Habit stacking involves linking a new habit to an existing one by performing them sequentially to build a routine effortlessly. Habit chaining connects multiple new habits in a specific order, creating a flow that encourages momentum and consistency. Both techniques enhance productivity by embedding habits into daily life, but habit stacking leverages established patterns while habit chaining forms entirely new sequences.
Table of Comparison
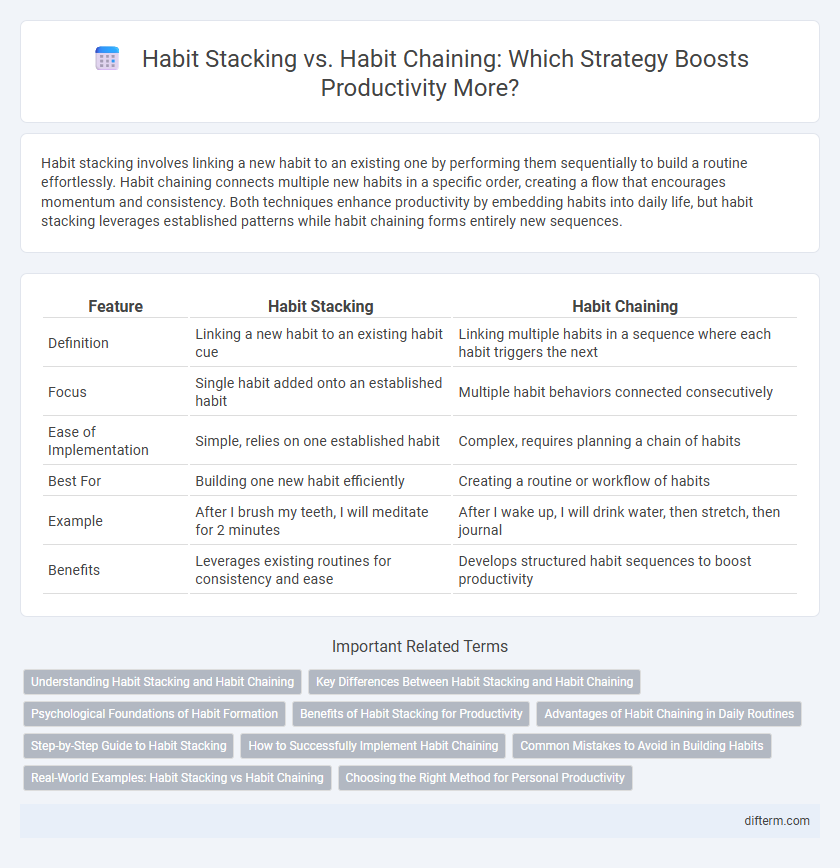
| Feature | Habit Stacking | Habit Chaining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Linking a new habit to an existing habit cue | Linking multiple habits in a sequence where each habit triggers the next |
| Focus | Single habit added onto an established habit | Multiple habit behaviors connected consecutively |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, relies on one established habit | Complex, requires planning a chain of habits |
| Best For | Building one new habit efficiently | Creating a routine or workflow of habits |
| Example | After I brush my teeth, I will meditate for 2 minutes | After I wake up, I will drink water, then stretch, then journal |
| Benefits | Leverages existing routines for consistency and ease | Develops structured habit sequences to boost productivity |
Understanding Habit Stacking and Habit Chaining
Habit stacking involves linking a new habit directly to an existing one to build routines effortlessly, while habit chaining connects multiple new habits sequentially, creating a flow of actions that reinforce each other. Understanding these techniques is key for enhancing productivity by leveraging existing behaviors and minimizing decision fatigue. Effective habit formation through stacking or chaining increases consistency, making complex routines easier to adopt and maintain over time.
Key Differences Between Habit Stacking and Habit Chaining
Habit stacking involves linking a new habit directly to an existing one by performing them sequentially, enhancing memory cues and routine formation. Habit chaining, however, focuses on creating a series of new habits that trigger one another in a specific order, building a continuous chain of behaviors. The key difference lies in habit stacking's reliance on an established habit as a cue, while habit chaining depends on each new habit acting as the stimulus for the next, promoting complex behavior sequences.
Psychological Foundations of Habit Formation
Habit stacking leverages the brain's associative learning by linking a new habit to an existing routine, capitalizing on neural pathways to reinforce behavior consistency. Habit chaining emphasizes a sequential series of small actions, strengthening habit networks through dopamine-driven rewards that enhance motivation and retention. Both methods rely on the psychological principle of cue-routine-reward loops rooted in habit formation theory and neuroplasticity.
Benefits of Habit Stacking for Productivity
Habit stacking leverages the power of linking new habits to existing ones, creating an effortless routine that boosts productivity by reducing decision fatigue and enhancing consistency. This strategy capitalizes on established neural pathways, making habit formation quicker and more sustainable, which leads to improved time management and goal achievement. By systematically building productive behaviors, habit stacking transforms small actions into powerful daily rituals that drive long-term success.
Advantages of Habit Chaining in Daily Routines
Habit chaining enhances productivity by creating a seamless flow of connected actions, reducing decision fatigue and increasing consistency in daily routines. This technique leverages the momentum of completing one task to naturally trigger the next, embedding positive behaviors into automatic sequences. Habit chaining also improves time management by minimizing gaps between activities, fostering sustained focus and accelerating habit formation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Habit Stacking
Habit stacking involves linking new habits to established routines by identifying a reliable anchor activity and attaching the desired action immediately after it, enhancing consistency and ease of integration. To implement habit stacking effectively, start by selecting a current habit that occurs daily, then clearly define the new habit you want to adopt, ensuring it's specific and manageable. Repeating the new habit consistently after the anchor habit in the same context reinforces the behavior, promoting lasting productivity improvements through incremental changes.
How to Successfully Implement Habit Chaining
To successfully implement habit chaining, identify a routine of small, interconnected actions where each new habit triggers the next, creating a seamless sequence. Use consistent cues and immediate rewards to reinforce the flow, enhancing automaticity and reducing decision fatigue. Tracking your progress with journals or apps that visualize the chain can maintain motivation and accountability over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Building Habits
Common mistakes in habit stacking include choosing unrelated habits that disrupt focus and failing to anchor new habits to consistent triggers. Habit chaining errors often stem from creating overly complex sequences that increase friction and reduce motivation to complete the entire chain. Avoid skipping habit review sessions, which prevent identifying weak links and adapting strategies for sustainable habit formation.
Real-World Examples: Habit Stacking vs Habit Chaining
Habit stacking involves linking a new habit to an existing one, such as doing 10 push-ups immediately after brushing your teeth, utilizing the natural cue of the current habit to trigger the new behavior. Habit chaining, however, requires completing a sequence of habits in a specific order, like meditation followed by journaling and then reading, creating a flow of related activities that reinforce each other. Real-world examples show habit stacking's effectiveness in integrating micro-habits into daily routines, while habit chaining excels in establishing complex productivity rituals that build momentum through deliberate progression.
Choosing the Right Method for Personal Productivity
Habit stacking involves linking new habits to existing routines, creating a simple trigger for each action, which enhances consistency and reduces decision fatigue. Habit chaining requires completing one habit entirely before starting the next, promoting a clear, step-by-step process that strengthens focus and mastery. Selecting between habit stacking and habit chaining depends on individual workflow patterns and cognitive preferences, with stacking suited for integrating quick tasks and chaining ideal for complex activities requiring sustained attention.
Habit stacking vs Habit chaining Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com