive tendencies by increasing present-moment awareness and fostering deliberate decision-making. Mindfulness techniques, such as focused breathing and reflective pauses, empower individuals to balance urgency with thoughtful prioritization, minimizing unproductive habits and enhancing overall productivity.
Procrastination vs Precrastination Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com