Hustle culture emphasizes constant work and long hours, often leading to burnout and reduced creativity. Slow productivity prioritizes mindful work, balance, and sustainable output, enhancing focus and overall well-being. Embracing slow productivity fosters deeper engagement and long-term success.
Table of Comparison
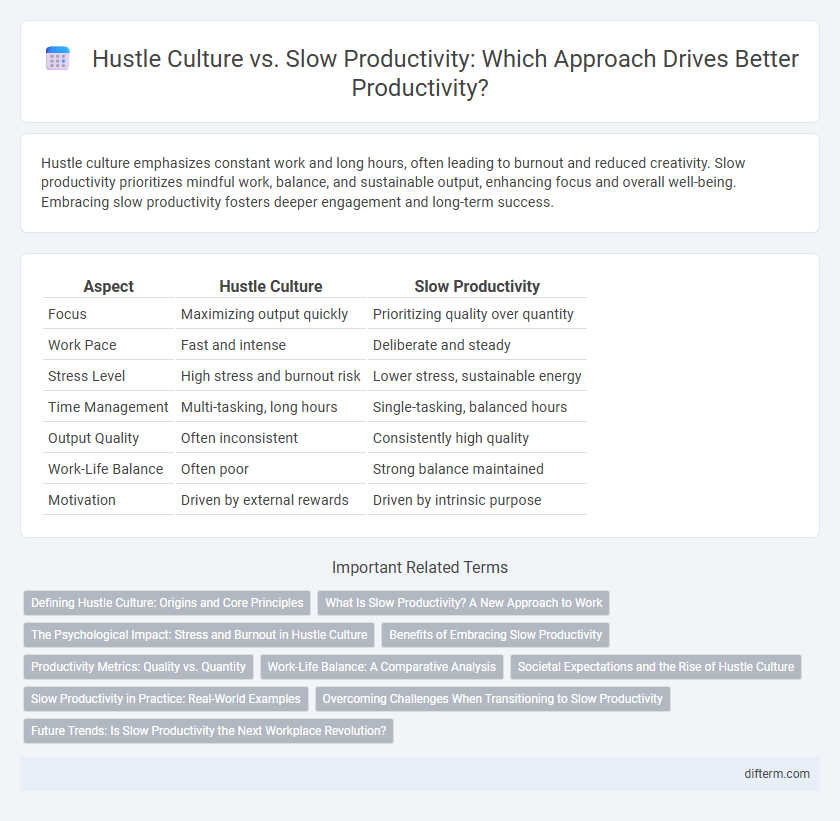
| Aspect | Hustle Culture | Slow Productivity |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Maximizing output quickly | Prioritizing quality over quantity |
| Work Pace | Fast and intense | Deliberate and steady |
| Stress Level | High stress and burnout risk | Lower stress, sustainable energy |
| Time Management | Multi-tasking, long hours | Single-tasking, balanced hours |
| Output Quality | Often inconsistent | Consistently high quality |
| Work-Life Balance | Often poor | Strong balance maintained |
| Motivation | Driven by external rewards | Driven by intrinsic purpose |
Defining Hustle Culture: Origins and Core Principles
Hustle culture emerged from entrepreneurial and startup mindsets, emphasizing relentless work, long hours, and constant busyness as indicators of success and dedication. Core principles include prioritizing productivity above personal well-being, valuing speed and output, and embracing a "grind" mentality that often blurs work-life boundaries. This culture contrasts with slow productivity, which advocates sustainable work practices, mindful pacing, and holistic balance for long-term effectiveness and health.
What Is Slow Productivity? A New Approach to Work
Slow productivity emphasizes quality over quantity by prioritizing deep focus, intentional work, and sustainable pacing to enhance long-term output and well-being. Unlike hustle culture, which values constant busyness and rapid task completion, slow productivity encourages mindfulness and balanced workflows to prevent burnout. This approach integrates pauses, reflection, and deliberate task management to foster creativity and consistent performance.
The Psychological Impact: Stress and Burnout in Hustle Culture
Hustle culture often leads to chronic stress and burnout due to relentless pressure to perform and constant overwork. Slow productivity, emphasizing balance and sustainable work habits, reduces mental fatigue and fosters long-term well-being. Psychological studies show that managing workload with intentional pacing improves focus and resilience, minimizing the negative effects of burnout.
Benefits of Embracing Slow Productivity
Embracing slow productivity enhances mental clarity and reduces burnout by encouraging deliberate, focused work rather than constant multitasking. This approach increases long-term efficiency and creativity, allowing for deeper problem-solving and more sustainable output. Prioritizing quality over quantity fosters better work-life balance and promotes overall well-being.
Productivity Metrics: Quality vs. Quantity
Productivity metrics that prioritize quality over quantity emphasize delivering meaningful and high-impact work rather than merely increasing output. Slow productivity encourages thoughtful, deliberate progress that enhances creativity and reduces burnout, contrasting with hustle culture's focus on constant activity and volume of tasks completed. Measuring success through outcome-based indicators like project effectiveness or innovation rates fosters sustainable performance and long-term growth.
Work-Life Balance: A Comparative Analysis
Hustle culture emphasizes constant work and long hours, often sacrificing personal time, while slow productivity advocates for balanced, mindful work strategies that prioritize well-being. Studies show that slow productivity enhances mental health and sustains long-term efficiency by integrating regular breaks and clear boundaries between work and personal life. Companies adopting slow productivity models report higher employee satisfaction and lower burnout rates compared to those enforcing hustle culture norms.
Societal Expectations and the Rise of Hustle Culture
Societal expectations increasingly valorize constant busyness and rapid achievement, fueling the rise of hustle culture that equates productivity with nonstop work and urgency. This cultural shift prioritizes visible output and immediate results, often at the cost of mental health and sustainable progress. Slow productivity emerges as a counter-movement, emphasizing deep focus, deliberate pacing, and long-term effectiveness to challenge the unsustainable demands of hustle culture.
Slow Productivity in Practice: Real-World Examples
Slow productivity emphasizes quality over quantity, as demonstrated by companies like Basecamp, which prioritize sustainable work hours and deliberate decision-making. In real-world practices, employees adopt mindfulness techniques and structured breaks to enhance focus and reduce burnout. This approach leads to improved creativity, higher job satisfaction, and long-term productivity gains compared to the constant hustle mindset.
Overcoming Challenges When Transitioning to Slow Productivity
Overcoming challenges when transitioning to slow productivity involves reprogramming mindsets that equate constant busyness with success and resisting societal pressures rooted in hustle culture. Embracing intentional work rhythms enhances long-term focus, reduces burnout, and fosters sustainable efficiency by prioritizing deep work over multitasking. Implementing structured routines and mindfulness techniques aids in maintaining consistent progress while rejecting the urgency-driven pace of traditional productivity models.
Future Trends: Is Slow Productivity the Next Workplace Revolution?
Slow productivity emphasizes deliberate work rhythms and mental well-being, contrasting the high-pressure demands of hustle culture. Emerging trends highlight that organizations adopting slow productivity report increased creativity, reduced burnout, and better long-term outcomes. Future workplace strategies are likely to prioritize sustainable work habits to enhance employee engagement and overall performance.
hustle culture vs slow productivity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com