Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often leading to inefficiency when deadlines are too flexible. Hofstadter's Law highlights the tendency to underestimate the time needed for tasks, even when accounting for delays. Balancing these laws involves setting realistic deadlines that prevent unnecessary procrastination while allowing enough time to accommodate unforeseen challenges.
Table of Comparison
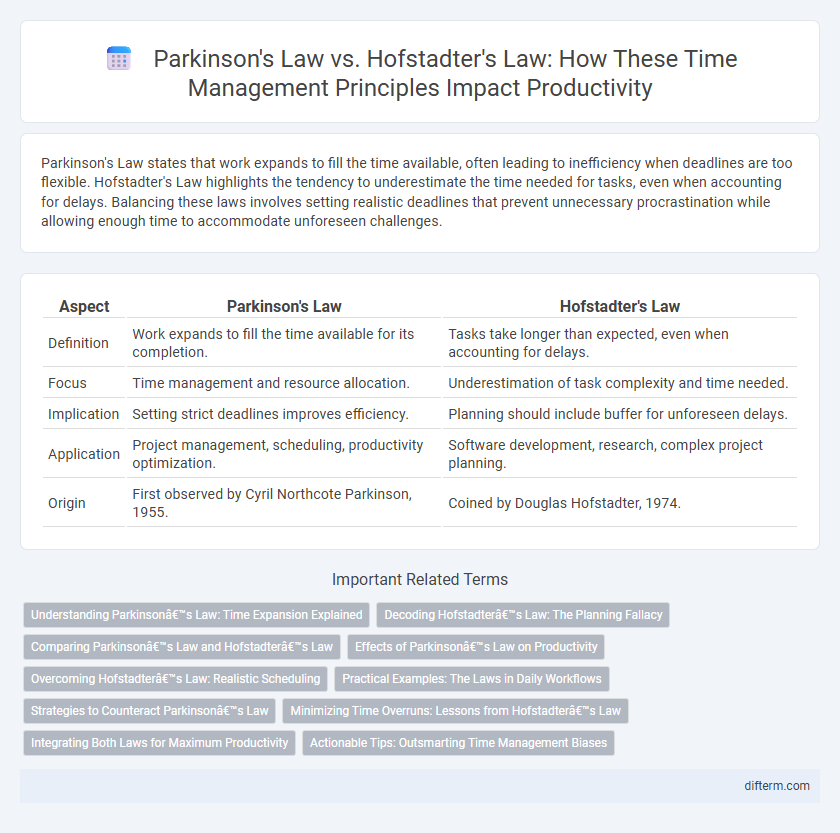
| Aspect | Parkinson's Law | Hofstadter's Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work expands to fill the time available for its completion. | Tasks take longer than expected, even when accounting for delays. |
| Focus | Time management and resource allocation. | Underestimation of task complexity and time needed. |
| Implication | Setting strict deadlines improves efficiency. | Planning should include buffer for unforeseen delays. |
| Application | Project management, scheduling, productivity optimization. | Software development, research, complex project planning. |
| Origin | First observed by Cyril Northcote Parkinson, 1955. | Coined by Douglas Hofstadter, 1974. |
Understanding Parkinson’s Law: Time Expansion Explained
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion, emphasizing how deadlines directly influence productivity and task duration. This principle highlights the tendency to over-allocate time, leading to inefficiencies and procrastination in project management. Understanding the psychological impact of perceived time availability helps optimize workflow by setting stricter deadlines to prevent unnecessary time expansion.
Decoding Hofstadter’s Law: The Planning Fallacy
Hofstadter's Law highlights the planning fallacy by emphasizing that projects often take longer than expected, even when accounting for possible delays. Unlike Parkinson's Law, which states work expands to fill the available time, Hofstadter's Law reveals how cognitive biases lead to systematic underestimation of task durations. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for improving time management and setting realistic deadlines in productivity frameworks.
Comparing Parkinson’s Law and Hofstadter’s Law
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion, often leading to inefficiency and procrastination. Hofstadter's Law highlights that tasks always take longer than expected, even when accounting for Hofstadter's Law itself, emphasizing inherent unpredictability in time estimation. Comparing both, Parkinson's Law stresses time management and avoiding unnecessary extension, while Hofstadter's Law warns about underestimating task duration despite careful planning.
Effects of Parkinson’s Law on Productivity
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often leading to unnecessary delays and reduced productivity. By setting tighter deadlines, individuals and teams are compelled to focus only on essential tasks, minimizing procrastination and boosting efficiency. This phenomenon highlights the importance of strategic time management in improving overall work performance.
Overcoming Hofstadter’s Law: Realistic Scheduling
Hofstadter's Law highlights the consistent underestimation of task completion times, emphasizing the need for realistic scheduling to enhance productivity. Overcoming this law requires incorporating buffer times and breaking projects into smaller, manageable segments for accurate time projections. Employing tools like time-tracking apps and regular progress reviews helps adjust schedules dynamically, ensuring deadlines remain achievable.
Practical Examples: The Laws in Daily Workflows
Parkinson's law states that work expands to fill the time available, causing tasks to drag if deadlines are loose, such as spending an entire week on a two-hour report when the deadline is seven days away. Hofstadter's law highlights the tendency to underestimate task duration despite experience, evident when software developers predict a coding project will take three days but it consistently takes a week or more. Applying strict time limits combats Parkinson's law by forcing focus, while building buffer time accounts for Hofstadter's law's underestimations, optimizing daily workflows for productivity.
Strategies to Counteract Parkinson’s Law
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often leading to inefficiency and procrastination. Implementing strict deadlines, using time-blocking techniques, and breaking tasks into smaller, manageable segments effectively counteract this tendency. Leveraging tools such as the Pomodoro Technique and setting clear, time-bound goals enhances focus and accelerates task completion, optimizing overall productivity.
Minimizing Time Overruns: Lessons from Hofstadter’s Law
Minimizing time overruns requires acknowledging Hofstadter's Law, which states tasks always take longer than expected, even when accounting for that delay. Unlike Parkinson's Law, which highlights work expanding to fill allotted time, Hofstadter's Law urges realistic deadline setting and buffer incorporation. Emphasizing accurate time estimation techniques can reduce schedule slip and enhance overall productivity.
Integrating Both Laws for Maximum Productivity
Parkinson's law states that work expands to fill the time allotted, while Hofstadter's law highlights that tasks always take longer than expected, even when accounting for Hofstadter's law itself. Integrating these laws for maximum productivity involves setting tight yet realistic deadlines that counteract Parkinson's law's tendency to create inefficiency while accounting for the inevitable underestimation described by Hofstadter's law. This balance optimizes task management by preventing both procrastination and excessive time underestimation, enhancing overall workflow efficiency.
Actionable Tips: Outsmarting Time Management Biases
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, while Hofstadter's Law highlights that tasks often take longer than expected, even when accounting for delays. To outsmart these biases, set strict, shorter deadlines to counter Parkinson's tendency and break large projects into smaller, manageable tasks with buffer times to address Hofstadter's underestimation. Prioritize frequent progress reviews and adjust schedules proactively to maintain realistic timelines and boost productivity.
Parkinson’s law vs Hofstadter’s law Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com